| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite 11g Release 1 (11.1.1) Part Number E10224-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite 11g Release 1 (11.1.1) Part Number E10224-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter describes how to use cross referencing feature of Oracle SOA Suite to associate identifiers for equivalent entities created in different applications.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Section 47.2, "Creating and Modifying Cross Reference Tables"
Section 47.6, "Creating and Running Cross Reference Use Case"
Section 47.7, "Creating and Running Cross Reference for 1M Functions"
Cross references enable you to dynamically map values for equivalent entities created in different applications.
Note:
The Cross Referencing feature enables you to dynamically integrate values between applications, whereas the domain value maps enables you to specify values at design time. For more information about domain value maps, see Chapter 46, "Working with Domain Value Maps".When you create or update objects in one application, you may also want to propagate the changes to other application. For example, when a new customer is created in a SAP application, you might want to create a new entry for the same customer in your Oracle E-Business Suite application named as EBS. However, the applications that you are integrating could be using different entities to represent the same information. For example, for each new customer in a SAP application, a new row is inserted in its Customer database with a unique identifier such as SAP_001. When the same information is propagated to an Oracle E-Business Suite application and a Siebel application, the new row should be inserted with different identifiers such as EBS_1001 and SBL001. In such cases, you need some kind of functionality to map these identifiers with each other so that they could be interpreted by different applications to be referring to the same entity. This can be done by using the cross references.
Cross references are stored in the form of tables. Table 47-1 shows a cross reference table containing information about customer identifiers in different applications.
The identifier mapping is also required when information about a customer is updated in one application and the changes must be propagated in other applications. You can integrate different identifiers by using a common value integration pattern, which maps to all identifiers in a cross reference table. For example, you can add one more column named Common to the cross reference table shown in Table 47-1. The updated cross reference table would appear, as shown in Table 47-2.
Table 47-2 Cross Reference Table with Common Column
| SAP | EBS | SBL | Common |
|---|---|---|---|
|
SAP_001 |
EBS_1001 |
SBL001 |
CM001 |
|
SAP_002 |
EBS_1002 |
SBL002 |
CM002 |
Figure 47-1 shows how you can use common value integration pattern to map identifiers in different applications.
Figure 47-1 Common Value Integration Pattern Example
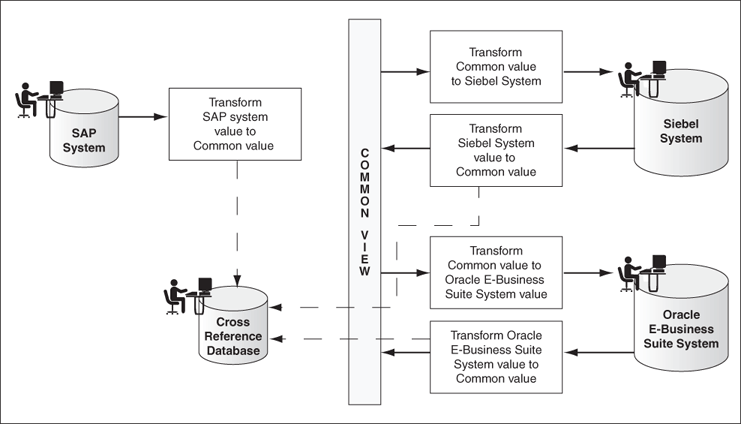
A cross reference table consists of the following two parts: metadata and the actual data. The metadata is the .xref file created in Oracle JDeveloper, and is stored in Metadata Services (MDS) as an XML file. By default, the actual data is stored in the XREF_DATA table of the database in the SOA infrastructure database schema.
You can create a cross reference table in a SOA composite application of Oracle JDeveloper and then use it to look up for column values at runtime. However, before using a cross reference to lookup a particular value, you must populate it at runtime. This can be done by using the cross reference XPath functions. The XPath functions enable you to populate a cross reference, perform lookups, and delete a column value. These XPath functions can be used in the Expression builder dialog to create an expression or in the XSLT Mapper to create transformations.
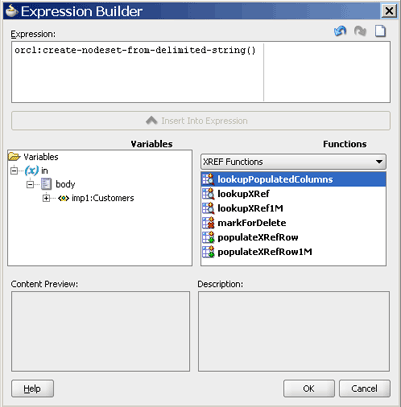
You can access the Expression builder dialog through Assign activity, XSL transformation, or Filter functionality of a BPEL service component or a Mediator service component. Figure 47-2 shows how you can select the cross reference functions in the Expression builder dialog.
Figure 47-2 Expression Builder Dialog with Cross Reference Functions
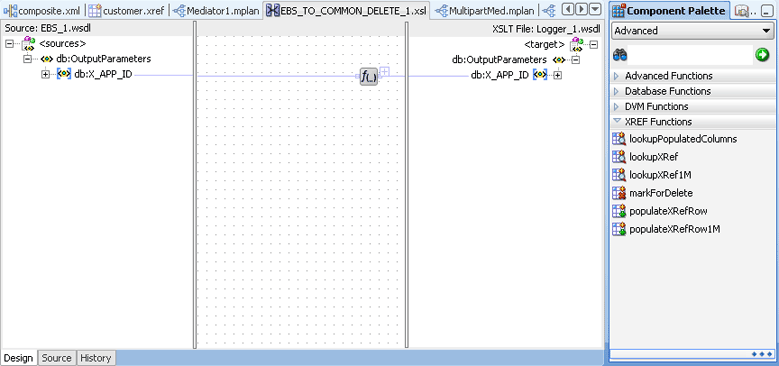
The XSLT Mapper dialog is displayed when you create an XSL file to transform data from one XML schema to another. Figure 47-3 shows how you can select the cross reference functions in the XSLT Mapper dialog.
Figure 47-3 XSLT Mapper Dialog with Cross Reference Functions
You can create cross references tables in a SOA composite application and then use it with a BPEL service component or a Mediator during transformations.
To create a cross reference table:
In Oracle JDeveloper, select the SOA project in which you want to create the cross reference.
Right-click the project and select New.
The New Gallery dialog is displayed.
Select SOA Tier from Categories and then select Transformations.
Select Cross Reference(XREF) from Items.
Click OK.
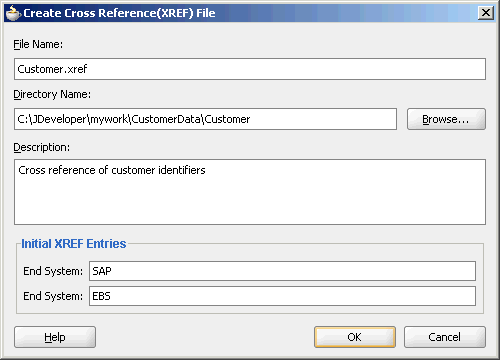
The Create Cross Reference(XREF) File dialog is displayed.
In the File Name field, specify the name of the cross reference file. For example, specify Customer.
A cross reference name is used to identify a cross reference table uniquely. Two cross reference tables cannot have same name in the cross reference repository. The cross reference file name is the name of the cross reference table with an extension of .xref.
In the Description field, enter a description for the cross reference. For example, Cross reference of Customer identifiers.
In the End System fields, enter the end system names.
The end systems map to the cross reference columns in a cross reference table. For example, you can change the first end system name to SAP and second end system name to EBS. Each end system name must be unique within a cross reference.
A sample Create Cross Reference(XREF) File dialog is displayed in Figure 47-4.
Figure 47-4 Create Cross Reference(XREF) File Dialog
Click OK.
The Cross Reference(XREF) editor is displayed, as shown in Figure 47-5. You can use this editor to modify the cross reference.
A file with extension .xref gets created and appears in the Application Navigator. All .xref files are based on the schema definition (XSD) file shown in Example 47-1.
Example 47-1 Cross Reference XSD File
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
targetNamespace="http://xmlns.oracle.com/xref"
xmlns:tns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/xref" elementFormDefault="qualified">
<element name="xref" type="tns:xrefType"/>
<complexType name="xrefType">
<sequence>
<element name="table">
<complexType>
<sequence>
<element name="description" type="string" minOccurs="0"
maxOccurs="1"/>
<element name="columns" type="tns:columnsType" minOccurs="0"
maxOccurs="1"/>
<element name="rows" type="tns:rowsType" maxOccurs="1"
minOccurs="0"/>
</sequence>
<attribute name="name" type="string" use="required"/>
</complexType>
</element>
</sequence>
</complexType>
<complexType name="columnsType">
<sequence>
<element name="column" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<complexType>
<attribute name="name" type="string" use="required"/>
</complexType>
</element>
</sequence>
</complexType>
<complexType name="rowsType">
<sequence>
<element name="row" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<complexType>
<sequence>
<element name="cell" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<complexType>
<attribute name="colName" type="string" use="required"/>
</complexType>
</element>
</sequence>
</complexType>
</element>
</sequence>
</complexType>
</schema>
A cross reference table needs be populated at runtime before using it. By default, the data is stored in the XREF_DATA table under the SOA infrastructure database schema. You can use the xref:populateXRefRow function to populate a cross reference column with a single value and the xref:populateXRefRow1M function to populate a cross reference column with multiple values.
Note:
You can also store the data in a different database schema by configuring a data source in the following way:The JNDI name of the data source should be jdbc/xref.
The ORACLE_HOME/rcu/integration/soainfra/sql/xref/createschema_xref_oracle.sql file should be loaded to create the XREF_DATA table in this data source.
The xref:populateXRefRow function populates a cross reference column with a single value. The xref:populateXRefRow function returns a string value which is the cross reference value being populated. For example, as shown in Table 47-3, the Order table has the following columns: EBS, Common, and SBL with values E100, 100, and SBL_001 respectively.
The syntax of the xref:populateXRefRow function is as follows:
xref:populateXRefRow(xrefLocation as string, xrefReferenceColumnName as string, xrefReferenceValue as string, xrefColumnName as string, xrefValue as string, mode as string) as string
xrefLocation: The cross reference table URI.
xrefReferenceColumnName: The name of the reference column.
xrefReferenceValue: The value corresponding to reference column name.
xrefColumnName: The name of the column to be populated.
xrefValue: The value to be populated in the column.
mode: The mode in which the xref:populateXRefRow function populates the column. You can specify any of the following values: ADD, LINK, or UPDATE. Table 47-4 describes these modes.
Table 47-4 xref:populateXRefRow Function Modes
| Mode | Description | Exception Reasons |
|---|---|---|
|
ADD |
Adds the reference value and the value to be added. For example, |
Exception can occur because of the following reasons:
|
|
LINK |
Adds the cross reference value corresponding to the existing reference value. For example, |
Exception can occur because of the following reasons:
|
|
UPDATE |
Updates the cross reference value corresponding to an existing reference column-value pair. For example, |
Exception can occur because of the following reasons:
|
Note:
Themode parameter values are case-sensitive and should be specified in the upper case only as shown in Table 47-4.Table 47-5 describes the xref:populateXRefRow function modes and exception conditions for these modes.
