| Oracle® Fusion Middleware WebLogic Web Services Reference for Oracle WebLogic Server 11g Release 1 (10.3.1) Part Number E13750-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Fusion Middleware WebLogic Web Services Reference for Oracle WebLogic Server 11g Release 1 (10.3.1) Part Number E13750-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
The following sections provide information about the WebLogic-specific Web Services deployment descriptor file, weblogic-webservices.xml:
The standard Java EE deployment descriptor for Web Services is called webservices.xml. This file specifies the set of Web Services that are to be deployed to WebLogic Server and the dependencies they have on container resources and other services. See the Web Services XML Schema at http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/j2ee_web_services_1_1.xsd for a full description of this file.
The WebLogic equivalent to the standard Java EE webservices.xml deployment descriptor file is called weblogic-webservices.xml. This file contains WebLogic-specific information about a WebLogic Web Service, such as the URL used to invoke the deployed Web Service, configuration settings such as timeout values, and so on.
Both deployment descriptor files are located in the same location on the Java EE archive that contains the Web Service. In particular:
For Java class-implemented Web Services, the Web Service is packaged as a Web application WAR file and the deployment descriptors are located in the WEB-INF directory.
For stateless session EJB-implemented Web Services, the Web Service is packaged as an EJB JAR file and the deployment descriptors are located in the META-INF directory.
The structure of the weblogic-webservices.xml file is similar to the structure of the Java EE webservices.xml file in how it lists and identifies the Web Services that are contained within the archive. For example, for each Web Service in the archive, both files have a <webservice-description> child element of the appropriate root element (<webservices> for the Java EE webservices.xml file and <weblogic-webservices> for the weblogic-webservices.xml file)
This section is published for informational purposes only. Typically, configuration updates are made using the Administration Console or using JWS annotations and you will not need to edit either of the deployment descriptor files directly.
Note:
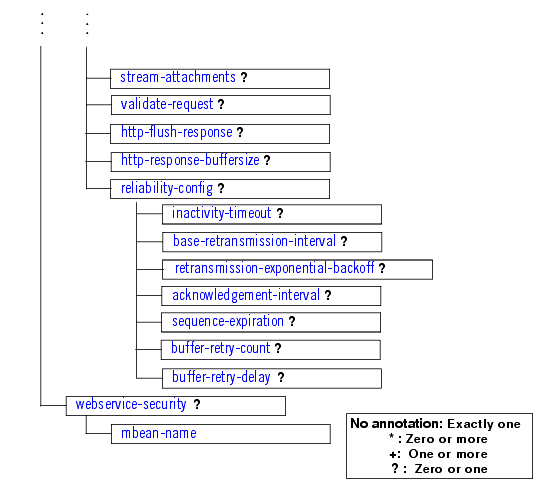
The data type definitions of two elements in theweblogic-webservices.xml file ( login-config and transport-guarantee) are imported from the Java EE Schema for the web.xml file. See the Servlet Deployment Descriptor Schema at http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd for details about these elements and data types.The following graphic describes the element hierarchy of the weblogic-webservices.xml deployment descriptor file.
Figure 6-1 Element Hierarchy of weblogic-webservices.xml

Figure 6-2 Element Hierarchy of weblogic-webservices.xml (Continued)
For the XML Schema file that describes the weblogic-webservices.xml deployment descriptor, see http://xmlns.oracle.com/weblogic/weblogic-webservices/1.0/weblogic-webservices.xsd.
The following example shows a simple weblogic-webservices.xml deployment descriptor:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<weblogic-webservices
xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/weblogic/weblogic-webservices">
<webservice-description>
<webservice-description-name>MyService</webservice-description-name>
<port-component>
<port-component-name>MyServiceServicePort</port-component-name>
<service-endpoint-address>
<webservice-contextpath>/MyService</webservice-contextpath>
<webservice-serviceuri>/MyService</webservice-serviceuri>
</service-endpoint-address>
<reliability-config>
<inactivity-timeout>P0DT600S</inactivity-timeout>
<base-retransmission-interval>P0DT3S</base-retransmission-interval>
<retransmission-exponential-backoff>true
</retransmission-exponential-backoff>
<acknowledgement-interval>P0DT3S</acknowledgement-interval>
<sequence-expiration>P1D</sequence-expiration>
<buffer-retry-count>3</buffer-retry-count>
<buffer-retry-delay>P0DT5S</buffer-retry-delay>
</reliability-config>
</port-component>
</webservice-description>
</weblogic-webservices>
The following sections describe each element in the weblogic-webservices.xml deployment descriptor file.
