| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Enterprise Deployment Guide for Oracle Identity Management 11g Release 1 (11.1.1) Part Number E12035-03 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Enterprise Deployment Guide for Oracle Identity Management 11g Release 1 (11.1.1) Part Number E12035-03 |
|
|
View PDF |
Oracle Identity Management presents a comprehensive suite of products for all aspects of identity management. In the context of Oracle Fusion Middleware, the Oracle Identity Management Infrastructure described in this book primarily includes Oracle Access Manager and Oracle Internet Directory (and/or Oracle Virtual Directory). The directory services provide core LDAP support for both authentication and authorization support in conjunction with Oracle Platform Security Services. Oracle Access Management is the recommended solution for single sign-on across Oracle Fusion Middleware components.
This guide describes a reference enterprise topology for the Oracle Identity Management Infrastructure components of Oracle Fusion Middleware. It also provides detailed instructions and recommendations to create the topology by following the enterprise deployment guidelines.
This chapter includes the following topics:
An enterprise deployment is an Oracle best practices blueprint based on proven Oracle high-availability technologies and recommendations for Oracle Fusion Middleware. The high-availability best practices described in this book make up one of several components of high-availability best practices for all Oracle products across the entire technology stack—Oracle Database, Oracle Fusion Middleware, Oracle Applications, Oracle Collaboration Suite, and Oracle Grid Control.
An Oracle Fusion Middleware enterprise deployment:
Considers various business service level agreements (SLA) to make high-availability best practices as widely applicable as possible
Leverages database grid servers and storage grid with low-cost storage to provide highly resilient, lower cost infrastructure
Uses results from extensive performance impact studies for different configurations to ensure that the high-availability architecture is optimally configured to perform and scale to business needs
Enables control over the length of time to recover from an outage and the amount of acceptable data loss from a natural disaster
Evolves with each Oracle version and is completely independent of hardware and operating system
For more information on high availability practices, visit:
http://www.oracle.com/technology/deploy/availability/htdocs/maa.htm
Table 1-1 provides definitions for some of the terms that define the architecture of an Oracle Fusion Middleware environment:
Table 1-1 Oracle Fusion Middleware Architecture Terminology
The Oracle Fusion Middleware configurations discussed in this guide are designed to ensure security of all transactions, maximize hardware resources, and provide a reliable, standards-compliant system for enterprise computing with a variety of applications. The security and high availability benefits of the Oracle Fusion Middleware configurations are realized through isolation in firewall zones and replication of software components.
The Enterprise Deployment architectures are secure because every functional group of software components is isolated in its own DMZ, and all traffic is restricted by protocol and port. The following characteristics ensure security at all needed levels, as well as a high level of standards compliance:
All external communication received on port 80 is redirected to port 443.
Communication from external clients does not go beyond the Load Balancing Router level.
No direct communication from the Load Balancing Router to the data tier DMZ is allowed.
Components are separated between DMZs on the web tier, application tier, and the directory tier.
Direct communication between two firewalls at any one time is prohibited.
If a communication begins in one firewall zone, it must end in the next firewall zone.
Oracle Internet Directory is isolated in the directory tier DMZ.
Identity Management components are in the application tier DMZ.
All communication between components across DMZs is restricted by port and protocol, according to firewall rules.
The instructions and diagrams in this guide describe a reference topology, to which variations may be applied.
This guide provides configuration instructions for an Oracle Identity Management Infrastructure enterprise deployment using the directory services product and Oracle Access Manager, as shown in Figure 1-1.