Table 47-5 xref:populateXRefRow Function Results with Different Modes
| Mode | Reference Value | Value to be Added | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ADD |
Absent Present Present |
Absent Absent Present |
Success Exception Exception |
|
LINK |
Absent Present Present |
Absent Absent Present |
Exception Success Exception |
|
UPDATE |
Absent Present Present |
Absent Absent Present |
Exception Exception Success |
Two values in an end system can correspond to a single value in another system. In such a scenario, you should use the xref:populateXRefRow1M function to populate a cross reference column with a value. For example, as shown in Table 47-6, SAP_001 and SAP_0011 values refer to one value of the EBS and the SBL application. To populate the columns such as SAP column, you can use the xref:populateXRefRow1M function.
Table 47-6 Cross Reference Table with Multiple Column Values
| SAP | EBS | SBL |
|---|---|---|
|
SAP_001 SAP_0011 |
EBS_1001 |
SBL001 |
|
SAP_002 |
EBS_1002 |
SBL002 |
The syntax of the xref:populateXRefRow1M function is as follows:
xref:populateXRefRow1M(xrefLocation as string, xrefReferenceColumnName as string, xrefReferenceValue as string, xrefColumnName as string, xrefValue as string, mode as string) as string
xrefLocation: The cross reference URI.
xrefReferenceColumnName: The name of the reference column.
xrefReferenceValue: The value corresponding to reference column name.
xrefColumnName: The name of the column to be populated.
xrefValue: The value to be populated in the column.
mode: The mode in which the xref:populateXRefRow function populates the column. You can specify either of the following values: ADD or LINK. Table 47-7 describes these modes:
Table 47-7 xref:populateXRefRow1M Function Modes
| Mode | Description | Exception Reasons |
|---|---|---|
|
ADD |
Adds the reference value and the value to be added. For example, |
Exception can occur because of the following reasons:
|
|
LINK |
Adds the cross reference value corresponding to the existing reference value. For example, |
Exception can occur because of the following reasons:
|
Table 47-8 describes the xref:populateXRefRow1M function modes and exception conditions for these modes.
To populate a column of a cross reference table:
In the XSLT Mapper window, expand the trees in the Source and Target panes.
Drag and drop the source element to the target element.
In the Component Palette, select Advanced.
Select XREF Functions.
Drag and drop the populateXRefRow function to the line that connects the source object to the target object.
A populateXRefRow icon appears on the connecting line.
Double-click the populateXRefRow icon.
The Edit Function – populateXRefRow dialog is displayed, as shown in Figure 47-6.
Figure 47-6 Edit Function – populateXRefRow Dialog
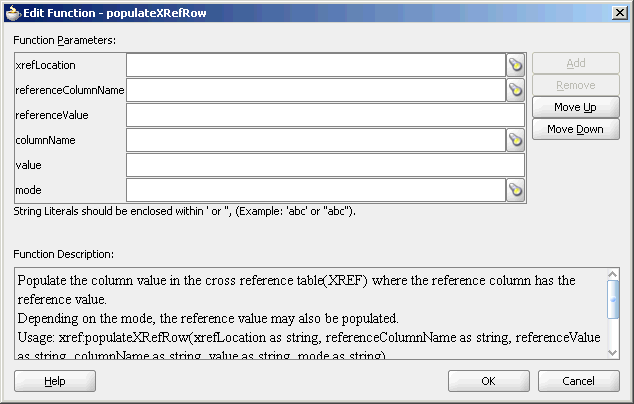
Specify the following values for the fields in the Edit Function – populateXRefRow dialog:
In the xrefLocation field, enter the location URI of the cross reference file.
Click Browse to the right of the xrefLocation field to select the cross reference file. You can select an already deployed cross reference from MDS and also from a shared location in MDS using the Resource Palette.
In the referenceColumnName field, enter the name of the cross reference column.
Click Browse to the right of the referenceColumnName field to select a column name from the columns defined for the cross reference you previously selected.
In the referenceValue field, you can manually enter a value or press Ctrl-Space to launch XPath Building Assistant. Press the up and down keys to locate an object in the list and press enter to select that object.
In the columnName field, enter the name of cross reference column.
Click the Browse icon to the right of the columnName field to select a column name from the columns defined for the cross reference you previously selected.
In the value field, you can manually enter a value or press Ctrl-Space to launch XPath Building Assistant.
In the mode field, enter a mode in which you want to populate the cross reference table column. For example, ADD.
You can also click Browse to select a mode. The Select Populate Mode dialog is displayed from which you can select a mode.
Click OK.
A populated Edit Function – populateXRefRow dialog is shown in Figure 47-7.
Figure 47-7 Populated Edit Function – populateXRefRow Dialog
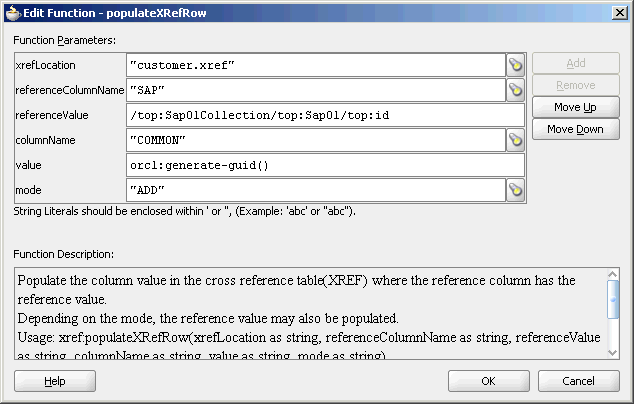
After populating the cross reference table, you can use it to lookup for a value. The xref:lookupXRef and xref:lookupXRef1M functions enable you to look up a cross reference for single and multiple values respectively.
You can use the xref:lookupXRef function to look up a cross reference column for a value that corresponds to a specific value in a reference column. For example, the following function looks up the Common column of the cross reference table, described in Table 47-2, for a value corresponding to SAP_001 value in SAP column.
xref:lookupXRef("customers.xref","SAP","SAP_001","Common",true())
The syntax of the xref:lookupXRef function is as follows:
xref:lookupXRef(xrefLocation as string, xrefReferenceColumnName as string, xrefReferenceValue as string, xrefColumnName as string, needAnException as boolean) as string
xrefLocation: The cross reference URI.
xrefReferenceColumnName: The name of the reference column.
xrefReferenceValue: The value corresponding to reference column name.
xrefColumnName: The name of the column to be looked up for the value.
needAnException: When value is set to true, an exception is thrown if the value is not found, else an empty value is returned.
At runtime, an exception can occur because of the following reasons:
The cross reference table with the given name is not found.
The specified column names are not found.
The specified reference value is empty.
If multiple values are found.
You can use the xref:lookupXRef1M function to look up a cross reference column for multiple values corresponding to a specific value in a reference column. The xref:lookupXRef1M function returns a node-set containing the multiple nodes. Each node in the node-set contains a value.
For example, the following function looks up the SAP column of Table 47-6 for multiple values corresponding to EBS_1001 value in the EBS column:
xref:lookupXRef1M("customers.xref","EBS","EBS_1001","SAP",true())
The syntax of the xref:lookupXRefRow1M function is as follows:
xref:lookupXRef1M(xrefLocation as String, xrefReferenceColumnName as String, xrefReferenceValue as String, xrefColumnName as String, needAnException as boolean) as node-set
xrefLocation: The cross reference URI.
xrefReferenceColumnName: The name of the reference column.
xrefReferenceValue: The value corresponding to reference column name.
xrefColumnName: The name of the column to be looked up for the value.
needAnException: If this value is set to true, then an exception is thrown when the referenced value is not found. Else, an empty node-set is returned.
Example
Consider the Order table with the following three columns: Siebel, Billing1,Billing2
For 1:1 mapping, the xref:lookupPopulatedColumns("Order","Siebel","100","false") method returns
<column name="BILLING1">101</column> <column name="BILLING2">102</column>
In this case, both the columns, Billing1 and Billing2 are populated.
For 1:M mapping, the xref:lookupPopulatedColumns("Order","Siebel","110","false") returns
<column name="BILLING2">111</column> <column name="BILLING2">112</column>
In this case, Billing1 is not populated.
An exception can occur because of the following reasons:
The cross reference table with the given name is not found.
The specified column names are not found.
The specified reference value is empty.
You can use the xref:lookupPopulatedColumns function to look up all the populated columns for a given cross reference table, a cross reference column and a specific values. The xref:lookupPopulatedColumns function returns a nodeset with each node containing a column name and the corresponding value.
The syntax of the xref:LookupPopulatedColumns function is as follows:
xref:LookupPopulatedColumns(xrefTableName as String,xrefColumnName as String,xrefValue as String,needAnException as boolean)as node-set
xrefTableName: The name of the reference table.
xrefColumnName: The name of the reference column.
xrefValue: The value corresponding to reference column name.
needAnException: If this value is set to true, then an exception is thrown when no value is found in the referenced column. Otherwise, an empty node-set is returned.
An exception can occur because of the following reasons:
The cross reference table with the given name is not found.
The specified column names are not found.
The specified reference value is empty.
To look up a cross reference table column:
In the XSLT Mapper dialog, expand the trees in the Source and Target panes.
Drag and drop the source element to the target element.
In the Component Palette, select Advanced.
Select XREF Functions.
Drag and drop the lookupXRef function to the line that connects the source object to the target object.
A lookupXRef icon appears on the connecting line.
Double-click the lookupXRef icon.
The Edit Function – lookupXRef dialog is displayed, as shown in Figure 47-8.
Figure 47-8 Edit Function – lookupXRef Dialog
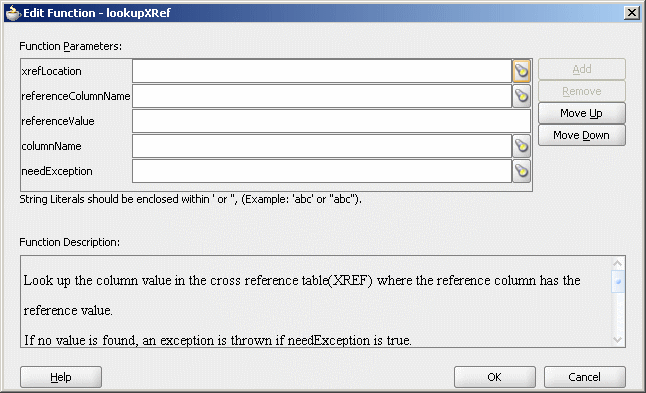
Specify the following values for the fields in the Edit Function – lookupXRef dialog:
In the xrefLocation field, enter the location URI of the cross reference file.
Click Browse to the right of the xrefLocation field to select the cross reference file. You can select an already deployed cross reference from MDS and also from shared location in MDS by using the Resource Palette.
In the referenceColumnName field, enter the name of the cross reference column.
Click Browse to the right of the referenceColumnName field to select a column name from the columns defined for the cross reference you previously selected.
In the referenceValue field, you can manually enter a value or press Ctrl-Space to use the XPath Building Assistant. Press the up and down keys to locate an object in the list and press enter to select that object.
In the columnName field, enter the name of the cross reference column.
Click Browse to the right of the columnName field to select a column name from the columns defined for the cross reference you previously selected.
Click Browse to the right of needException field. The Need Exception dialog is displayed. Select YES to raise an exception if no value is found else select No.
