| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle Data Integrator 11g Release 1 (11.1.1) Part Number E12643-03 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle Data Integrator 11g Release 1 (11.1.1) Part Number E12643-03 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter describes how to work with Oracle Data Integrator Console. An overview of the Console user interface is provided.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Oracle Data Integrator Console is a web-based console for managing and monitoring an Oracle Data Integrator run-time architecture and for browsing design-time objects.
This section contains the following topics:
Oracle Data Integrator Console is a web-based console available for different types of users:
Administrators use Oracle Data Integrator Console to create and import repositories and to configure the Topology (data servers, schemas, and so forth).
Production operators use Oracle Data Integrator Console to manage scenarios, monitor sessions, and manage the content of the error tables generated by Oracle Data Integrator.
Business users and developers browse development artifacts in this interface, using, for example, the Data Lineage and Flow Map features.
This web interface integrates seamlessly with Oracle Fusion Middleware Control Console and allows Fusion Middleware administrators to drill down into the details of Oracle Data Integrator components and sessions.
Note:
Oracle Data Integrator Console is required for the Fusion Middleware Control Extension for Oracle Data Integrator. It must be installed and configured for this extension to discover and display the Oracle Data Integrator components in a domain.Oracle Data Integrator Console is a web interface using the ADF-Faces framework.
Figure 21-1 shows the layout of Oracle Data Integrator Console.
Figure 21-1 Oracle Data Integrator Console
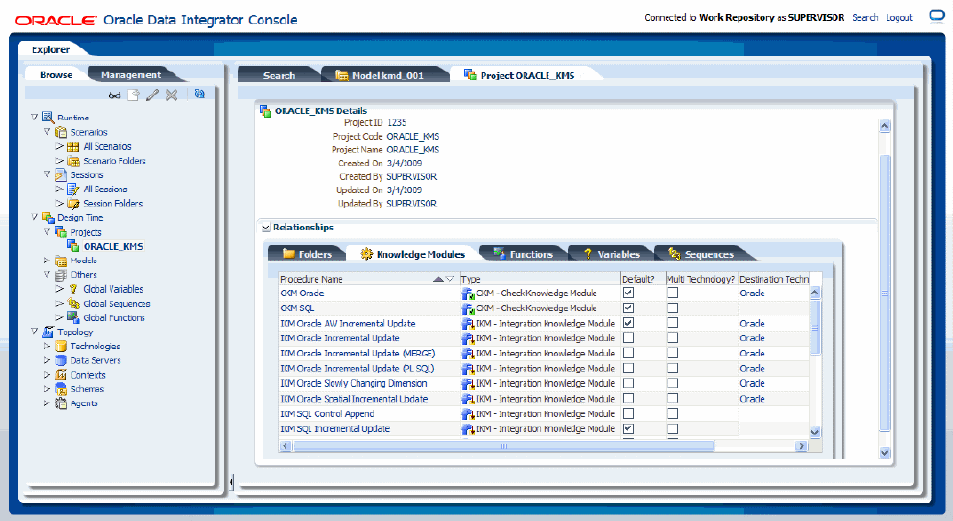
Oracle Data Integrator Console displays the objects available to the current user in two Navigation tabs in the left panel:
Browse tab displays the repository objects that can be browsed and edited. In this tab you can also manage sessions and error tables.
Management tab is used to manage the repositories and the repository connections. This tab is available to connection users having Supervisor privileges, or to any user to set up the first repository connections.
The right panel displays the following tabs:
Search tab is always visible and allows you to search for objects in the connected repository.
One Master/Details tab is displayed for each object that is being browsed or edited. Note that it is possible to browse or edit several objects at the same time.
The search field above the Navigation tabs allows you to open the search tab when it is closed.
Working with the Navigation Tabs
In the Navigation tabs, you can browse for objects contained in the repository. When an object or node is selected, the Navigation Tab toolbar displays icons for the actions available for this object or node. If an action is not available for this object, the icon is grayed out. For example, you can edit and add data server objects under the Topology node in the Browse Tab, but you cannot edit Projects under the Designer node. Note that the number of tabs that you can open at the same time is limited to ten.
This section explains the different types of operations available in Oracle Data Integrator console. It does not focus on each type of object that can be managed with the console, but gives keys to manage objects with the console.
This section includes the following topics:
Note:
Oracle Data Integrator Console uses the security defined in the master repository. Operations that are not allowed for a user will appear grayed out for this user.In addition, the Management tab is available only for users with Supervisor privileges.
Oracle Data Integrator console connects to a repository via a Repository Connection, defined by an administrator.
Note that you can only connect to Oracle Data Integrator Console if it has been previously installed. See the Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation and Upgrade Guide for Oracle Data Integrator for more information about installing Oracle Data Integrator Console.
Note:
The first time you connect to Oracle Data Integrator Console, if no repository connection is configured, you will have access to the Management tab to create a first repository connection. See "Creating a Repository Connection" for more information. After your first repository connection is created, the Management tab is no longer available from the Login page, and is available only for users with Supervisor privileges.Connecting to Oracle Data Integrator Console
To connect to Oracle Data Integrator Console:
Open a web browser, and connect to the URL where Oracle Data Integrator Console is installed. For example: http://odi_host:8001/odiconsole/.