The <acknowledgement-interval> child element of the <reliability-config> element specifies the maximum interval during which the destination endpoint must transmit a stand-alone acknowledgement.
A destination endpoint can send an acknowledgement on the return message immediately after it has received a message from a source endpoint, or it can send one separately as a stand-alone acknowledgement. If a return message is not available to send an acknowledgement, a destination endpoint may wait for up to the acknowledgement interval before sending a stand-alone acknowledgement. If there are no unacknowledged messages, the destination endpoint may choose not to send an acknowledgement.
This value must be a positive value and conform to the XML schema duration lexical format, as follows:
PYMDTHS
The following table describes the duration format fields.
Table 6-1 Duration Format Description
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Number of years ( |
|
|
Number of months ( |
|
|
Number of days ( |
|
T |
Date and time separator. |
|
|
Number of hours ( |
|
|
Number of minutes ( |
|
|
Number of seconds ( |
This value defaults to P0DT3S (3 seconds).
The <base-retransmission-interval> child element of the <reliability-config> element specifies the interval of time that must pass before a message is retransmitted to the RM destination.
If the source endpoint does not receive an acknowledgement for a given message within the specified interval, the source endpoint retransmits the message. The source endpoint can modify this retransmission interval at any point during the lifetime of the sequence of messages.
This element can be used in conjunction with the <retransmission-exponential-backoff> element to specify the algorithm that is used to adjust the retransmission interval.
This value must be a positive value and conform to the XML schema duration lexical format, as follows:
PYMDTHS
For information about the duration format, see Table 6-1. This value defaults to P0DT3S (3 seconds).
The <buffer-retry-count> child element of the <reliability-config> element specifies the number of times that the JMS queue on the destination WebLogic Server instance attempts to deliver the message from a client that invokes the reliable operation to the Web Service implementation. This value defaults to 3.
The <buffer-retry-delay> child element of the <reliability-config> element specifies the amount of time that elapses between message delivery retry attempts. The retry attempts are between the client's request message on the JMS queue and delivery of the message to the Web Service implementation.
This value must be a positive value and conform to the XML schema duration lexical format, as follows:
PYMDTHS
For information about the duration format, see Table 6-1. This value defaults to P0DT5S (5 seconds).
The <callback-protocol> child element of the <port-component> element specifies the protocol used for callbacks to notify clients of an event. Valid values include: http, https, or jms.
For internal use only.
For internal use only.
The <exposed> child element of the <wsdl> element is a boolean attribute indicating whether the WSDL should be exposed to the public when the Web Service is deployed.
The <http-flush-response> child element of the <port-component> element specifies whether or not you want to flush the reliable response. This value defaults to true.
The <http-response-buffersize> child element of the <port-component> element specifies the size of the reliable response buffer that is used to cache the request on the server. This value defaults to 0.
The <j2ee:login-config> element specifies the authentication method that should be used, the realm name that should be used for this application, and the attributes that are needed by the form login mechanism.
The XML Schema data type of the <j2ee:login-config> element is <j2ee:login-configType>, and is defined in the Java EE Schema that describes the standard web.xml deployment descriptor. For the full reference information, see http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd.
The <inactivity-timeout> child element of the <reliability-config> element specifies an inactivity interval. If, during the specified interval, an endpoint (RM source or RM destination) has not received application or control messages, the endpoint may consider the RM sequence to have been terminated due to inactivity.
This value must be a positive value and conform to the XML schema duration lexical format, as follows:
PnYnMnDTnHnMnS
For information about the duration format, see Table 6-1. This value defaults to P0DT600S (600 seconds).
The <mbean-name> child element of the <webservice-security> element specifies the name of the Web Service security configuration (specifically an instantiation of the WebserviceSecurityMBean) that is associated with the Web Services described in the deployment descriptor file. The default configuration is called default_wss.