Click OK.
A populated Edit Function – lookupXRef dialog is shown in Figure 47-9.
Figure 47-9 Populated Edit Function – lookupXRef Dialog
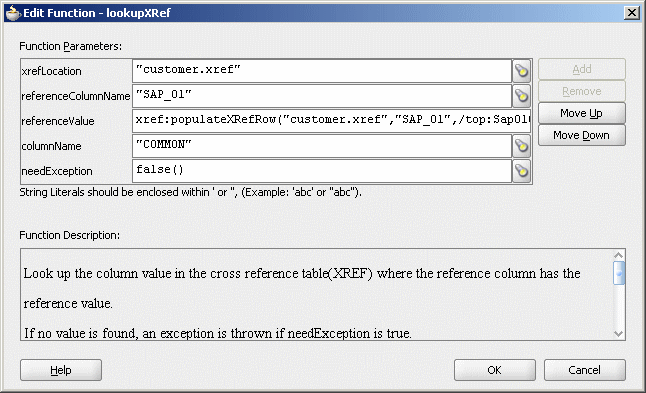
You can use the xref:markForDelete function to delete a value in a cross reference table. The value in the column is marked as deleted. This function returns true if deletion is successful else returns false.
Any column value marked for delete is treated as if the value does not exist. Therefore, you can populate the same column with xref:populateXRefRow function in ADD mode.
Note:
Using a column value marked for delete as a reference value in the LINK mode ofxref:populateXRefRow function, raises an error.A cross reference table row should have at least two mappings. if you have only two mappings in a row and you mark one value for delete, then the value in another column is also deleted.
The syntax for the xref:markForDelete function is as follows:
xref:markForDelete(xrefTableName as string, xrefColumnName as string, xrefValueToDelete as string) return as boolean
xrefTableName: The cross reference table name.
xrefColumnName: The name of the column from which you want to delete a value.
xrefValueToDelete: The value to be deleted.
An exception can occur because of the following reasons:
The cross reference table with the given name is not found.
The specified column name is not found.
The specified value is empty.
The specified value is not found in the column.
Multiple values are found.
To delete a cross reference table value:
In the XSLT Mapper window, expand the trees in the Source and Target panes.
Drag and drop the source element to the target element.
In the Component Palette, select Advanced.
Select XREF Functions.
Drag and drop the markForDelete function to the line that connects the source object to the target object.
A markForDelete icon appears on the connecting line.
Double-click the markForDelete icon.
The Edit Function – markForDelete dialog is displayed, as shown in Figure 47-10.
Figure 47-10 Edit Function – markForDelete Dialog
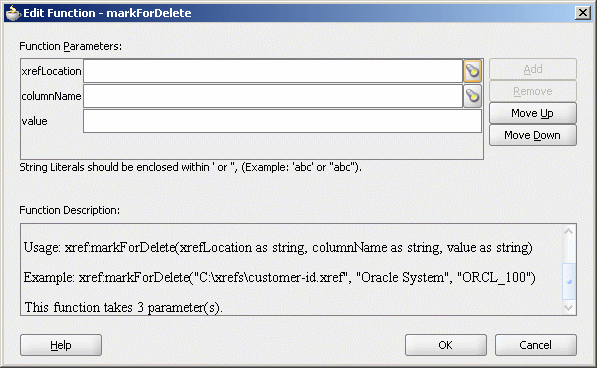
Specify the following values for the fields in the Edit Function – markForDelete dialog:
In the xrefLocation field, enter the location URI of the cross reference file.
Click the flashlight icon to the right of the xrefLocation field to select the cross reference file. You can select an already deployed cross reference from MDS and also from shared location in MDS by using the Resource Palette.
In the columnName field, enter the name of cross reference table column.
Click the flashlight icon to the right of the columnName field to select a column name from the columns defined for the cross reference you previously selected.
In the Value field, you can manually enter a value or press Ctrl-Space to launch XPath Building Assistant. Press the up and down keys to locate an object in the list and press enter to select that object.
A populated Edit Function – markForDelete dialog is shown in Figure 47-11.
Figure 47-11 Populated Edit Function – markForDelete Dialog
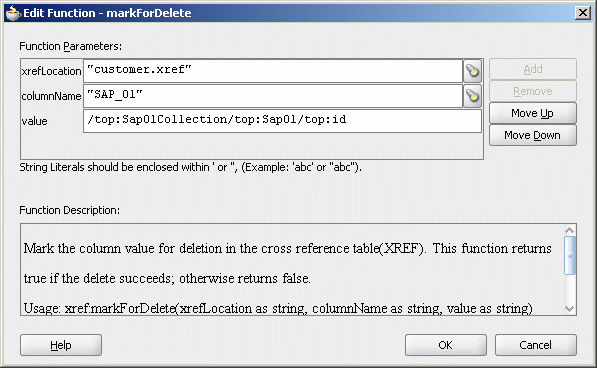
Click OK.
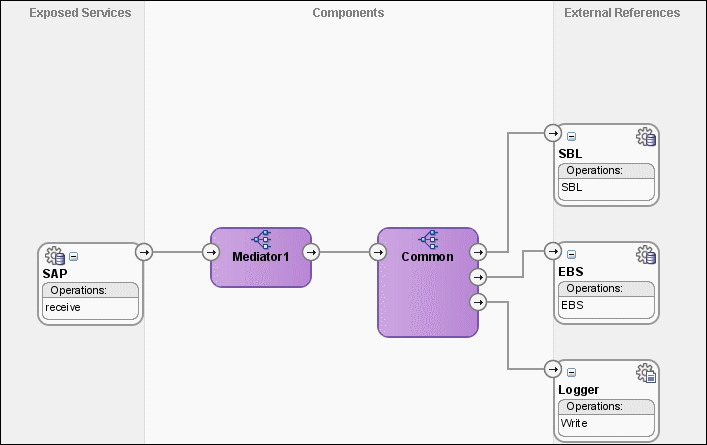
The cross reference use case implements an integration scenario between Oracle EBS, SAP and Siebel instances. In this use case, when an insert, update, or delete operation is performed on the SAP_01 table, the corresponding data is inserted or updated in the EBS and SBL tables. Figure 47-12 provides an overview of this use case.
Figure 47-12 XrefCustApp Use Case in SOA Composite Editor
For downloading the sample files mentioned in this section, visit the following URL:
http://www.oracle.com/technology/sample_code/products/mediator
This section provides the design-time tasks for creating, building, and deploying your SOA Composite application. These tasks should be performed in the order in which they are presented.
Section 47.6.1.1, "Task 1: Configuring Oracle Database and Database Adapter"
Section 47.6.1.2, "Task 2: Creating an Oracle JDeveloper Application and Project"
Section 47.6.1.4, "Task 4: Creating a Database Adapter Service"
Section 47.6.1.5, "Task 5: Creating EBS and SBL External References"
Section 47.6.1.6, "Task 6: Creating Logger External Reference"
Section 47.6.1.8, "Task 8: Specifying Routing Rules for Mediator Component"
Section 47.6.1.9, "Task 9: Specifying Routing Rules for Common Mediator"
Section 47.6.1.10, "Task 10: Configuring Oracle Application Server Connection"
Section 47.6.1.11, "Task 11: Deploying the Composite Application"
To configure Oracle Database and the Database adapter
You need SCOTT database account with password TIGER for this use case. You must ensure that the SCOTT account is unlocked.
You can log in as SYSDBA and then run the setup_user.sql script available in the XrefOrderApp1M/sql folder to unlock the account.
Run the create_schema.sql script available in the XrefOrderApp1M/sql folder to create the tables required for this use case.
Run the create_app_procedure.sql script available in the XrefOrderApp1M/sql folder to create a procedure that simulates the various applications participating in this integration.
Run the createschema_xref_oracle.sql script available in the OH/rcu/integration/soainfra/sql/xref/ folder to create a Cross Reference table to store runtime Cross Reference data.
Copy the ra.xml and weblogic-ra.xml files from $BEAHOME/META-INF to the newly created directory called META-INF on your computer.
Edit the weblogic-ra.xml file, available in the $BEAHOME/META-INF folder as follows:
Modify the property to xADataSourceName as follows:
<property> <name>xADataSourceName</name> <value>jdbc/DBConnection1</value> </property>
Modify the jndi-name as follows:
<jndi-name> eis/DB/DBConnection1</jndi-name>
This sample uses eis/DB/DBConnection1 to poll SAP table for new messages and to connect to the procedure that simulates Oracle EBS and Siebel instances.
Package the ra.xml and weblogic-ra.xml files as a RAR file and deploy the RAR file by using the Weblogic console.
Create a data source using the Weblogic console with the following values:
jndi-name=jdbc/DBConnection1
user=scott
password=tiger
url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@host:port:service
connection-factory factory-class=oracle.jdbc.pool.OracleDataSource
Create a data source using the Weblogic console with the following values:
jndi-name=jdbc/xref
user=scott
password=tiger
url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@host:port:service
connection-factory factory-class=oracle.jdbc.pool.OracleDataSource
To create an application and a project:
In Oracle JDeveloper, click File and select New.
The New Gallery dialog appears.
In the New Gallery, expand the General node, and select the Applications category.
In the Items list, select SOA Application and click OK.
The Create SOA Application wizard appears.
In the Application Name field, enter XrefCustApp, and then click Next.
The Name your SOA project screen appears.
In the Project Name field, enter XrefCustApp and click Next.
The Configure SOA settings for the SOA project screen appears.
In the Composite Template list, select Empty Composite and then click Finish.
The Applications Navigator of Oracle JDeveloper is updated with the new application and project and the Design tab contains, a blank palette.
From the File menu, click Save All.
After creating an application and a project for the use case, you must create a cross reference table.
To create a cross reference table:
In the Application Navigator, right-click the XrefCustApp project and select New.
In the New Gallery dialog, expand the SOA Tier node, and then select the Transformations category.
In the Items list, select Cross Reference(XREF) and click OK.
The Create Cross Reference(XREF) File dialog is displayed.
In the File Name field, enter customer.xref.
In the End System fields, enter SAP_01 and EBS_i76.
Click OK.
The Cross Reference Editor is displayed.
Click Add.
A new row is added.
Enter SBL_78 as the End System name in the newly added row.
Click Add and enter Common as End System name.
The Cross Reference Editor would appear as shown in Figure 47-13.
From the File menu, click Save All and close the Cross Reference Editor.
To create a Database adapter service:
In the Component Palette, select SOA.
Select Database Adapter and drag it to the Exposed Services design area.
The Adapter Configuration wizard Welcome page is displayed.
Click Next.
The Service Name page is displayed.
In the Service Name field, enter SAP.
Click Next.
The Service Connection page is displayed.
In the Application Connection field, select DBConnection1.
In the JNDI Name field, enter eis/DB/DBConnection1.
Click Next.
The Operation Type page is displayed.
Select Poll for New or Changed Records in a Table and click Next.
The Select Table page is displayed.
Click Import Tables.
The Import Tables dialog is displayed.
Select Scott from Schema.
In the Name Filter field, enter %SAP% and click Query.
The Available field is populated with SAP_01 table name.
Double-click SAP_01.
The selected field is populated with SAP_01.
Click OK.
The Select Table page now contains the SAP_01 table.
Select SAP_01 and click Next.
