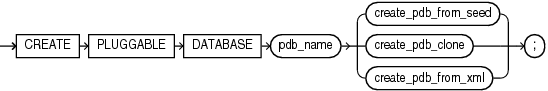
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE
Use the CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement to create a pluggable database (PDB).
This statement enables you to perform the following tasks:
-
Create a PDB by using the seed as a template
Use the
create_pdb_from_seedclause to create a PDB by using the seed in the multitenant container database (CDB) as a template. The files associated with the seed are copied to a new location and the copied files are then associated with the new PDB. -
Create a PDB by cloning an existing PDB or non-CDB
Use the
create_pdb_cloneclause to create a PDB by copying an existing PDB or non-CDB and then plugging the copy into the CDB. The files associated with the existing PDB or non-CDB are copied to a new location and the copied files are associated with the new PDB.Note:
Creating a PDB by cloning a non-CDB is available starting with Oracle Database 12c Release 1 (12.1.0.2). -
Create a PDB by plugging an unplugged PDB or a non-CDB into a CDB
Use the
create_pdb_from_xmlclause to plug an unplugged PDB or a non-CDB into a CDB, using an XML metadata file.
Note:
When a new PDB is established in a CDB, it is possible that the name of a service offered by the new PDB will collide with an existing service name. The namespace in which a collision can occur is that of the listener that gives access to the CDB. Within that namespace, collisions are possible among the names of non-CDB's default services, CDB's default services, PDB's default services, and user-defined services. For example, if two or more CDBs on the same computer system use the same listener, and the newly established PDB has the same service name as another PDB in these CDBs, then a collision occurs.You must not attempt to operate a PDB that causes a collision with an existing service name. If the colliding name is that of the PDB's default service, then you must rename the PDB. If the colliding name is that of a user-created service within the PDB, then you must drop that service and create one in its place, with a non-colliding name, that has the same purpose and properties.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Concepts for general information on PDBs
-
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for information on managing PDBs
-
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE and DROP PLUGGABLE DATABASE for information on modifying and dropping PDBs
You must be connected to a CDB and the current container must be the root.
You must have the CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE system privilege.
The CDB in which the PDB is being created must be in READ WRITE mode.
To specify the create_pdb_clone clause:
-
If
src_pdb_namerefers to a PDB in the same CDB, then you must have theCREATEPLUGGABLEDATABASEsystem privilege in the root of the CDB in which the new PDB will be created and in the PDB being cloned. -