From the Repository list, select the Repository connection corresponding to the master or work repository you want to connect.
Provide a User ID and a Password.
Click Sign In.
This section describes the generic operations available in Oracle Data Integrator Console for a typical user.
This section includes the following operations:
Viewing an Object
To view an object:
Select the object in the Browse or Management Navigation tab.
Click View in the Navigation tab toolbar. The simple page or the Master/Detail page for the object opens.
Editing an Object
To edit an object:
Select the object in the Browse or Management Navigation tab.
Click Update in the Navigation tab toolbar. The edition page for the object opens.
Change the value for the object fields.
Click Save in the edition page for this object.
Creating an Object
To create an object:
Navigate to the parent node of the object you want to create in the Browse or Management Navigation tab. For example, to create a Context, navigate to the Topology > Contexts node in the Browse tab.
Click Create in the Navigation tab toolbar. An Add dialog for this object appears.
Provide the values for the object fields.
Click Save in the Add dialog of this object. The new object appears in the Navigation tab.
Deleting an Object
To delete an object:
Select the object in the Browse or Management Navigation tab.
Click Delete in the Navigation tab toolbar.
Click OK in the confirmation window.
Searching for an Object
To search for a design-time or Topology object:
In the Search tab, select the tab corresponding to the object you want to search:
Designer tab allows you to search for design-time objects.
Topology tab allows you to search for topology objects.
In the Search Text field, enter a part of the name of the object that you want to search. Select Case sensitive if you want the search to be case sensitive.
Select in Models/Project (Designer tab) or Topology (Topology tab) the type of object you want to search for. Select All to search for all objects.
Click Search.
The Search Results appear, grouped by object type. You can click an object in the search result to open its master/details page.
This section describes the operations related to scenarios and sessions available in Oracle Data Integrator Console.
This section includes the following operations:
Importing a Scenario
To import a scenario:
Select the Browse Navigation tab.
Navigate to Runtime > Scenarios > All Scenarios.
Click Import in the Navigation tab toolbar.
Select an Import Mode and select an export file in Scenario XML File.
Click Import Scenario.
Exporting a Scenario
To export a scenario:
Select the Browse Navigation tab.
Navigate to Runtime > Scenarios > All Scenarios.
Click Import in the Navigation tab toolbar.
Select an Import Mode and select an export file in Scenario XML File.
Click Import Scenario.
Running a Scenario
To execute a scenario:
Select the Browse Navigation tab.
Navigate to Runtime > Scenarios > All Scenarios.
Select the scenario you want to execute.
Click Execute in the Navigation tab toolbar.
Select an Agent, a Context, and a Log Level for this execution.
Click Execute Scenario.
Stopping a Session
Note that you can perform a normal or an immediate kill of a running session. Sessions with the status Done, Warning, or Error cannot be killed.
To kill a session:
Select the Browse Navigation tab.
Navigate to Runtime > Scenarios > All Sessions.
Select the session you want to stop.
Click Kill in the Navigation tab toolbar.
Restarting a Session
To restart a session:
Select the Browse Navigation tab.
Navigate to Runtime > Scenarios > All Sessions.
Select the session you want to restart.
Click Restart in the Navigation tab toolbar.
Cleaning Stale Sessions
To clean stale sessions:
Select the Browse Navigation tab.
Navigate to Runtime > Scenarios > All Sessions.
Click Clean in the Navigation tab toolbar.
In the Clean Stale Sessions dialog, select the Agent for which you want to clean stale sessions.
Click OK.
Managing Data Statistics and Erroneous Records
Oracle Data Integrator Console allows you to browse the details of a session, including the record statistics. When a session detects erroneous data during a flow or static check, these errors are isolated into error tables. You can also browse and manage the erroneous rows using Oracle Data Integrator Console.
Note:
Sessions with erroneous data detected finish in Warning status.To view the erroneous data:
Select the Browse Navigation tab.
Navigate to a given sessions using Runtime > Sessions > All Sessions, the Search panel or from the Session tab of Scenario page.
Expand the Relationships section and then select the Record Statistics tab. This tab shows each physical table targeting in this session, as well as the record statistics.
Click the number shown in the Errors column. The content of the error table appears.
You can filter the errors by Constraint Type, Name, Message Content, Detection date, and so forth. Click Filter Result to apply a filter.
Select a number of errors in the Query Results table and click Delete to delete these records.
Click Delete All to delete all the errors.
Note:
Delete operations cannot be undone.This section describes how to use the Data Lineage and Flow Map features available in Oracle Data Integrator Console.
Data Lineage provides graph displaying the flows of data from the point of view of a given datastore. In this graph, you can navigate back and forth and follow this data flow.
Flow Map provides a map of the relations that exist between the data structures (models, sub-models and datastores) and design-time objects (projects, folders, packages, interfaces). This graph allows you to draw a map made of several data structures and their data flows.