The Define Primary Key page is displayed.
Select ID as primary key and click Next.
The Relationships page is displayed.
Click Next.
The Attribute Filtering page is displayed.
Click Next.
The After Read page is displayed.
Select Update a Field in the [SAP_01] Table (Logical Delete) and click Next.
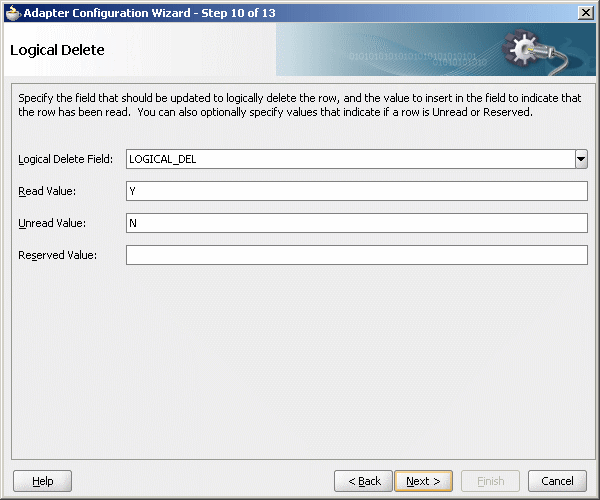
The Logical Delete page is displayed.
In the Logical Delete field, select LOGICAL_DEL.
In the Read Value field, enter Y.
In the Unread Value field, enter N.
Figure 47-14 shows the Logical Delete page of the Adapter Configuration Wizard.
Figure 47-14 Logical Delete Page: Adapter Configuration Wizard
Click Next.
The Polling Options page is displayed.
Click Next.
The Define Selection Criteria page is displayed.
Click Next.
The Finish page is displayed.
Click Finish.
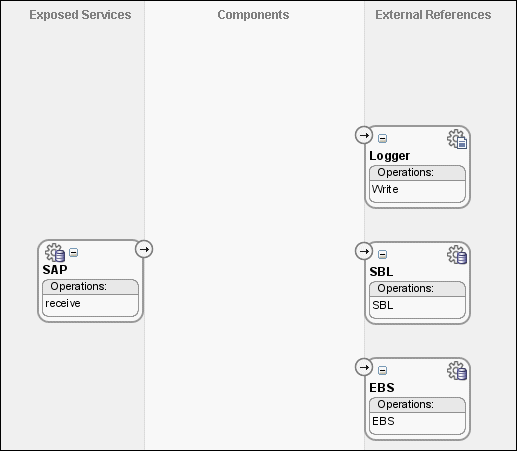
A Database adapter service SAP is created, as shown in Figure 47-15.
Figure 47-15 SAP Database Adapter Service in SOA Composite Editor
From the File menu, click Save All.
To create external references named EBS and SBL:
In the Component Palette, select SOA.
Select Database Adapter and drag it to the External References design area.
The Adapter Configuration wizard Welcome page is displayed.
Click Next.
The Service Name page is displayed.
In the Service Name field, enter EBS.
Click Next.
The Service Connection page is displayed.
In the Application Connection field, select DBConnection1.
In the JNDI Name field, enter eis/DB/DBConnection1.
Click Next.
The Operation Type page is displayed.
Select Call a Stored Procedure or Function and click Next.
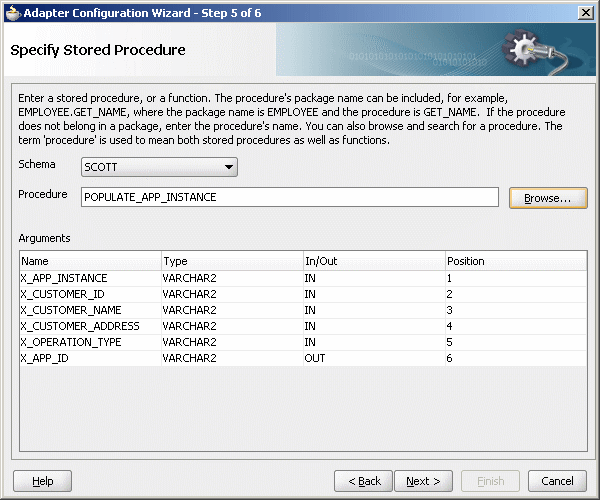
The Specify Stored Procedure page is displayed.
Select Scott from Schema.
Click Browse.
The Stored Procedures dialog is displayed.
Select POPULATE_APP_INSTANCE as shown in Figure 47-16.
Click OK.
The Specify Stored Procedure page appears as shown in Figure 47-17.
Figure 47-17 Specify Stored Procedure Page of Adapter Configuration Wizard
Click Next.
The Finish page is displayed.
Click Finish.
Figure 47-18 shows the EBS reference in SOA Composite Editor.
Figure 47-18 EBS Reference in SOA Composite Editor
From the File menu, click Save All.
Repeat Step 2 through Step 16 to create another external references names SBL.
After completing this task, the SOA Composite Editor would appear as shown in Figure 47-19.
Figure 47-19 SBL Reference in SOA Composite Editor
To create a file adapter reference:
From the Component Palette, select SOA.
Select File Adapter and drag it to the External References design area.
The Adapter Configuration wizard Welcome page is displayed.
Click Next.
The Service Name page is displayed.
In the Service Name field, enter Logger.
Click Next.
The Operation page is displayed.
In the Operation Type field, select Write File.
Click Next.
The File Configuration page is displayed.
In the Directory for Outgoing Files (physical path) field, enter the name of the directory where you want to write the files.
In the File Naming Convention field, enter output.xml and click Next.
The Messages page is displayed.
Click Search.
The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
Navigate to Type Explorer, Project Schema Files, SCOTT_POPULATE_APP_INSTANCE.xsd and then select OutputParameters.
Click OK.
Click Next.
The Finish page is displayed.
Click Finish.
Figure 47-20 shows the Logger reference in the SOA Composite Editor.
Figure 47-20 Logger Reference in SOA Composite Editor
From the File menu. click Save All.
To create a Mediator:
Drag and drop a Mediator from Components Palette to the Components design area.
The Create Mediator dialog is displayed.
Select Define Interface Later from Template.
Click OK.
A Mediator with name Mediator1 is created.
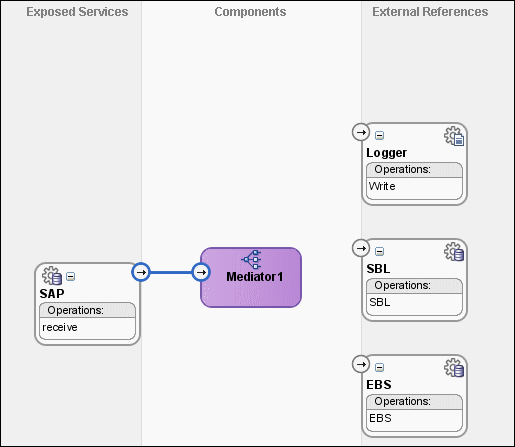
Connect the SAP service to the Mediator1 as shown in Figure 47-21.
Figure 47-21 SAP Service Connected to Mediator1
Click Save All.
Drag and drop another Mediator from Components Palette to the Components design area.
The Create Mediator dialog is displayed.
Select Interface Definition From WSDL from Template.
Deselect Create Composite Service with SOAP Bindings.
Click Find Existing WSDLs to the right of the WSDL File field.
Navigate to and then select the Common.wsdl file. The Common.wsdl file is available in the Samples folder.
Click OK.
Click OK.
A Mediator with name Common is created.
You must specify routing rules for following operations:
Insert
Update
UpdateID
Delete
To create routing rules for insert operation:
Double-click Mediator1 Mediator.
The Mediator Editor is displayed.
In Routing Rules panel, click the Create a new Routing Rule icon.
The Target Type dialog is displayed.
Select Service.
The Target Services dialog is displayed.
Navigate to XrefCustApp, Mediators, Common, Services, Common.
Select Insert and click OK.
Click the Filter icon.
The Expression Builder dialog is displayed.
Enter the following expression in the Expression field:
$in.Sap01Collection/top:Sap01Collection/top:Sap01/top:operation='INSERT'
Click OK.
Click the Transformation icon next to the Transform Using field.
The Request Transformation map dialog is displayed.
Select Create New Mapper File and enter SAP_TO_COMMON_INSERT.xsl.
Click OK.
A SAP_TO_COMMON_INSERT.xsl tab is displayed.
Drag and drop the top:SAP01 source element to the inp1:Customer target element.
The Auto Map Preferences dialog is displayed.
From the During Auto Map options, deselect Match Elements Considering their Ancestor Names.
Click OK.
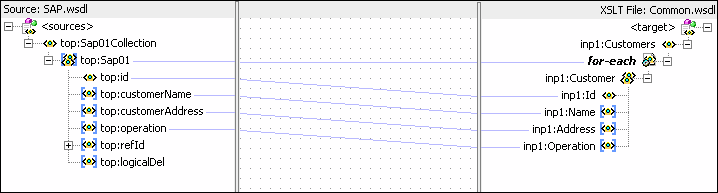
The transformation is created as shown in Figure 47-22.
Figure 47-22 SAP_TO_COMMON_INSERT.xsl Transformation
From the Components Palette, select Advanced.
Select XREF Functions.
Drag and drop the populateXRefRow function from Components Palette to the line connecting top:id and inp1:id elements.
Double-click the populateXRefRow icon.
The Edit Function-populateXRefRow dialog is displayed.
Click Search to the right of xrefLocation field.
The SCA Resource Lookup dialog is displayed.
Select customer.xref and click OK.
In the referenceColumnName field, enter "SAP_01" or click Search to select the column name.
In the referenceValue column, enter /top:Sap01Collection/top:Sap01/top:id.
In the columnName field, enter "Common" or click Search to select the column name.
In the value field, enter oraext:generate-guid().
In the mode field, enter "Add" or click Search to select this mode.
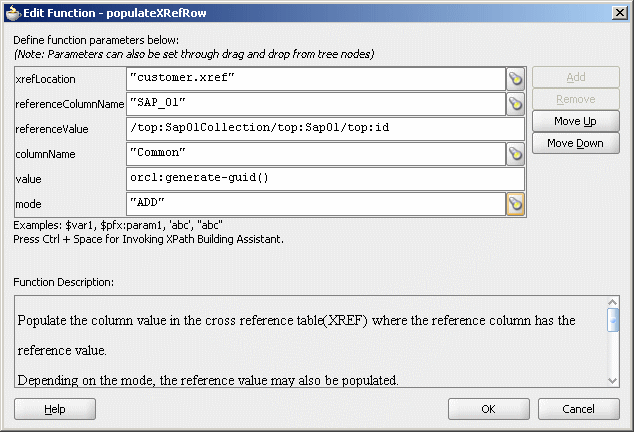
Figure 47-23 shows populated Edit Function – populateXRefRow dialog.
Figure 47-23 Edit Function – populateXRefRow Dialog: XrefCustApp Use Case
Click OK.
From the File menu, click Save All and close the SAP_TO_COMMON_INSERT.xsl tab.
The Routing Rules panel would appear as shown in Figure 47-24.