If
src_pdb_namerefers to a PDB in a remote database or a non-CDB, then you must have theCREATEPLUGGABLEDATABASEsystem privilege in the root of the CDB in which the new PDB will be created and the remote user must have theCREATEPLUGGABLEDATABASEsystem privilege in the PDB or non-CDB to whichsrc_pdb_namerefers.
Description of the illustration create_pluggable_database.gif
(create_pdb_from_seed::=, create_pdb_clone::=, create_pdb_from_xml::=)
Description of the illustration create_pdb_from_seed.gif
(pdb_dba_roles::=, default_tablespace::=, file_name_convert::=, pdb_storage_clause::=, path_prefix_clause::=, tempfile_reuse_clause::=, user_tablespaces_clause::=, standbys_clause::=, logging_clause::=, create_file_dest_clause::=)
Description of the illustration pdb_dba_roles.gif
Description of the illustration default_tablespace.gif
(datafile_tempfile_spec::=, extent_management_clause::=)
Description of the illustration file_name_convert.gif
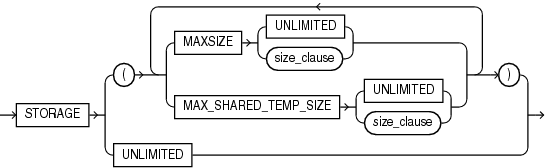
Description of the illustration pdb_storage_clause.gif
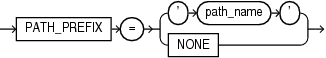
Description of the illustration path_prefix_clause.gif
Description of the illustration tempfile_reuse_clause.gif
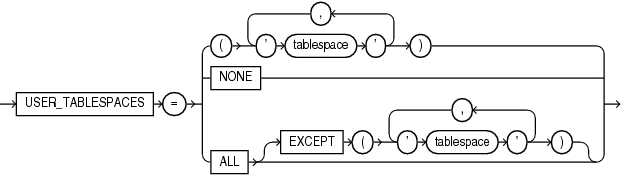
Description of the illustration user_tablespaces_clause.gif
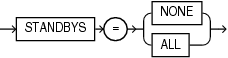
Description of the illustration standbys_clause.gif
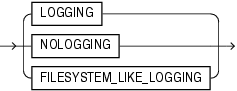
Description of the illustration logging_clause.gif
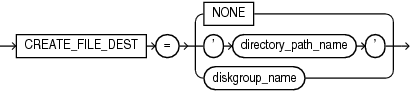
Description of the illustration create_file_dest_clause.gif
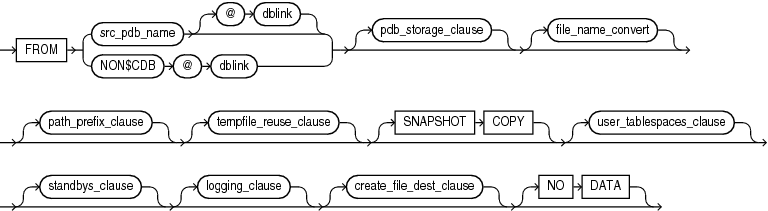
Description of the illustration create_pdb_clone.gif
(pdb_storage_clause::=, file_name_convert::=, path_prefix_clause::=, tempfile_reuse_clause::=, user_tablespaces_clause::=, standbys_clause::=, logging_clause::=, create_file_dest_clause::=)
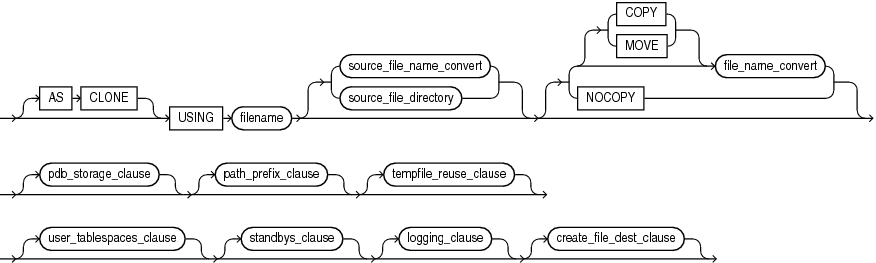
Description of the illustration create_pdb_from_xml.gif
(source_file_name_convert::=, source_file_directory::=, file_name_convert::=, pdb_storage_clause::=, path_prefix_clause::=, tempfile_reuse_clause::=, user_tablespaces_clause::=, standbys_clause::=, logging_clause::=, create_file_dest_clause::=)
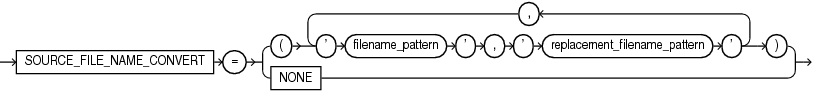
Description of the illustration source_file_name_convert.gif
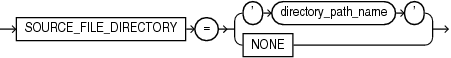
Description of the illustration source_file_directory.gif
Specify the name of the PDB to be created. The first character of a PDB name must be alphanumeric and the remaining characters can be alphanumeric or the underscore character (_).
The PDB name must be unique in the CDB, and it must be unique within the scope of all the CDBs whose instances are reached through a specific listener.
This clause enables you to create a PDB by using the seed in the CDB as a template.