Figure 1-1 MyCompany Topology with Oracle Access Manager
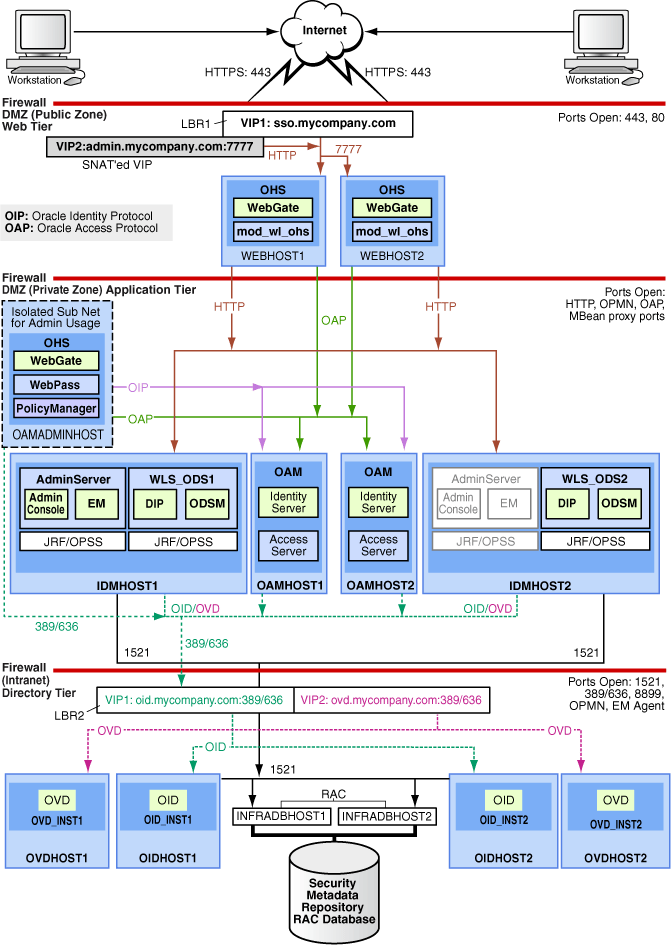
The computers in the myIDMCompany topology are grouped into the directory tier, application tier, and web tier. These tiers are described in the following sections.
The directory tier is in the Intranet Zone. The directory tier is the deployment tier where all the LDAP services reside. This tier includes products such as Oracle Internet Directory and Oracle Virtual Directory. The directory tier is managed by directory administrators providing enterprise LDAP service support.
The directory tier is closely tied with the data tier, therefore access to the data tier is important:
Oracle Internet Directory relies on RDBMS as its backend.
Oracle Virtual Directory provides virtualization support for other LDAP services or databases or both.
In some cases, the directory tier and data tier may be managed by the same group of administrators. In many enterprises, however, database administrators own the data tier while directory administrators own the directory tier.
Typically protected by firewalls, applications above the directory tier access LDAP services through a designated LDAP host port. The standard LDAP port is 389 for the non-SSL port and 636 for the SSL port. LDAP services are often used for white pages lookup by clients such as email clients in the intranet.
The application tier is the tier where J2EE applications are deployed. Products such as Oracle Directory Integration Platform, Oracle Identity Federation, Oracle Directory Services Manager and Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control are the key J2EE components that can be deployed in this tier. Applications in this tier benefit from the High Availability support of Oracle WebLogic Server.
The Identity Management applications in the application tier interact with the directory tier:
In some cases, they leverage the directory tier for enterprise identity information.
In some cases, they leverage the directory tier (and sometimes the database in the data tier) for application metadata.
Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control and Oracle Directory Services Manager are administration tools that provide administrative functionalities to the components in the application tier as well as the directory tier.
WebLogic Server has built-in web server support. If enabled, the HTTP listener will exist in the application tier as well. However, for the enterprise deployment shown in Figure 1-1, customers will have a separate web tier relying on web servers such as Apache or Oracle HTTP Server.
In the application tier:
IDMHOST1 and IDMHOST2 have the WebLogic Server with the Administration Console, Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control, Oracle Directory Integration Platform, and Oracle Directory Services Manager installed.
IDMHOST1 and IDMHOST2 run both the WebLogic Server Administration Servers and Managed Servers. Note that the administration server is configured to be active-passive, that is, although it is installed on both nodes, only one instance is active at any time. If the active instance goes down, then the passive instance starts up and becomes the active instance.
On the firewall protecting the application tier, the HTTP ports, OIP port, and OAP port are open. The OIP (Oracle Identity Protocol) port is for the WebPass module running in Oracle HTTP Server in the web tier to communicate with Oracle Access Manager to perform operations such as querying user groups. The OAP (Oracle Access Protocol) port is for the WebGate module running in Oracle HTTP Server in the web tier to communicate with Oracle Access Manager to perform operations such as user authentication.
OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2 have Oracle Access Manager (with the Identity Server and Access Server components) installed. Oracle Access Manager is the single sign-on component for Oracle Fusion Middleware. It communicates with Oracle Internet Directory in the directory tier to verify user information.
OAMADMINHOST is on an isolated subnet (for Oracle Access Manager administration), and it has Oracle HTTP Server, WebGate, WebPass, and Policy Manager installed.
Architecture Notes
Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control is integrated with Oracle Access Manager using the Oracle Platform Security Service (OPSS) agent.
