| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite 11g Release 1 (11.1.1) Part Number E10224-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite 11g Release 1 (11.1.1) Part Number E10224-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
An SOA composite application is an assembly of services, service components, references, and wires designed and deployed together to meet a business need. This chapter provides a high-level introduction to the various components that together form an SOA composite application.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Changing markets, increasing competitive pressures and evolving customer needs are placing greater pressure on IT to deliver greater flexibility and speed. Today every organization is faced with the must predict change in a global business environment, to rapidly respond to competitors, and to best exploit organizational assets for growth. In response to these challenges, leading companies are adopting SOA to deliver on these requirements by overcoming the complexity of their application and IT environments.
SOA provides an enterprise architecture that supports building connected enterprise applications. SOA facilitates the development of enterprise applications as modular business web services that can be easily integrated and reused, creating a truly flexible, adaptable IT infrastructure.
Oracle SOA Suite provides a complete set of service infrastructure components for designing, deploying, and managing composite applications. Oracle SOA Suite enables services to be created, managed, and orchestrated into composite applications and business processes. Composites enable you to easily assemble multiple technology components into one SOA composite application. Oracle SOA Suite plugs into heterogeneous IT infrastructures and enables enterprises to incrementally adopt SOA.
The components of the suite benefit from common capabilities including a single deployment and management model and tooling, end-to-end security, and unified metadata management. Oracle SOA Suite is unique in that it provides the following set of integrated capabilities:
Messaging
Service discovery
Orchestration
Activity monitoring
Web services management and security
Business rules
Events framework
Oracle SOA Suite puts a strong emphasis on standards and interoperability. Among the standards it leverages are:
Service Component Architecture (SCA) assembly model
Provides the service details and their interdependencies to form composite applications. SCA enables you to represent business logic as reusable service components that can be easily integrated into any SCA-compliant application. The resulting application is known as an SOA composite application. The specification for the SCA standard is maintained by the Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards (OASIS) through the Open Composite Services Architecture (CSA) Member Section:
Specifies a standard data method and can modify business data regardless of how it is physically accessed. Knowledge is not required about how to access a particular back-end data source to use SDO in an SOA composite application. Consequently, you can use static or dynamic programming styles and obtain connected and disconnected access.
Business Process Execution Language (BPEL)
Provides enterprises with an industry standard for business process orchestration and execution. Using BPEL, you design a business process that integrates a series of discrete services into an end-to-end process flow. This integration reduces process cost and complexity.
Processes XML documents and transforms document data from one XML schema to another.
Java Connector Architecture (JCA)
Provides a Java technology solution to the problem of connectivity between the many application servers in Enterprise Information Systems (EIS).
Provides a messaging standard that allows application components based on the Java 2 Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE) to access business logic distributed among heterogeneous systems.
Web Services Description Language (WSDL) file
Provides the entry points into an SOA composite application. The WSDL file provides a standard contract language and is central for understanding the capabilities of a service.
Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP)
Provides the default network protocol for message delivery.
For more information about standards, see the following:
Section 2.1, "Introduction to the SOA Composite Editor" for additional details about these key building blocks
The following URL for SCA and SDO specifications and related material:
http://www.osoa.org
A composite is an assembly of services, service components, wires, and references designed and deployed together in a single application. The composite processes the information described in the messages.
Figure 1-1 describes the operability of an SOA composite application using SCA technology. In this example, an external application (.NET payment calculator) initiates contact with the SOA composite application.
For more information about descriptions of the tasks that services, references, service components, and wires perform in an application, see Section 1.3, "Introduction to SCA Technologies."
Figure 1-1 Introduction to an SOA Composite Application
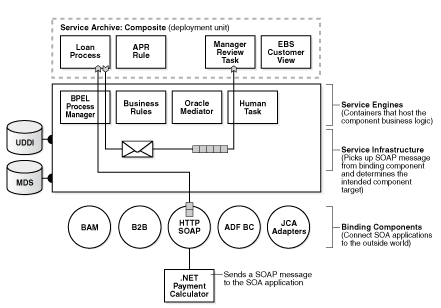
The .NET payment calculator is an external application that sends a SOAP message to the SOA application to initiate contact. The Service Infrastructure picks up the SOAP message from the binding component and determines the intended component target. The BPEL service engine receives the message from the Service Infrastructure for processing by the BPEL Loan Process application and posts the message back to the Service Infrastructure after completing the processing.
Table 1-1 describes the operability of the SOA composite application shown in Figure 1-1.
SCA is the executable model for the assembly of service components into composite applications. SCA provides a programming model for the following:
Creating service components written with a wide range of technologies, including programming languages such as Java, BPEL, C++, and declarative languages such as XSLT. The use of specific programming languages and technologies (including web services) is not required with SCA.
Assembling the service components into an SOA composite application. In the SCA environment, service components are the building blocks of applications.
SCA lets you describe the details of a service and how services and service components interact by providing a model for assembling distributed groups of service components into an application. Composites are used to group service components and wires are used to connect service components. SCA aims to remove middleware concerns from the programming code by applying infrastructure concerns declaratively to compositions, including security and transactions.
The key benefits of SCA include the following:
Loose coupling
Service components integrate with other service components without needing to know how other service components are implemented.
Flexibility
Service components can easily be replaced by other service components.
Services invocation
Services can be invoked either synchronously or asynchronously.
Productivity
Service components are easily integrated to form an SOA composite application.
Easy Maintenance and Debugging
Service components can be easily maintained and debugged when encountered an issue.
Figure 1-2 provides an example of a composite that includes an inbound service binding component, a BPEL process service component (named Account), a business rules service component (named AccountRule), and two outbound reference binding components. The details of this composite are stored in the composite.xml file.