Figure 47-24 Routing Rules Panel with Insert Operation
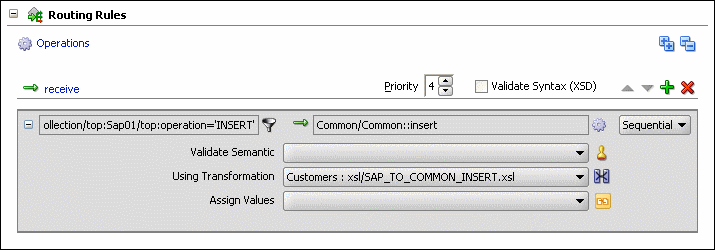
To create routing rules for update operation:
Perform the following tasks to create routing rules for Update operation:
In Routing Rules panel, click the Create a new Routing Rule icon.
The Target Type dialog is displayed.
Select Service.
The Target Services dialog is displayed.
Navigate to XrefCustApp, Mediators, Common, Services, Common.
Select Update and click OK.
Click the Filter icon.
The Expression Builder dialog is displayed.
Enter the following expression in the Expression field:
$in.Sap01Collection/top:Sap01Collection/top:Sap01/top:operation='UPDATE'
Click OK.
Click the Transformation icon next to the Transform Using field.
The Request Transformation map dialog is displayed.
Select Create New Mapper File and enter SAP_TO_COMMON_UPDATE.xsl.
Click OK.
A SAP_TO_COMMON_UPDATE.xsl tab is displayed.
Drag and drop the top:Sap01 source element to the inp1:Customer target element.
The Auto Map Preferences dialog is displayed.
Click OK.
From the Components Palette, select Advanced.
Select XREF Functions.
Drag and drop the lookupXRef function from Components Palette to the line connecting top:id and inp1:id elements.
Double-click the lookupXRef icon.
The Edit Function-lookupXRef dialog is displayed.
Click Search to the right of xrefLocation field.
The SCA Resource Lookup dialog is displayed.
Select customer.xref and click OK.
In the referenceColumnName field, enter "SAP_01" or click Search to select the column name.
In the referenceValue column, enter /top:Sap01Collection/top:Sap01/top:id.
In the columnName field, enter "COMMON" or click Search to select the column name.
In the needException field, enter true() or click Search to select this mode.
Figure 47-25 shows populated Edit Function – looupXRef dialog.
Figure 47-25 Edit Function – lookupXRef Dialog: XrefCustApp Use Case
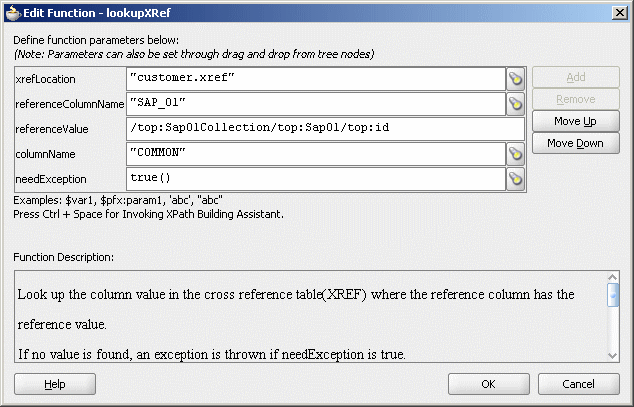
Click OK.
From the File menu, click Save All and close the SAP_TO_COMMON_UPDATE.xsl tab.
The Routing Rules panel would appear as shown in Figure 47-26.
Figure 47-26 Insert Operation and Update Operation
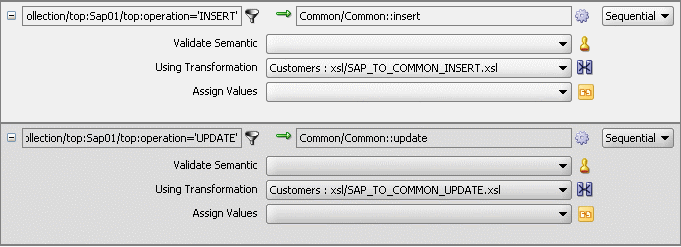
To create routing rules for updateID operation:
Perform the following tasks to create routing rules for UpdateID operation:
In Routing Rules panel, click the Create a new Routing Rule icon.
The Target Type dialog is displayed.
Select Service.
The Target Services dialog is displayed.
Navigate to XrefCustApp, Mediators, Common, Services, Common.
Select updateid and click OK.
Click the Filter icon.
The Expression Builder dialog is displayed.
Enter the following expression in the Expression field:
$in.Sap01Collection/top:Sap01Collection/top:Sap01/top:operation = 'UPDATEID'
Click OK.
Click the Transformation icon next to the Transform Using field.
The Request Transformation map dialog is displayed.
Select Create New Mapper File and enter SAP_TO_COMMON_UPDATEID.xsl.
Click OK.
A SAP_TO_COMMON_UPDATEID.xsl tab is displayed.
Drag and drop the top:Sap01 source element to the inp1:Customer target element.
The Auto Map Preferences dialog is displayed.
Click OK.
From the Components Palette, select Advanced.
Select XREF Functions.
Drag and drop the populateXRefRow function from Components Palette to the line connecting top:id and inp1:id elements.
Double-click the populateXRefRow icon.
The Edit Function-populateXRefRow dialog is displayed.
Click Search to the right of xrefLocation field.
The SCA Resource Lookup dialog is displayed.
Select customer.xref and click OK.
In the referenceColumnName field, enter "SAP_01" or click Search to select the column name.
In the referenceValue column, enter /top:Sap01Collection/top:Sap01/top:refId.
In the columnName field, enter "SAP_01" or click Search to select the column name.
In the value field, enter /top:Sap01Collection/top:Sap01/top:Id.
In the mode field, enter "UPDATE" or click Search to select this mode.
Figure 47-27 shows a populated Edit Function – populateXRefRow dialog.
Figure 47-27 Edit Function – populateXRefRow Dialog: XrefCustApp Use Case
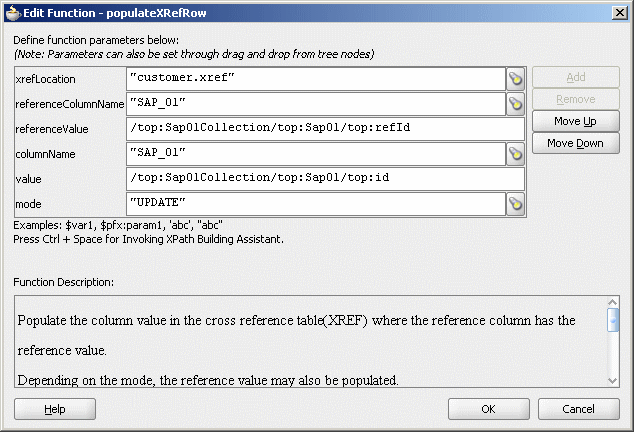
Drag and drop the lookupXRef function from Components Palette to the line connecting top:id and inp1:id elements.
Double-click the lookupXRef icon.
The Edit Function-lookupXRef dialog is displayed.
Click Search to the right of xrefLocation field.
The SCA Resource Lookup dialog is displayed.
Select customer.xref and click OK.
In the referenceColumnName field, enter "SAP_01" or click Search to select the column name.
In the referenceValue column, enter the following:
xref:populateXRefRow("customer.xref","SAP_
01",/top:Sap01Collection/top:Sap01/top:refId,"SAP_
01",/top:Sap01Collection/top:Sap01/top:id,"UPDATE").
In the columnName field, enter "COMMON" or click Search to select the column name.
In the needException field, enter false() or click Search to select this mode.
Figure 47-28 shows a populated Edit Function – lookupXRef dialog.
Figure 47-28 Edit Function – lookupXRef Dialog: XrefCustApp Use Case
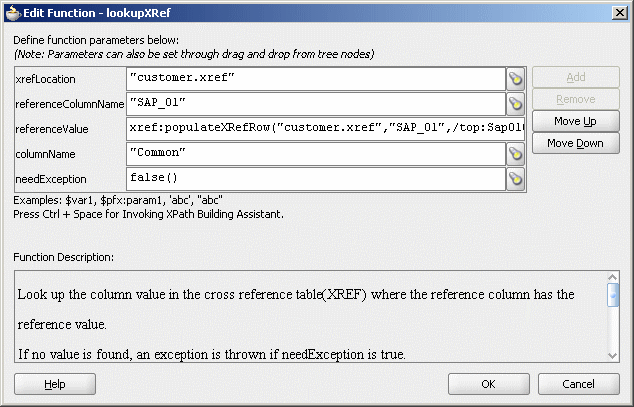
Click OK.
Click Save All and close the SAP_TO_COMMON_UPDATEID.xsl window.
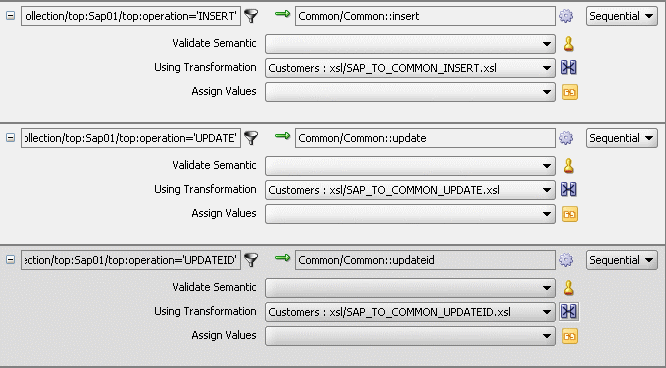
The Routing Rules panel would appear as shown in Figure 47-29.
Figure 47-29 Insert, Update, and UpdateID Operations
To create routing rules for delete operation:
In Routing Rules panel, click the Create a new Routing Rule icon.
The Target Type dialog is displayed.
Select Service.
The Target Services dialog is displayed.
Navigate to XrefCustApp, Mediators, Common, Services, Common.
Select delete and click OK.
Click the Filter icon.
The Expression Builder dialog is displayed.
Enter the following expression in the Expression field:
$in.Sap01Collection/top:Sap01Collection/top:Sap01/top:operation = 'DELETE'
Click OK.
Click the Transformation icon next to the Transform Using field.
The Request Transformation map dialog is displayed.
Select Create New Mapper File and enter SAP_TO_COMMON_DELETE.xsl.
Click OK.
A SAP_TO_COMMON_DELETE.xsl tab is displayed.
Right-click <sources> and select Add Parameter.
The Add Parameter dialog is displayed.
In the Local Name field, enter COMMONID.
Select Set Default Value.
Select Expression.
In the XPath Expression field, enter xref:lookupXRef("customer.xref","SAP_01",/top:Sap01Collection/top:Sap01/top:id,"COMMON",false()).
Click OK.
Drag and drop the top:Sap01 source element to the inp1:Customer target element.
The Auto Map Preferences dialog is displayed.
Click OK.
Delete the line connecting top:id and inp1:id.
Connect the COMMONID to inp1:id.
Right-click inp1:id and select Add XSL node and then if.
A new node if is inserted between inp1:customer and inp1:id.
Connect top:id to the if node.
From the Components Palette, select Advanced.
Select XREF Functions.
Drag and drop the markForDelete function from Component Palette to the line connecting top:id and if node.
Double-click the markForDelete icon.
The Edit Function-markForDelete dialog is displayed.
Click Search to the right of xrefLocation field.