The associated security configuration specifies information such as whether to use an X.509 certificate for identity, whether to use password digests, the keystore to be used for encryption and digital signatures, and so on.
You must create the security configuration (even the default one) using the Administration Console before you can successfully invoke the Web Service.
Note:
The Web Service security configuration described by this element applies to all Web Services contained in theweblogic-webservices.xml file. The jwsc Ant task always packages a Web Service in its own JAR or WAR file, so this limitation is not an issue if you always use the jwsc Ant task to generate a Web Service. However, if you update the weblogic-webservices.xml deployment descriptor manually and add additional Web Service descriptions, you cannot associate different security configurations to different services.The <port-component> element is a holder of other elements used to describe a Web Service port. The child elements of the <port-component> element specify WebLogic-specific characteristics of the Web Service port, such as the context path and service URI used to invoke the Web Service after it has been deployed to WebLogic Server.
The <port-component-name> child element of the <port-component> element specifies the internal name of the WSDL port. The value of this element must be unique for all <port-component-name> elements within a single weblogic-webservices.xml file.
The <reliability-config> element groups together the reliable messaging configuration elements. The child elements of the <reliability-config> element specify runtime configuration values such as retransmission and timeout intervals for reliable messaging.
The <retransmission-exponential-backoff> child element of the <reliability-config> element is a boolean attribute that specifies whether the message retransmission interval will be adjusted using the exponential backoff algorithm.
This element is used in conjunction with the <base-retransmission-interval> element. If a destination endpoint does not acknowledge a sequence of messages for the time interval specified by <base-retransmission-interval>, the exponential backoff algorithm is used for timing successive retransmissions by the source endpoint, should the message continue to go unacknowledged.
The exponential backoff algorithm specifies that successive retransmission intervals should increase exponentially, based on the base retransmission interval. For example, if the base retransmission interval is 2 seconds, and the exponential backoff element is set, successive retransmission intervals if messages continue to go unacknowledged are 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, and so on.
This value defaults to false—the same retransmission interval is used in successive retries, rather than the interval increasing exponentially.
The <sequence-expiration> child element of the <reliability-config> element specifies the expiration time for a sequence regardless of activity.
This value must be a positive value and conform to the XML schema duration lexical format, as follows:
PnYnMnDTnHnMS
For information about the duration format, see Table 6-1. This value defaults to P1D (1 day).
The <service-endpoint-address> element groups the WebLogic-specific context path and service URI values that together make up the Web Service endpoint address, or the URL that invokes the Web Service after it has been deployed to WebLogic Server.
These values are specified with the <webservice-contextpath> and <webservice-serviceuri> child elements.
The <stream-attachments> child element of the <port-component> element is a boolean value that specifies whether the WebLogic Web Services runtime uses streaming APIs when reading the parameters of all methods of the Web Service. This increases the performance of Web Service operation invocation, in particular when the parameters are large, such as images.
You cannot use this annotation if you are also using the following features in the same Web Service:
Conversations
Reliable Messaging
JMS Transport
A proxy server between the client application and the Web Service it invokes
The j2ee:transport-guarantee element specifies the type of communication between the client application invoking the Web Service and WebLogic server.
The value of this element is either NONE, INTEGRAL, or CONFIDENTIAL. NONE means that the application does not require any transport guarantees. A value of INTEGRAL means that the application requires that the data sent between the client and server be sent in such a way that it cannot be changed in transit. CONFIDENTIAL means that the application requires that the data be transmitted in a way that prevents other entities from observing the contents of the transmission. In most cases, the presence of the INTEGRAL or CONFIDENTIAL flag indicates that the use of SSL is required.
The XML Schema data type of the j2ee:transport-guarantee element is j2ee:transport-guaranteeType, and is defined in the Java EE Schema that describes the standard web.xml deployment descriptor. For the full reference information, see http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd.
The <transaction-timeout> child element of the <port-component> element specifies a timeout value for the current transaction, if the Web Service operation(s) are running as part of a transaction.
This value must be a positive value and conform to the XML schema duration lexical format, as follows:
PnYnMnDTnHnMnS
For information about the duration format, see Table 6-1. This value defaults to P0DT3S (3 seconds).