See Also:
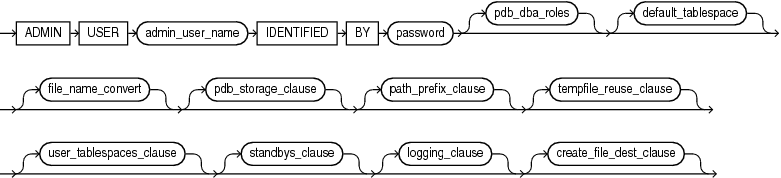
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for the complete steps for creating a PDB using the seedUse this clause to create an administrative user who can be granted the privileges required to perform administrative tasks on the PDB. For admin_user_name, specify name of the user to be created. Use the IDENTIFIED BY clause to specify the password for admin_user_name. Oracle Database creates a local user in the PDB and grants the PDB_DBA local role to that user.
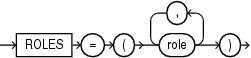
This clause lets you grant one or more roles to the PDB_DBA role. Use this clause to grant roles that have the privileges required by the administrative user of the PDB. For role, specify a predefined role. For a list of predefined roles, refer to Oracle Database Security Guide.
You can also use the GRANT statement to grant roles to the PDB_DBA role after the PDB has been created. Until you have granted the appropriate privileges to the PDB_DBA role, the SYS and SYSTEM users can perform administrative tasks on a PDB.
Specify this clause to create a default permanent tablespace for the PDB. The default_tablespace clause has the same semantics that it has for the CREATE DATABASE statement. For full information, refer to default_tablespace in the documentation on CREATE DATABASE.
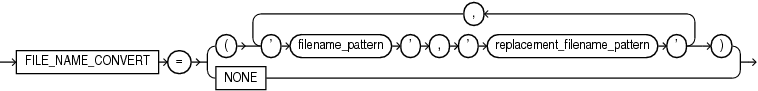
Use this clause to determine how the database generates the names of files (such as data files and wallet files) for the PDB.
-
For
filename_pattern, specify a string found in names of files associated with the seed (when creating a PDB by using the seed), associated with the source PDB (when cloning a PDB), or listed in the XML file (when plugging a PDB into a CDB). -
For
replacement_filename_pattern, specify a replacement string.
Oracle Database will replace filename_pattern with replacement_filename_pattern when generating the names of files associated with the new PDB.
File name patterns cannot match files or directories managed by Oracle Managed Files.
You can specify FILE_NAME_CONVERT = NONE, which is the same as omitting this clause. If you omit this clause, then the database first attempts to use Oracle Managed Files to generate file names. If you are not using Oracle Managed Files, then the database uses the PDB_FILE_NAME_CONVERT initialization parameter to generate file names. If this parameter is not set, then an error occurs.
Use this clause to specify storage limits for the PDB.
-
Use
MAXSIZEto limit the amount of storage that can be used by all tablespaces in the PDB to the value specified withsize_clause. This limit includes the size of data files and temporary files for tablespaces belonging to the PDB. SpecifyMAXSIZEUNLIMITEDto enforce no limit. -
Use
MAX_SHARED_TEMP_SIZEto limit the amount of storage in the shared temporary tablespace that can be used by sessions connected to the PDB to the value specified withsize_clause. SpecifyMAX_SHARED_TEMP_SIZEUNLIMITEDto enforce no limit.
If you omit this clause, or specify STORAGE UNLIMITED, then there are no storage limits for the PDB. This is equivalent to specifying STORAGE (MAXSIZE UNLIMITED MAX_SHARED_TEMP_SIZE UNLIMITED).
Use this clause to ensure that file paths for directory objects associated with the PDB are restricted to the specified directory or its subdirectories. You cannot modify the setting of this clause after you create the PDB. This clause does not affect files created by Oracle Managed Files.
-
For
path_name, specify the absolute path name of an operating system directory. The single quotation marks are required, with the result that the path name is case sensitive. Oracle Database usespath_nameas a prefix to the relative paths for directory objects associated with the PDB. If a directory object has an absolute path, then thepath_prefix_clauseis ignored.Be sure to specify
path_nameso that the resulting path name will be properly formed when relative paths are appended to it. For example, on UNIX systems, be sure to endpath_namewith a forward slash (/), such as:PATH_PREFIX = '/disk1/oracle/dba/salespdb/'
-
If you specify
PATH_PREFIX=NONE, then the relative paths for directory objects associated with the PDB are treated as absolute paths and are not restricted to a particular directory.