The SCA Resource Lookup dialog is displayed.
Select customer.xref and click OK.
In the columnName field, enter "SAP_01" or click Search to select the column name.
In the value field, enter /top:Sap01Collection/top:Sap01/top:Id.
Figure 47-30 shows a populated Edit Function – markForDelete dialog.
Figure 47-30 Edit Function – markForDelete Dialog: XrefCustApp Use Case
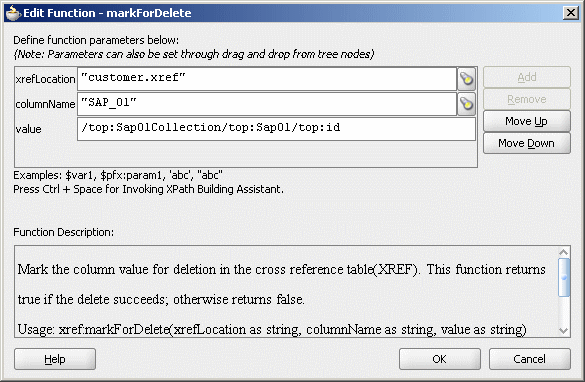
Click OK.
The SAP_TO_COMMON_DELETE.xsl would appear as shown in Figure 47-31.
Click Save All and close the SAP_TO_COMMON_DELETE.xsl tab.
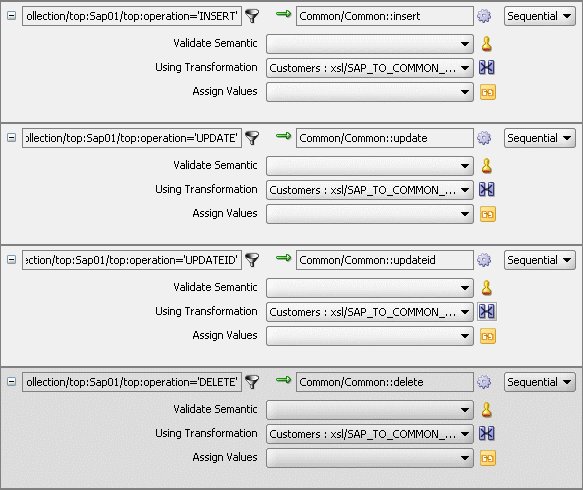
The Routing Rules panel would appear as shown in Figure 47-32.
Figure 47-32 Insert, Update, UpdateID, and Delete Operations
You must specify routing rules for following operations of Common Mediator:
Insert
Delete
Update
UpdateID
To create routing rules for insert operation:
Double-click Common Mediator.
The Mediator Editor is displayed.
In Routing Rules panel, click the Create a new Routing Rule icon.
The Target Type dialog is displayed.
Select Service.
The Target Services dialog is displayed.
Navigate to XrefCustApp, References, SBL.
Select SBL and click OK.
Click the Transformation icon next to the Transform Using field.
The Request Transformation map dialog is displayed.
Select Create New Mapper File and enter COMMON_TO_SBL_INSERT.xsl.
Click OK.
A COMMON_TO_SBL_INSERT.xsl tab is displayed.
Drag and drop the inp1:Customers source element to the db:InputParameters target element.
The Auto Map Preferences dialog is displayed.
Click OK.
The transformation is created as shown in Figure 47-33.
Figure 47-33 COMMON_TO_SBL_INSERT.xsl Transformation

From the File menu, click Save All and close the COMMON_TO_SBL_INSERT.xsl window.
In the Synchronous Reply panel, click Browse for target service operations.
The Target Type dialog is displayed.
Select Service.
The Target Services dialog is displayed.
Navigate to XrefCustApp, References, Logger.
Select Write and click OK.
Click the Transformation icon next to the Transform Using field.
The Reply Transformation map dialog is displayed.
Select Create New Mapper File and enter SBL_TO_COMMON_INSERT.xsl.
Select Include Request in the Reply Payload.
Click OK.
A SBL_TO_COMMON_INSERT.xsl window is displayed.
Connect inp1:Customers source element to the db:X:APP_ID.
Drag and drop the populateXRefRow function from Components Palette to the connecting line.
Double-click the populateXRefRow icon.
The Edit Function-populateXRefRow dialog is displayed.
Enter the information in the following fields:
xrefLocation: "customer.xref"
referenceColumnName: "Common"
referenceValue: $initial.Customers/inp1:Customers/inp1:Customer/inp1:Id
columnName:"SBL_78"
value:/db:OutputParameters/db:X_APP_ID
mode:"LINK"
Click OK.
The SBL_TO_COMMON_INSERT.xsl would appear as shown in Figure 47-34.
Figure 47-34 SBL_TO_COMMON_INSERT.xsl Transformation
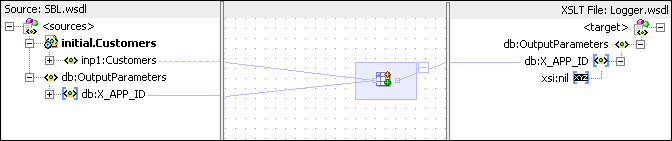
From the File menu, click Save All and close the SBL_TO_COMMON_INSERT.xsl tab.
In the Synchronous Reply panel, click the Assign Values icon.
The Assign Values dialog is displayed.
Click Add.
The Assign Value dialog is displayed.
In the From section, select Expression.
Click the Invoke Expression Builder icon.
The Expression Builder dialog is displayed.
Enter the following expression in the Expression field and click OK.
concat('INSERT-',$in.OutputParameters/db:OutputParameters/db:X_APP_ID,'.xml')
In the To section, select Property.
Select jca.file.FileName property and click OK.
Click OK.
The insert operation panel would appear as shown in Figure 47-35.
Figure 47-35 Insert Operation with SBL Target Service
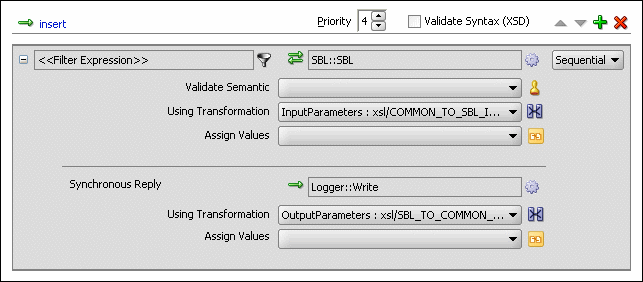
From the File menu, click Save All.
Repeat the Step 2 through Step 34 to specify another target service EBS and its routing rules.
Figure 47-36 shows the insert operation panel with SBL and EBS target service.
Figure 47-36 Insert Operation with SBL and EBS Target Service
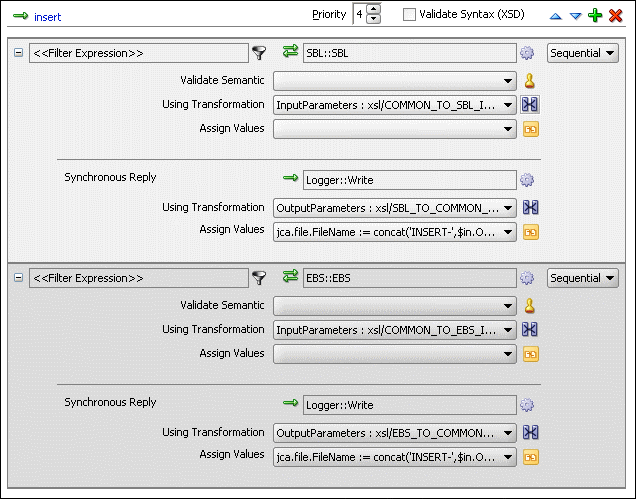
To create routing rules for delete operation:
Perform the following tasks to create the routing rules for delete operation:
In Routing Rules panel, click the Create a new Routing Rule icon.
The Target Type dialog is displayed.
Select Service.
The Target Services dialog is displayed.
Navigate to XrefCustApp, References, SBL.
Select SBL and click OK.
Click the Transformation icon next to the Transform Using field.
The Request Transformation map dialog is displayed.
Select Create New Mapper File and enter COMMON_TO_SBL_DELETE.xsl.
Click OK.
A COMMON_TO_SBL_DELETE.xsl tab is displayed.
Drag and drop the inp1:Customers source element to the db:InputParameters target element.
The Auto Map Preferences dialog is displayed.
Click OK.
The transformation is created as shown in Figure 47-37.
Figure 47-37 COMMON_TO_SBL_DELETE.xsl Transformation
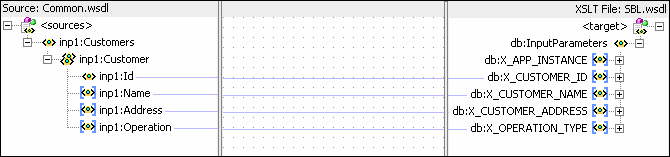
Drag and drop the lookupXRef function from Components Palette to the line connecting inp1:id and db:XCUSTOMER_ID.
Double-click the lookupXRef icon.
The Edit Function: lookupXRef dialog is displayed.
Enter the information in the following fields:
xrefLocation: "customer.xref"
referenceColumnName: "Common"
referenceValue: /inp1:Customers/inp1:Customer/inp1:Id
columnName:"SBL_78"
needException:false()
Click OK.
From the File menu, click Save All and close the COMMON_TO_SBL_DELETE.xsl window.
In the Synchronous Reply panel, click Browse for target service operations.
The Target Type dialog is displayed.
Select Service.
The Target Services dialog is displayed.
Navigate to XrefCustApp, References, Logger.
Select Write and click OK.
Click the Transformation icon next to the Transform Using field.
The Reply Transformation map dialog is displayed.
Select Create New Mapper File and enter SBL_TO_COMMON_DELETE.xsl.
Click OK.
A SBL_TO_COMMON_DELETE.xsl window is displayed.
Connect db:X_APP_ID source element to the db:X:APP_ID target.
Drag and drop the markForDelete function from Components Palette to the connecting line.
Double-click the markForDelete icon.
The Edit Function-markForDelete dialog is displayed.
Enter the information in the following fields:
xrefLocation: "customer.xref"
columnName:"SBL_78"
value:/db:OutputParameters/db:X_APP_ID
Click OK.
From the File menu, click Save All and close the SBL_TO_COMMON_DELETE.xsl tab.
In the Synchronous Reply panel, click the Assign Values icon.
The Assign Values dialog is displayed.
Click Add.
The Assign Value dialog is displayed.
In the From section, select Expression.
Click the Invoke Expression Builder icon.
The Expression Builder dialog is displayed.
Enter following expression in the Expression field and click OK.
concat('DELETE-',$in.OutputParameters/db:OutputParameters/db:X_APP_ID,'.xml')
In the To section, select Property.
Select jca.file.FileName property and click OK.
Click OK.
The delete operation panel would appear as shown in Figure 47-38.
Figure 47-38 Delete Operation with SBL Target Service
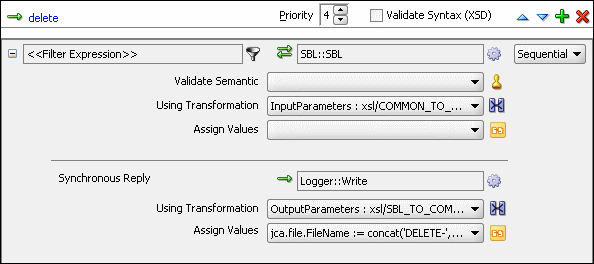
From the File menu, click Save All.