The Administration Server and Oracle Enterprise Manager are always bound to the listen address of the Administration Server.
The WLS_ODS1 Managed Server on IDMHOST1 and WLS_ODS2 Managed Server on IDMHOST2 are in a cluster and the Oracle Directory Services Manager and Oracle Directory Integration Platform applications are targeted to the cluster.
Oracle Directory Services Manager and Oracle Directory Integration Platform are bound to the listen addresses of the WLS_ODS1 and WLS_ODS2 Managed Servers. By default, the listen address for these Managed Servers is set to IDMHOST1 and IDMHOST2 respectively.
High Availability Provisions
The Identity Servers and Access Servers are active-active deployments; the Access Server may communicate with the Identity Server at run time.
The WebLogic Administration Server and Oracle Enterprise Manager deployment is active-passive (where other components are active-active).
The WebLogic Administration Server is a singleton component deployed in an active-passive configuration. If IDMHOST1 fails or the Administration Server on IDMHOST1 does not start, the Administration Server on IDMHOST2 can be started. All Managed Servers and components on IDMHOST1 and IDMHOST2 must be configured with the Administration Server virtual IP.
Security Provisions
WebPass communication from the public DMZ to Identity and Access Servers is not allowed.
The Policy Manager (an Oracle HTTP Server module secured with both WebGate and WebPass) is deployed in an isolated administrative subnet, which communicates directly with Oracle Internet Directory.
The web tier is in the DMZ Public Zone. The HTTP Servers are deployed in the web tier.
Most of the Identity Management components can function without the web tier, but for most enterprise deployments, the web tier is desirable. To support enterprise level single sign-on using products such as Oracle Single Sign-On and Oracle Access Manager, the web tier is required.
While components such as Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control and Oracle Directory Services Manager can function without a web tier, they can be configured to use a web tier, if desired.
In the web tier:
WEBHOST1 and WEBHOST2 have Oracle HTTP Server, WebGate (an Oracle Access Manager component), and the mod_wl_ohs plug-in module installed. The mod_wl_ohs plug-in module allows requests to be proxied from Oracle HTTP Server to a WebLogic Server running in the application tier.
WebGate (an Oracle Access Manager component) in Oracle HTTP Server uses Oracle Access Protocol (OAP) to communicate with Oracle Access Manager running on OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2, in the Identity Management DMZ. WebGate and Oracle Access Manager are used to perform operations such as user authentication.
On the firewall protecting the web tier, only the HTTP ports are open: 443 for HTTPS and 80 for HTTP.
Architecture Notes
Oracle HTTP Servers on WEBHOST1 and WEBHOST2 are configured with mod_wl_ohs, and proxy requests for the Oracle Enterprise Manager, Oracle Directory Integration Platform, and Oracle Directory Services Manager J2EE applications deployed in WebLogic Server on IDMHOST1 and IDMHOST2.
Security Provisions
WebPass is installed on OAMADMINHOST along with the Policy Manager. The Policy Manager and the WebPass are used to configure the Access Servers and the Identity Servers on OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2.
WebGate is installed on OAMADMINHOST to protect the Policy Manager, and configured on WEBHOST1 and WEBHOST2 to protect inbound access.
Oracle Access Manager Identity Assertion Provider for WebLogic Server 11gR1 is installed on IDMHOST1 and IDMHOST2.
Table 1-2 identifies the source for installation of each software component:
Table 1-2 Components and Installation Sources
| Component | CD |
|---|---|
|
Oracle Database 10g or 11g |
Oracle Database CD (10.2.0.4 or higher) Oracle Database CD (11.1.0.7) |
|
Oracle WebLogic Server |
WebLogic Server 10.3.1 CD |
|
Oracle Identity and Access Management Components |
This includes 11g Oracle Internet Directory, Oracle Virtual Directory, Oracle Directory Integration Platform, Oracle Directory Services Manager, Oracle Identity Federation, as well as Oracle Access Manager 10.1.4.3 components. Oracle Identity Management CD (11.1.1.1.0) |
|
Repository Creation Utility |
Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository Creation Utility CD (11.1.1.1.0) |
|
Oracle HTTP Server |
Oracle Fusion Middleware Web Tier and Utilities CD (11.1.1.1.0) |
For information about the order in which to perform the installations, see Section 1.5, "How to Use This Guide."
The chapters in the guide are arranged chronologically. Complete the procedures in the sections as shown in the table according to the desired configuration.