Omitting the path_prefix_clause is equivalent to specifying PATH_PREFIX = NONE.
When you create a PDB, Oracle Database associates temp files with the new PDB. Depending on how you create the PDB, the temp files may already exist and may have been previously used.
Specify TEMPFILE REUSE to instruct the database to format and reuse a temp file associated with the new PDB if it already exists. If you specify this clause and a temp file does not exist, then the database creates the temp file.
If you do not specify TEMPFILE REUSE and a temp file to be associated with the new PDB already exists, then the database returns an error and does not create the PDB.
Note:
Theuser_tablespaces_clause is available starting with Oracle Database 12c Release 1 (12.1.0.2).This clause lets you specify the tablespaces to be made available in the new PDB. The SYSTEM, SYSAUX, and TEMP tablespaces are available in all PDBs and cannot be specified in this clause.
-
Specify
tablespaceto make the tablespace available in the new PDB. You can specify more than one tablespace in a comma-separated list. -
Specify
NONEto make only theSYSTEM,SYSAUX, andTEMPtablespaces available in the new PDB. -
Specify
ALLto make all tablespaces available in the new PDB. This is the default. -
Specify
ALLEXCEPTto make all tablespaces available in the new PDB, except the specified tablespaces.
Tablespaces that are unavailable in a PDB are offline in the PDB, and all data files that belong to those tablespaces are unnamed and offline in the PDB.
Note:
Thestandbys_clause is available starting with Oracle Database 12c Release 1 (12.1.0.2).Use this clause to specify whether the new PDB is included in standby CDBs.
-
Specify
ALLto include the new PDB in all standby CDBs. During standby recovery, the standby CDB will search for the data files for the PDB. If the data files are not found, then standby recovery will stop and you must copy the data files to the correct location before you can restart recovery. This is the default. -
Specify
NONEto exclude the new PDB from all standby CDBs. When a PDB is excluded from all standby CDBs, the PDB's data files are unnamed and marked offline on all of the standby CDBs. Standby recovery will not stop if the data files for the PDB are not found on the standby. If you instantiate a new standby CDB after the PDB is created, then you must explicitly disable the PDB for recovery on the new standby CDB.You can enable a PDB on a standby CDB after it was excluded on that standby CDB by copying the data files to the correct location, bringing the PDB online, and marking it as enabled for recovery.
Note:
Thelogging_clause is available starting with Oracle Database 12c Release 1 (12.1.0.2).Use this clause to specify the default logging attribute for tablespaces created within the PDB. The logging attribute controls whether certain DML operations are logged in the redo log file (LOGGING) or not (NOLOGGING).The default is LOGGING.
When creating a tablespace, you can override the default logging attribute by specifying the logging_clause of the CREATE TABLESPACE statement.
Refer to logging_clause for a full description of this clause.
Note:
Thecreate_file_dest_clause is available starting with Oracle Database 12c Release 1 (12.1.0.2).By default, a newly created PDB inherits its Oracle Managed Files settings from the root. If the root uses Oracle Managed Files, then the PDB also uses Oracle Managed Files. The PDB shares the same base file system directory for Oracle Managed Files with the root and has its own subdirectory named with the GUID of the PDB. If the root does not use Oracle Managed Files, then the PDB also does not use Oracle Managed Files.
This clause lets you override the default behavior. You can enable or disable Oracle Managed Files for the PDB and you specify a different base file system directory or Oracle ASM disk group for the PDB's files.
-
Specify
NONEto disable Oracle Managed Files for the PDB. -
Specify either
directory_path_nameordiskgroup_nameto enable Oracle Managed Files for the PDB.Specify
directory_path_nameto designate the base file system directory for the PDB's files. Specify the full path name of the operating system directory. The directory must exist and Oracle processes must have appropriate permissions on the directory. The single quotation marks are required, with the result that the path name is case sensitive.Specify
diskgroup_nameto designate the default Oracle ASM disk group for the PDB's files.