Repeat the Step 1 through Step 36 to specify another target service EBS and specify the routing rules.
Figure 47-39 shows the delete operation panel with SBL and EBS target service.
Figure 47-39 Delete Operation with SBL and EBS Target Service
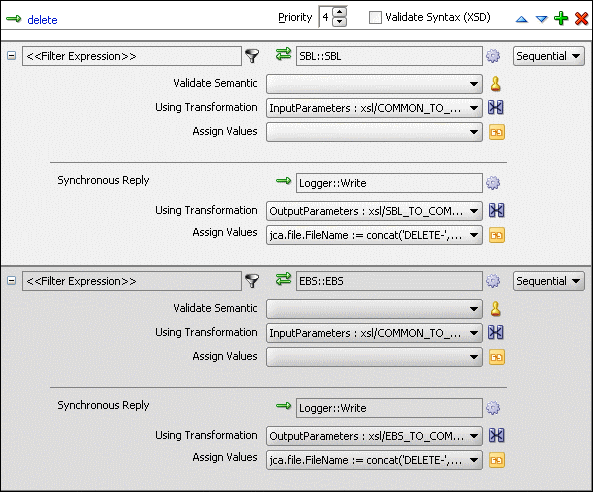
To create routing rules for update operation:
Perform the following tasks to create routing rules for Update operation:
In Routing Rules panel, click the Create a new Routing Rule icon.
The Target Type dialog is displayed.
Select Service.
The Target Services dialog is displayed.
Navigate to XrefCustApp, References, SBL.
Select SBL and click OK.
Click the Transformation icon next to the Transform Using field.
The Request Transformation map dialog is displayed.
Select Create New Mapper File and enter COMMON_TO_SBL_UPDATE.xsl.
Click OK.
A COMMON_TO_SBL_UPDATE.xsl tab is displayed.
Drag and drop the inp1:Customers source element to the db:InputParameters target element.
The Auto Map Preferences dialog is displayed.
Click OK.
The transformation is created as shown in Figure 47-37.
Drag and drop the lookupXRef function from Components Palette to the line connecting inp1:id and db:XCUSTOMER_ID.
Double-click the lookupXRef icon.
The Edit Function: lookupXRef dialog is displayed.
Enter the information in the following fields:
xrefLocation: "customer.xref"
referenceColumnName: "Common"
referenceValue: /inp1:Customers/inp1:Customer/inp1:Id
columnName:"SBL_78"
needException:true()
Click OK.
From the File menu, click Save All and close the COMMON_TO_SBL_UPDATE.xsl window.
In the Synchronous Reply panel, click Browse for target service operations.
The Target Type dialog is displayed.
Select Service.
The Target Services dialog is displayed.
Navigate to XrefCustApp, References, Logger.
Select Write and click OK.
Click the Transformation icon next to the Transform Using field.
The Reply Transformation map dialog is displayed.
Select Create New Mapper File and enter SBL_TO_COMMON_UPDATE.xsl.
Click OK.
A SBL_TO_COMMON_UPDATE.xsl window is displayed.
Connect db:X:APP_ID source element to the db:X:APP_ID.
From the File menu, click Save All and close the SBL_TO_COMMON_UPDATE.xsl tab.
In the Synchronous Reply panel, click the Assign Values icon.
The Assign Values dialog is displayed.
Click Add.
The Assign Value dialog is displayed.
In the From section, select Expression.
Click the Invoke Expression Builder icon.
The Expression Builder dialog is displayed.
Enter following expression in the Expression field and click OK.
concat('UPDATE-',$in.OutputParameters/db:OutputParameters/db:X_APP_ID,'.xml')
In the To section, select Property.
Select jca.file.FileName property and click OK.
Click OK.
The update operation panel would appear as shown in Figure 47-40.
Figure 47-40 Update Operation with SBL Target Service
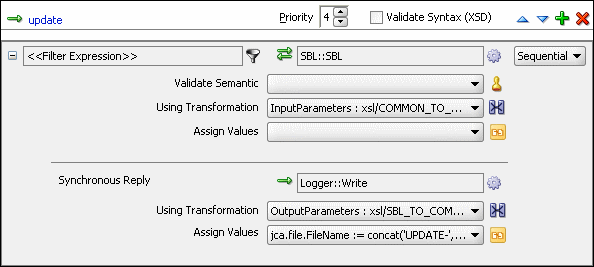
From the File menu, click Save All.
Repeat the Step 1 through Step 32 to specify another target service EBS and its routing rules.
Figure 47-41 shows the update operation panel with SBL and EBS target service.
Figure 47-41 Update Operation with SBL and EBS Target Service
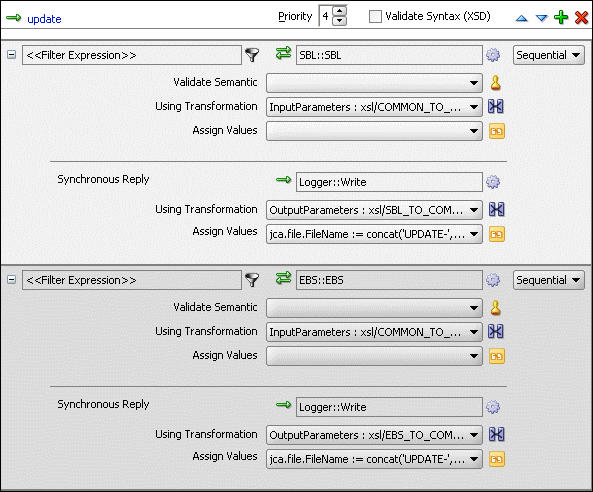
To create routing rules for updateID operation:
Perform the following tasks to create routing rules for UpdateID operation:
In Routing Rules panel, click the Create a new Routing Rule icon.
The Target Type dialog is displayed.
Select Service.
The Target Services dialog is displayed.
Navigate to XrefCustApp, References, SBL.
Select SBL and click OK.
Click the Transformation icon next to the Transform Using field.
The Request Transformation map dialog is displayed.
Select Create New Mapper File and enter COMMON_TO_SBL_UPDATEID.xsl.
Click OK.
A COMMON_TO_SBL_UPDATEID.xsl tab is displayed.
Drag and drop inp1:Customers source element to the db:InputParameters target element.
The Auto Map Preferences dialog is displayed.
Click OK.
The transformation is created as shown in Figure 47-37.
Drag and drop the lookupXRef function from Components Palette to the line connecting inp1:id and db:X_CUSTOMER_ID.
Double-click the lookupXRef icon.
The Edit Function: lookupXRef dialog is displayed.
Enter the information in the following fields:
xrefLocation: "customer.xref"
referenceColumnName: "Common"
referenceValue: /inp1:Customers/inp1:Customer/inp1:Id
columnName:"SBL_78"
needException:false()
Click OK.
From the File menu, click Save All and close the COMMON_TO_SBL_UPDATEID.xsl window.
In the Synchronous Reply panel, click Browse for target service operations.
The Target Type dialog is displayed.
Select Service.
The Target Services dialog is displayed.
Navigate to XrefCustApp, References, Logger.
Select Write and click OK.
Click the Transformation icon next to the Transform Using field.
The Reply Transformation map dialog is displayed.
Select Include Request in the Reply Payload.
Click OK.
A SBL_TO_COMMON_UPDATEID.xsl window is displayed.
Connect inp1:Customers source element to the db:X:APP_ID.
Drag and drop the populateXRefRow function from Component Palette to the connecting line.
Double-click the populateXRefRow icon.
The Edit Function-populateXRefRow dialog is displayed.
Enter the information in the following fields:
xrefLocation: "customer.xref"
referenceColumnName: "Common"
referenceValue: $initial.Customers/inp1:Customers/inp1:Customer/inp1:Id
columnName:"SBL_78"
value:/db:OutputParameters/db:X_APP_ID
mode:"UPDATE"
Click OK.
From the File menu, click Save All and close the SBL_TO_COMMON_UPDATEID.xsl tab.
In the Synchronous Reply panel, click the Assign Values icon.
The Assign Values dialog is displayed.
Click Add.
The Assign Value dialog is displayed.
In the From section, select Expression.
Click the Invoke Expression Builder icon.
The Expression Builder dialog is displayed.
Enter following expression in the Expression field and click OK.
concat('UPDATEID-',$in.OutputParameters/db:OutputParameters/db:X_APP_ID,'.xml')
In the To section, select Property.
Select jca.file.FileName property and click OK.
Click OK.
The updateid operation panel would appear as shown in Figure 47-42.
Figure 47-42 Updateid Operation with SBL Target Service
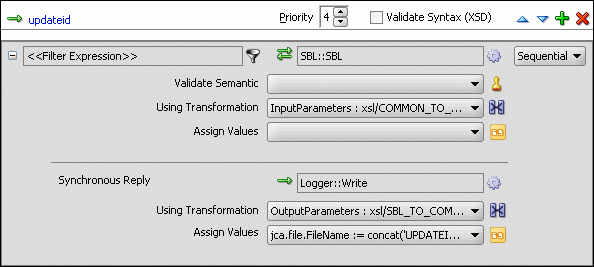
From the File menu, click Save All.
Repeat the Step 1 through Step 36 to specify another target service EBS and specify the routing rules.
Figure 47-43 shows the updateid operation panel with SBL and EBS target service.
Figure 47-43 Updateid Operation with SBL and EBS Target Service
An Oracle Application Server connection is required for deploying your SOA composite application. For information on creating Oracle Application Server connection, refer to Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Technology Adapters.
Deploying the XrefCustApp composite application to Oracle Application Server consists of following steps:
Creating an Application Deployment Profile
Deploying the Application to Oracle Application Server
For detailed information about these steps, see Section 43.2, "Deploying a Single SOA Composite in Oracle JDeveloper".
After deploying the XrefCustApp application, you can run it by using any command from the insert_sap_record.sql file present in the XrefCustApp/sql folder. On successful completion, the records are inserted or updated in EBS and SBL tables and the Logger reference writes the output to the output.xml file.
For monitoring the running instance, you can use the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console at the following URL:
http://hostname:portnumber/em
where hostname is the host on which you installed the Oracle SOA Suite infrastructure and portnumber is the port running the service.
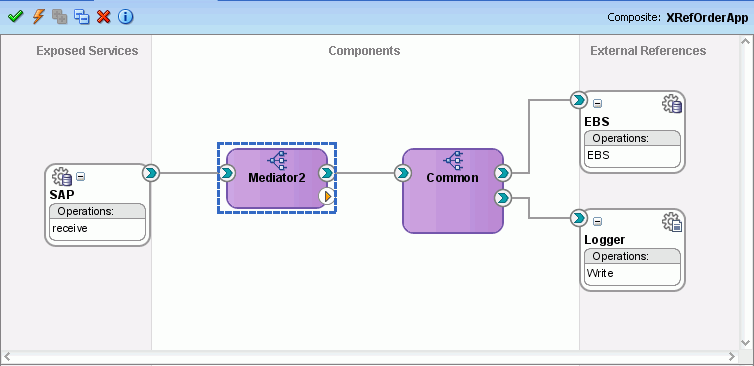
The cross reference use case implements an integration scenario between two end-systems Oracle EBS and SAP instances. In this use case, the order passes from SAP to EBS. SAP represents the orders with a unique ID, whereas EBS splits the order into two order ID1 and ID2. This scenario is created using Database Adapters. When you poll the SAP table for updated or created records, a SAP instance is created. In EBS, the instance is simulated by a procedure and the table is populated. Figure 47-44 provides an overview of this use case.