This value defaults to 30 seconds.
The <validate-request> child element of the <port-component> element is a boolean value that specifies whether the request should be validated.
The value specified must be a positive value and conform to the XML schema duration lexical format, as follows:
PnYnMnDTnHnMnS
For information about the duration format, see Table 6-1. This value defaults to P0DT3S (3 seconds).
The <weblogic-webservices> element is the root element of the WebLogic-specific Web Services deployment descriptor (weblogic-webservices.xml).
The element specifies the set of Web Services contained in the Java EE component archive in which the deployment descriptor is also contained. The archive is either an EJB JAR file (for stateless session EJB-implemented Web Services) or a WAR file (for Java class-implemented Web Services)
The <webservice-contextpath> element specifies the context path portion of the URL used to invoke the Web Service. The URL to invoke a Web Service deployed to WebLogic Server is:
http://host:port/contextPath/serviceURI
where
host is the host computer on which WebLogic Server is running.
port is the port address to which WebLogic Server is listening.
contextPath is the value of this element
serviceURI is the value of the webservice-serviceuri element.
When using the jwsc Ant task to generate a Web Service from a JWS file, the value of the <webservice-contextpath> element is taken from the contextPath attribute of the WebLogic-specific @WLHttpTransport annotation or the <WLHttpTransport> child element of jwsc.
The <webservice-description> element is a holder of other elements used to describe a Web Service. The <webservice-description> element defines a set of port components (specified using one or more <port-component> child elements) that are associated with the WSDL ports defined in the WSDL document.
There may be multiple <webservice-description> elements defined within a single weblogic-webservices.xml file, each corresponding to a particular stateless session EJB or Java class contained within the archive, depending on the implementation of your Web Service. In other words, an EJB JAR contains the EJBs that implement a Web Service, a WAR file contains the Java classes.
The <webservice-description-name> element specifies the internal name of the Web Service. The value of this element must be unique for all <webservice-description-name> elements within a single weblogic-webservices.xml file.
Element used to group together all the security-related elements of the weblogic-webservices.xml deployment descriptor.
The <webservice-serviceuri> element specifies the Web Service URI portion of the URL used to invoke the Web Service. The URL to invoke a Web Service deployed to WebLogic Server is:
http://host:port/contextPath/serviceURI
where
host is the host computer on which WebLogic Server is running.
port is the port address to which WebLogic Server is listening.
contextPath is the value of the webservice-contextpath element
serviceURI is the value of this element.
When using the jwsc Ant task to generate a Web Service from a JWS file, the value of the <webservice-serviceuri> element is taken from the serviceURI attribute of the WebLogic-specific @WLHttpTransport annotation or the <WLHttpTransport> child element of jwsc.
The <webservice-type> element specifies whether the Web Service is based on the JAX-WS or JAX-RPC standard. Valid values include: JAXWS and JAXRPC. This value defaults to JAXRPC.
Element used to group together all the WSDL-related elements of the weblogic-webservices.xml deployment descriptor.
The <wsdl-publish-file> element specifies a directory (on the computer which hosts the Web Service) to which WebLogic Server should publish a hard-copy of the WSDL file of a deployed Web Service; this is in addition to the standard WSDL file accessible via HTTP.
For example, assume that your Web Service is implemented with an EJB, and its WSDL file is located in the following directory of the EJB JAR file, relative to the root of the JAR:
META-INF/wsdl/a/b/Fool.wsdl
Further assume that the weblogic-webservices.xml file includes the following element for a given Web Service:
<wsdl-publish-file>d:/bar</wsdl-publish-file>
This means that when WebLogic Server deploys the Web Service, the server publishes the WSDL file at the standard HTTP location, but also puts a copy of the WSDL file in the following directory of the computer on which the service is running:
d:/bar/a/b/Foo.wsdl
Note:
Only specify this element if client applications that invoke the Web Service need to access the WSDL via the local file system or FTP; typically, client applications access the WSDL using HTTP, as described in "Browsing to the WSDL of the Web Service" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Getting Started With JAX-WS Web Services for Oracle WebLogic Server.The value of this element should be an absolute directory pathname. This directory must exist on every machine which hosts a WebLogic Server instance or cluster to which you deploy the Web Service.