If you specify a value other than NONE, then the database implicitly sets the DB_CREATE_FILE_DEST initialization parameter with SCOPE=SPFILE in the PDB.
This clause enables you to create a new PDB by cloning a source to a target PDB. The source can be a PDB in the local CDB, a PDB in a remote CDB, or a non-CDB. The target PDB is the clone of the source.
If the source is a PDB in the local CDB, then the source PDB can be plugged in or unplugged. If the source is a PDB in a remote CDB, then the source PDB must be plugged in.
If the source is a non-CDB or a PDB in a remote CDB, then the source and the CDB that contains the target PDB must meet the following requirements:
-
They must have the same endian format.
-
They must have compatible character sets and national character sets, which means:
-
Every character in the source character set is available in the local CDB character set.
-
Every character in the source character set has the same code point value in the local CDB character set.
-
-
They must have the same set of database options installed.
Users in the source who use the CDB default temporary tablespace are assigned the default temporary tablespace of the CDB that contains the new PDB. Users who use the default temporary tablespace local to the PDB continue to use that temporary tablespace.
See Also:
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for the complete steps for creating a PDB by cloning an existing PDBUse this clause to specify the source PDB or non-CDB. The source must be open with open mode READ ONLY. The files associated with the source are copied to a new location and these copied files are then associated with the new PDB.
-
If the source is a PDB in the local CDB, then use
src_pdb_nameto specify the name of the source PDB. You cannot specifyPDB$SEEDforsrc_pdb_name. Instead, use the create_pdb_from_seed clause to create a PDB by using the seed as a template. -
If the source is a PDB in a remote CDB, then use
src_pdb_nameto specify the name of the source PDB anddblinkto specify the name of the database link to use to connect to the remote CDB. -
If the source is a non-CDB, then specify
NON$CDB@dblink, where dblink is the name of the database link to use to connect to the non-CDB.
Use this clause to specify storage limits for the new PDB. Refer to pdb_storage_clause for the full semantics of this clause.
Use this clause to determine how the database generates the names of files for the new PDB. Refer to file_name_convert for the full semantics of this clause.
Use this clause to ensure that all directory object paths associated with the PDB are restricted to the specified directory or its subdirectories. Refer to path_prefix_clause for the full semantics of this clause.
Specify TEMPFILE REUSE to instruct the database to format and reuse a temp file associated with the new PDB if it already exists. Refer to tempfile_reuse_clause for the full semantics of this clause.
You can specify SNAPSHOT COPY only when cloning a PDB. This clause is not supported when cloning a non-CDB. The source PDB can be in the local CDB or a remote CDB. The SNAPSHOT COPY clause instructs the database to clone the source PDB using storage snapshots. This reduces the time required to create the clone because the database does not need to make a complete copy of the source data files.
When you use the SNAPSHOT COPY clause to create a clone of a source PDB and the CLONEDB initialization parameter is set to FALSE, the underlying file system for the source PDB's files must support storage snapshots. Such file systems include Oracle Automatic Storage Management Cluster File System (Oracle ACFS) and Direct NFS Client storage.
When you use the SNAPSHOT COPY clause to create a clone of a source PDB and the CLONEDB initialization parameter is set to TRUE, the underlying file system for the source PDB's files can be any local file system, network file system (NFS), or clustered file system that has Direct NFS enabled. However, the source PDB must remain in open read-only mode as long as any clones exist.
Direct NFS Client enables an Oracle database to access network attached storage (NAS) devices directly, rather than using the operating system kernel NFS client. If the PDB files are stored on Direct NFS Client storage, then the following additional requirements must be met:
-
The source PDB files must be located on an NFS volume.
-
Storage credentials must be stored in a Transparent Data Encryption keystore.