This section includes the following operations:
Working with the Data Lineage
To view the Data Lineage:
Select the Browse Navigation tab.
Navigate to Design Time > Models > Data Lineage.
Click View in the Navigation tab toolbar.
In the Data Lineage page, select a Model, then a Sub-Model and a datastore in this model.
Select Show Interfaces if you want that interfaces are displayed between the datastores nodes.
Select the prefix to add in your datastores and interface names in the Naming Options section.
Click View to draw the Data Lineage graph. This graph is centered on the datastore selected in step 4.
In this graph, you can use the following actions:
Click Go Back to return to the Data Lineage options and redraw the graph.
Use the Hand tool and then click a datastore to redraw the lineage centered on this datastore.
Use the Hand tool and then click an interface to view this interface's page.
Use the Arrow tool to expand/collapse groups.
Use the Move tool to move the graph.
Use the Zoom In/Zoom Out tools to resize the graph.
Select View Options to change the display options have the graph refreshed with this new option.
Working with the Flow Map
To view the Flow Map:
Select the Browse Navigation tab.
Navigate to Design Time > Models > Flow Map.
Click View in the Navigation tab toolbar.
In the Data Lineage page, select one or more Model. Select All to select all models.
Select one of more Projects. Select All to select all projects.
In the Select the level of details of the map section, select the granularity of the map. The object that you select here will be the nodes of your graph.
Check Do not show Projects, Folders... if you want the map to show only data structure.
Optionally, indicate the grouping for the data structures and design-time objects in the map, using the options in the Indicate how to group Objects in the Map section.
Click View to draw the Flow Map graph.
In this graph, you can use the following actions:
Click Go Back to return to the Flow Map options and redraw the graph.
Use the Hand tool and then click a node (representing a datastore, an interface, and so forth) in the map to open this object's page.
Use the Arrow tool to expand/collapse groups.
Use the Move tool to move the graph.
Use the Zoom In/Zoom Out tools to resize the graph.
This section describes the different administrative operations available in Oracle Data Integrator Console. These operations are available for a user with Supervisor privileges.
This section includes the following operations:
Creating a Repository Connection
A repository connection is a connection definition for Oracle Data Integrator Console. A connection does not include Oracle Data Integrator user and password information.
To create a repository connection:
Navigate to the Repository Connections node in the Management Navigation tab.
Click Create in the Navigation tab toolbar. A Create Repository Connection dialog for this object appears.
Provide the values for the repository connection:
Connection Alias: Name of the connection that will appear on the Login page.
Master JNDI URL: JNDI URL of the datasource to connect the master repository database.
Supervisor User Name: Name of the Oracle Data Integrator user with Supervisor privileges that Oracle Data Integrator Console will use to connect to the repository. This user's password must be declared in the WLS Credential Store.
Work JNDI URL: JNDI URL of the datasource to connect the work repository database. If no value is given in this field. The repository connection will allow connection to the master only, and the Navigation will be limited to Topology information.
JNDI URL: Check this option if you want to use the environment naming context (ENC). When this option is checked, Oracle Data Integrator Console automatically prefixes the data source name with the string java:comp/env/ to identify it in the application server's JNDI directory. Note that the JNDI Standard is not supported by Oracle WebLogic Server and for global data sources.
Default: Check this option if you want this Repository Connection to be selected by default on the login page.
Click Save. The new Repository Connection appears in the Management Navigation tab.
Administering Repositories
Oracle Data Integrator Console provides you with features to perform management operations (create, import, export) on repositories. These operations are available from the Management Navigation tab, under the Repositories node. These management operations reproduce in a web interface the administrative operations available via the Oracle Data Integrator Studio and allow setting up and maintaining your environment from the ODI Console.
See Chapter 3, "Administering the Oracle Data Integrator Repositories" and Chapter 18, "Exporting/Importing" for more information on these operations.
Administering Java EE Agents
Oracle Data Integrator Console allows you to add JDBC datasources and create templates to deploy physical agents into WebLogic Server.
See Chapter 4, "Setting-up the Topology" for more information on Java EE Agents, datasources and templates.
To add a datasource to a physical agent:
Select the Browse Navigation tab.
Navigate to Topology > Agents > Physical Agents.
Select the agent you want to manage.
Click Edit in the Navigation tab toolbar.
Click Add Datasource
Provide a JNDI Name for this datasource and select the Data Server Name. This datasource will be used to connect to this data server from the machine into which the Java EE Agent will be deployed.
Click OK.
Click Save to save the changes to the physical agent.
To create a template for a physical agent:
Select the Browse Navigation tab.
Navigate to Topology > Agents > Physical Agents.
Select the agent you want to manage.
Click Edit in the Navigation tab toolbar.
Click Agent Deployment.
Follow the steps of the Agent Deployment wizard. This wizard reproduces in a web interface the WLS Template Generation wizard. See Chapter 4, "Deploying an Agent in a Java EE Application Server (Oracle WebLogic Server)" for more details.