Table 1-1 describes the operability of the SOA composite application shown in Figure 1-1. References are made to sections that provide additional details.
Table 1-1 Introduction to an SOA Composite Application Using SCA Technologies
| Part | Description | Example of Use in Figure 1-1 | See Section |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Binding Components |
Establishes the connectivity between a SOA composite and the external world. There are two types:
|
The SOAP binding component service:
An example of a binding component reference in Figure 1-1 is the Loan Process application. |
|
|
Service Infrastructure |
The Service Infrastructure:
|
||
|
Service Engines (containers hosting service components) |
Host the business logic or processing rules of the service components. Each service component has its own service engine. |
The BPEL service engine:
|
|
|
UDDI and MDS |
The MDS (Metadata Service) repository stores descriptions of available services. The UDDI advertises these services, and enables discovery as well as dynamic binding at runtime. |
The SOAP service used in this composite application is stored in the MDS and can also be published to UDDI. |
Oracle Fusion Middleware Getting Started for Oracle SOA Suite |
|
SOA Archive: Composite (deployment unit) |
The deployment unit that describes the composite application. |
The SOA archive (SAR) of the composite application is deployed to the Service Infrastructure. |
Binding components establish the connection between a SOA composite and the external world. There are two types of binding components:
Services
Provide the outside world with an entry point to the SOA composite application. The WSDL file of the service advertises its capabilities to external applications. These capabilities are used for contacting the SOA composite application components. The binding connectivity of the service describes the protocols that can communicate with the service, for example, SOAP/HTTP or a JCA adapter.
References
Enable messages to be sent from the SOA composite application to external services in the outside world.
Table 1-2 lists and describes the web services provided by Oracle SOA Suite.
Table 1-2 Web Services Provided by Oracle SOA Suite
| Web Services | Description |
|---|---|
|
SOAP over HTTP |
For connecting to standards-based services using SOAP over HTTP. |
|
For integrating services and references with technologies (for example, databases, file systems, FTP servers, messaging: JMS, IBM WebSphere MQ, and so on) and applications (Oracle E-Business Suite, PeopleSoft, and so on). This includes AQ Adapter, Database Adapter, File Adapter, FTP Adapter, JMS Adapter, MQ Adapter, and Socket Adapter. |
|
|
B2B binding component |
For browsing B2B metadata in the MDS repository and selecting document definitions. |
|
For connecting Oracle Application Development Framework (ADF) applications using SDO with the SOA platform. |
|
|
Oracle Applications |
For integrating Oracle Application Adapter with Oracle Applications. |
|
BAM Adapter |
For integrating Java EE applications with Oracle BAM Server to send data and also used as a reference binding component in an SOA composite application. |
|
EJB Service |
For integrating SDO parameters with Enterprise JavaBeans. |
Note:
Business events provide an alternative to using the direct service invocation of the WSDL file contract. Business events are messages sent as the result of an occurrence or situation. When a business event is published, other applications can subscribe to it.The Service Infrastructure provides the internal message routing infrastructure capabilities for connecting components and enabling data flow:
Receives messages from the service providers or external partners through SOAP services or adapters
Sends the message to the appropriate service engine
Receives the message back from the service engine and sends it to any additional service engines in the composite or to a reference binding component based on the wiring
Service components are the building blocks that you use to construct an SOA composite application. Service engines are containers that host the business logic or processing rules of these service components. Service engines process the message information received from the Service Infrastructure.
The following service components are available. There is a corresponding service engine of the same name for each service component. All service engines can interact together in a single composite.
For process orchestration and storage of synchronous or asynchronous process. You design a business process that integrates a series of business activities and services into an end-to-end process flow.
Business rules
For designing a business decision based on rules.
Human task
For modeling a workflow that describes the tasks for users or groups to perform as part of an end-to-end business process flow.
Mediator
For routing events (messages) between different components.
The SAR is a SOA archive deployment unit. The SAR file is deployed to the Service Infrastructure. The SAR packages service components such as BPEL processes, business rules, human tasks, and mediator routing services into a single application. The SAR file is analogous to the BPEL suitcase archive of previous releases, but at the higher composite level and with any additional service components that your application includes (for example, human tasks, business rules, and mediator routing services).
In addition to this developers guide, Oracle also offers the following resources to help you learn how you can best use Oracle SOA Suite in your applications:
Getting Started and Tutorials: The Oracle Fusion Middleware Getting Started with Oracle SOA Suite guide introduces you to Oracle SOA Suite, its components, and provides you with a high-level understanding of what you can accomplish with the suite. The Oracle Fusion Middleware Tutorial for Running and Building an Application with Oracle SOA Suite tutorial describe the step-by-step instructions for running an application developed with Oracle SOA Suite and how to build the SOA elements of the Fusion Order Demo application respectively. Also, you could refer to the Oracle SOA Suite section of the Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g Release 1 documentation library for additional documentation.
Cue Cards in Oracle JDeveloper: Oracle JDeveloper cue cards provide step-by-step support for the application development process using Oracle SOA Suite. They are designed to be used either with the included examples and a sample schema, or with your own data. Cue cards also include topics that provide more detailed background information, viewlets that demonstrate how to complete the steps in the card. Cue cards provide a fast, easy way to become familiar with the basic features of Oracle SOA Suite, and to work through a simple end-to-end task. In Oracle JDeveloper, click Help, Cue Cards to access the cue cards.
http://www.oracle.com/technology/sample_code/products/soa: The SOA OTN provides access to various use case samples for Oracle SOA Suite and its components.