-
The storage user must have the privileges required to create and destroy snapshots on the volume that hosts the source PDB files.
-
Credentials must be stored in the keystore using an
ADMINISTERKEYMANAGEMENTADDSECRETSQL statement.
When you use the SNAPSHOT COPY clause to create a clone of a source PDB, the following restrictions apply to the source PDB as long as any clones exist:
-
It cannot be unplugged.
-
It cannot be dropped.
PDB clones created using the SNAPSHOT COPY clause cannot be unplugged. They can only be dropped. Attempting to unplug a clone created using the SNAPSHOT COPY clause results in an error.
For a PDB created using the SNAPSHOT COPY clause in an Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) environment, each node that must access the PDB's files must be mounted.
Storage clones are named and tagged using the new PDB GUID. You can query the CLONETAG column of DBA_PDB_HISTORY view to view clone tags for storage clones.
Note:
TheNO DATA clause is available starting with Oracle Database 12c Release 1 (12.1.0.2).The NO DATA clause applies only when cloning a PDB. This clause specifies that the source PDB's data model definition is cloned, but not the PDB's data. The dictionary data in the source PDB is cloned, but all user-created table and index data from the source PDB is discarded.
Restrictions on the NO DATA Clause The following restrictions apply to the NO DATA clause:
-
You cannot specify
NODATAwhen cloning a non-CDB. -
You cannot specify
NODATAif the source PDB contains clustered tables, Advanced Queuing (AQ) tables, index-organized tables, or tables that contain abstract data type columns.
This clause enables you to create a PDB by plugging an unplugged PDB or a non-CDB (the source database) into a CDB (the target CDB). If the source database is an unplugged PDB, then it may have been unplugged from the target CDB or a different CDB.
The source database and the target CDB must meet the following requirements:
-
They must have the same endian format.
-
They must have compatible character sets and national character sets, which means:
-
Every character in the source database character set is available in the target CDB character set.
-
Every character in the source database character set has the same code point value in the target CDB character set.
-
-
They must have the same set of database options installed.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for the complete steps for creating a PDB by plugging an unplugged PDB into a CDB and creating a PDB using a non-CDB
-
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for more information on the
DBMS_PDBpackage
Specify this clause only if the target CDB already contains a PDB that was created using the same set of data files. The source files remain as an unplugged PDB and can be used again. Specifying AS CLONE also ensures that Oracle Database generates new identifiers, such as DBID and GUID, for the new PDB.
Use filename to specify the name of the XML file that contains the metadata that describes the source database that you are plugging in. The XML file and the files associated with the source database must exist in a location that is accessible to the CDB. You can obtain this file as follows:
-
If the source database is an unplugged PDB, then the XML metadata file was created by the
pdb_unplug_clauseofALTERPLUGGABLEDATABASE. -
If the source database is a non-CDB, then you must create the XML metadata file using the
DBMS_PDBpackage.
Specify this clause only if the contents of the XML file do not accurately describe the locations of the source files. If the files that must be used to plug in the source database are no longer in the location specified in the XML file, then use this clause to map the specified file names to the actual file names.
-
For
filename_pattern, specify the string for the location of the files as specified in the XML file. -
For
replacement_filename_pattern, specify the string for the actual location that contains the files that must be used to create the PDB.
Oracle Database will replace filename_pattern with replacement_filename_pattern when searching for the source database files.
File name patterns cannot match files or directories managed by Oracle Managed Files.
If the files that must be used to create the PDB exist in the location specified in the XML file, you can either omit this clause or specify SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERT=NONE.
Note:
Thesource_file_directory clause is available starting with Oracle Database 12c Release 1 (12.1.0.2).Specify this clause only if the contents of the XML file do not accurately describe the locations of the source files and the source files are all present in a single directory. This clause is convenient when you have a large number of data files and specifying a replacement file name pattern for each file using the source_file_name_convert clause is not feasible.
-
For
directory_path_name, specify the absolute path of the directory that contains the source files. The directory is scanned to find the appropriate files based on the unplugged PDB's XML file.
You can specify this clause for configurations that use Oracle Managed Files and for configurations that do not use Oracle Managed Files.
If the files that must be used to create the PDB exist in the location specified in the XML file, you can either omit this clause or specify SOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORY=NONE.
Specify COPY if you want the files listed in the XML file to be copied to the new location and used for the new PDB. This is the default. You can use the optional file_name_convert clause to use pattern replacement in the new file names. Refer to file_name_convert for the full semantics of this clause.
Specify MOVE if you want the files listed in the XML file to be moved, rather than copied, to the new location and used for the new PDB. You can use the optional file_name_convert clause to use pattern replacement in the new file names. Refer to file_name_convert for the full semantics of this clause.
Specify NOCOPY if you want the files for the PDB to remain in their current locations. Use this clause if there is no need to copy or move the files required to plug in the PDB.
Use this clause to specify storage limits for the new PDB. Refer to pdb_storage_clause for the full semantics of this clause.
Use this clause to ensure that all directory object paths associated with the PDB are restricted to the specified directory or its subdirectories. Refer to path_prefix_clause for the full semantics of this clause.
Specify TEMPFILE REUSE to instruct the database to format and reuse a temp file associated with the new PDB if it already exists. Refer to tempfile_reuse_clause for the full semantics of this clause.
Creating a PDB by Using the Seed: Example The following statement creates a PDB salespdb by using the seed in the CDB as a template. The administrative user salesadm is created and granted the dba role. The default tablespace assigned to any non-SYSTEM users for whom no permanent tablespace is assigned is sales. File names for the new PDB will be constructed by replacing /disk1/oracle/dbs/pdbseed/ in the file names in the seed with /disk1/oracle/dbs/salespdb/. All tablespaces that belong to sales must not exceed 2G. The location of all directory object paths associated with salespdb are restricted to the directory /disk1/oracle/dbs/salespdb/.
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE salespdb
ADMIN USER salesadm IDENTIFIED BY password
ROLES = (dba)
DEFAULT TABLESPACE sales
DATAFILE '/disk1/oracle/dbs/salespdb/sales01.dbf' SIZE 250M AUTOEXTEND ON
FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/disk1/oracle/dbs/pdbseed/',
'/disk1/oracle/dbs/salespdb/')
STORAGE (MAXSIZE 2G)
PATH_PREFIX = '/disk1/oracle/dbs/salespdb/';
Cloning a PDB From an Existing PDB: Example The following statement creates a PDB newpdb by cloning PDB salespdb. PDBs newpdb and salespdb are in the same CDB. Because no storage limits are explicitly specified, there is no limit on the amount of storage for newpdb. The files are copied from /disk1/oracle/dbs/salespdb/ to /disk1/oracle/dbs/newpdb/. The location of all directory object paths associated with newpdb are restricted to the directory /disk1/oracle/dbs/newpdb/.
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE newpdb FROM salespdb
FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/disk1/oracle/dbs/salespdb/', '/disk1/oracle/dbs/newpdb/')
PATH_PREFIX = '/disk1/oracle/dbs/newpdb';
Plugging a PDB into a CDB: Example The following statement plugs the PDB salespdb, which was previously unplugged, into the CDB. The details about the metadata describing salespdb are stored in the XML file /disk1/usr/salespdb.xml. The XML file does not accurately describe the current locations of the files. Therefore, the SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERT clause is used to indicate that the files are in /disk2/oracle/dbs/salespdb/, not /disk1/oracle/dbs/salespdb/. The NOCOPY clause indicates that the files are already in the correct location. All tablespaces that belong to sales must not exceed 2G. A file with the same name as the temp file specified in the XML file exists in the target location. Therefore, the TEMPFILE REUSE clause is required.
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE salespdb
USING '/disk1/usr/salespdb.xml'
SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERT =
('/disk1/oracle/dbs/salespdb/', '/disk2/oracle/dbs/salespdb/')
NOCOPY
STORAGE (MAXSIZE 2G)
TEMPFILE REUSE;