Figure 47-44 XrefOrderApp Use Case in SOA Composite Editor
For downloading the sample files mentioned in this section, visit the following URL:
http://www.oracle.com/technology/sample_code/products/mediator
This section provides the design-time tasks for creating, building, and deploying your SOA Composite application. These tasks should be performed in the order in which they are presented.
Section 47.7.1.1, "Task 1: Configuring Oracle Database and Database Adapter"
Section 47.7.1.2, "Task 2: Creating an Oracle JDeveloper Application and Project"
Section 47.7.1.4, "Task 4: Creating a Database Adapter Service"
Section 47.7.1.6, "Task 6: Creating Logger External Reference"
Section 47.7.1.8, "Task 8: Specifying Routing Rules for Mediator Component"
Section 47.7.1.9, "Task 9: Specifying Routing Rules for Common Mediator"
Section 47.7.1.10, "Task 10: Configuring Oracle Application Server Connection"
Section 47.7.1.11, "Task 11: Deploying the Composite Application"
To configure Oracle Database and the Database adapter
You need SCOTT database account with password TIGER for this use case. You must ensure that the SCOTT account is unlocked.
You can log in as SYSDBA and then run the setup_user.sql script available in the XrefOrderApp1M/sql folder to unlock the account.
Run the create_schema.sql script available in the XrefOrderApp1M/sql folder to create the tables required for this use case.
Run the create_app_procedure.sql script available in the XrefOrderApp1M/sql folder to create a procedure that simulates the various applications participating in this integration.
Run the createschema_xref_oracle.sql script available in the OH/rcu/integration/soainfra/sql/xref/ folder to create a Cross Reference table to store runtime Cross Reference data.
Copy the ra.xml and weblogic-ra.xml files from $BEAHOME/META-INF to the newly created directory called META-INF on your computer.
Edit the weblogic-ra.xml file, available in the $BEAHOME/src/oracle/tip/adapter/db/test/deploy/weblogic/META-INF folder from the ADE label that you are using for your SOA application, as follows:
Modify the property to xADataSourceName as follows:
<property> <name>xADataSourceName</name> <value>jdbc/DBConnection1</value> </property>
Modify the jndi-name as follows:
<jndi-name> eis/DB/DBConnection1</jndi-name>
This sample uses eis/DB/DBConnection1 to poll SAP table for new messages and to connect to the procedure that simulates Oracle EBS and Siebel instances.
Package the ra.xml and weblogic-ra.xml files as a RAR file and deploy the RAR file by using the Weblogic console.
Create a data source using the Weblogic console with the following values:
jndi-name=jdbc/DBConnection1
user=scott
password=tiger
url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@host:port:service
connection-factory factory-class=oracle.jdbc.pool.OracleDataSource
Create a data source using the Weblogic console with the following values:
jndi-name=jdbc/xref
user=scott
password=tiger
url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@host:port:service
connection-factory factory-class=oracle.jdbc.pool.OracleDataSource
To create an application and a project:
In Oracle JDeveloper, click File and select New.
The New Gallery dialog appears.
In the New Gallery, expand the General node, and select the Applications category.
In the Items list, select SOA Application and click OK.
The Create SOA Application wizard appears.
In the Application Name field, enter XRefOrderApp, and then click Next.
The Name your project screen appears.
In the Project Name field, enter XRefOrderApp and click Next.
The Configure SOA Settings screen appears.
In the Composite Template list, select Empty Composite and then click Finish.
The Applications Navigator of Oracle JDeveloper is updated with the new application and project and the Design tab contains, a blank palette.
From the File menu, click Save All.
After creating an application and a project for the use case, you must create a cross reference table.
To create a cross reference table:
In the Application Navigator, right-click the XRefOrderApp project and select New.
In the New Gallery dialog, expand the SOA Tier node, and then select the Transformations category.
In the Items list, select Cross Reference(XREF) and click OK.
The Create Cross Reference(XREF) File dialog is displayed.
In the File Name field, enter order.xref.
In the End System fields, enter SAP_05 and EBS_i75.
Click OK.
The Cross Reference Editor is displayed.
Click Add.
A new row is added.
Enter COMMON as End System name.
The Cross Reference Editor would appear as shown in Figure 47-45.
From the File menu, click Save All and close the Cross Reference Editor.
To create a Database adapter service:
In the Component Palette, select SOA.
Select Database Adapter and drag it to the Exposed Services design area.
The Adapter Configuration wizard Welcome page is displayed.
Click Next.
The Service Name page is displayed.
In the Service Name field, enter SAP.
Click Next.
The Service Connection page is displayed.
In the Connection field, select DBConnection1.
In the JNDI Name field, enter eis/DB/DBConnection1.
Click Next.
The Operation Type page is displayed.
Select Poll for New or Changed Records in a Table and click Next.
The Select Table page is displayed.
Click Import Tables.
The Import Tables dialog is displayed.
Select Scott from Schema.
In the Name Filter field, enter %SAP% and click Query.
The Available field is populated with SAP_05 table name.
Double-click SAP_05.
The selected field is populated with SAP_05.
Click OK.
The Select Table page now contains the SAP_05 table.
Select SAP_05 and click Next.
The Define Primary Key page is displayed.
Select ID as primary key and click Next.
The Relationships page is displayed.
Click Next.
The Attribute Filtering page is displayed.
Click Next.
The After Read page is displayed.
Select Update a Field in the [SAP_05] Table (Logical Delete) and click Next.
The Logical Delete page is displayed.
In the Logical Delete field, select LOGICAL_DEL.
In the Read Value field, enter Y.
In the Unread Value field, enter N.
Figure 47-14 shows the Logical Delete page of the Adapter Configuration Wizard.
Click Next.
The Polling Options page is displayed.
Click Next.
The Define Selection Criteria page is displayed.
Click Next.
The Advanced Options page is displayed.
Click Next.
The Finish page is displayed.
Click Finish.
A Database adapter service SAP is created, as shown in Figure 47-46.
Figure 47-46 SAP Database Adapter Service in SOA Composite Editor

From the File menu, click Save All.
To create external references named EBS:
In the Component Palette, select SOA.
Select Database Adapter and drag it to the External References design area.
The Adapter Configuration wizard Welcome page is displayed.
Click Next.
The Service Name page is displayed.
In the Service Name field, enter EBS.
Click Next.
The Service Connection page is displayed.
In the Connection field, select DBConnection1.
In the JNDI Name field, enter eis/DB/DBConnection1.
Click Next.
The Operation Type page is displayed.
Select Call a Stored Procedure or Function and click Next.
The Specify Stored Procedure page is displayed.
Select Scott from Schema.
Click Browse.
The Stored Procedures dialog is displayed.
Select POPULATE_APP_INSTANCE_IM as shown in Figure 47-47.
Click OK.
The Specify Stored Procedure page appears as shown in Figure 47-48.
Figure 47-48 Specify Stored Procedure Page of Adapter Configuration Wizard
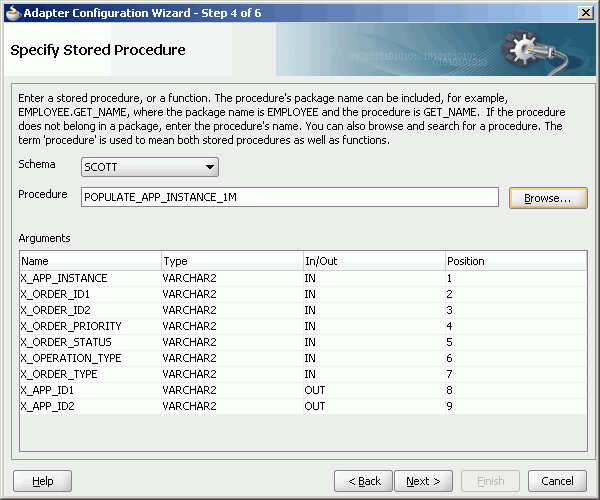
Click Next.
The Advanced Options page is displayed.
Click Next.The Finish page is displayed.
Click Finish.
Figure 47-49 shows the EBS reference in SOA Composite Editor.
Figure 47-49 EBS Reference in SOA Composite Editor

From the File menu, click Save All.
To create a file adapter reference:
From the Component Palette, select SOA.
Select File Adapter and drag it to the External References design area.
The Adapter Configuration wizard Welcome page is displayed.
Click Next.
The Service Name page is displayed.
In the Service Name field, enter Logger.
Click Next.
The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
Click Define from operation and schema (specified later).
The Operation page is displayed.
In the Operation Type field, select Write File.
Click Next.
The File Configuration page is displayed.
In the Directory for Outgoing Files (physical path) field, enter the name of the directory where you want to write the files.
In the File Naming Convention field, enter output.xml and click Next.
The Messages page is displayed.
Click Search.
The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
Navigate to Type Explorer, Project Schema Files, SCOTT_POPULATE_APP_INSTANCE_1M.xsd and then select OutputParameters.
Click OK.
Click Next.
The Finish page is displayed.
Click Finish.
Figure 47-50 shows the Logger reference in the SOA Composite Editor.
Figure 47-50 Logger Reference in SOA Composite Editor
From the File menu. click Save All.
To create a Mediator:
Drag and drop a Mediator from Components Palette to the Components design area.
The Create Mediator dialog is displayed.
Select Define Interface Later from Template.
Click OK.
A Mediator with name Mediator2 is created.
Connect the SAP service to the Mediator2 as shown in Figure 47-51.
Figure 47-51 SAP Service Connected to Mediator2
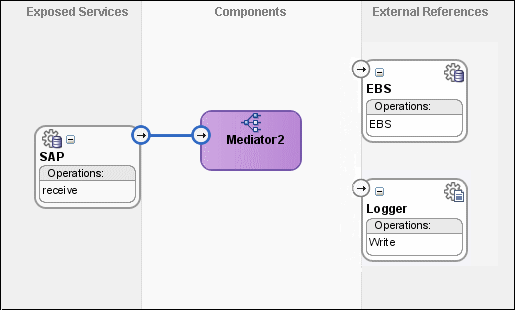
Click Save All.
Drag and drop another Mediator from Components Palette to the Components design area.
The Create Mediator dialog is displayed.
Select Interface Definition From WSDL from Template.
Deselect Create Composite Service with SOAP Bindings.
Click Find Existing WSDLs to the right of the WSDL File field.
Navigate to and then select the Common.wsdl file. The Common.wsdl file is available in the Samples folder.
Click OK.
Click OK.
A Mediator with name Common is created.
You must specify routing rules for following operations:
Insert
Update
To create routing rules for insert operation:
Double-click Mediator2 Mediator.
The Mediator Editor is displayed.
In Routing Rules panel, click the Create a new Routing Rule icon.
The Target Type dialog is displayed.
Select Service.
The Target Services dialog is displayed.
Navigate to XrefOrderApp, Mediators, Common, Services, Common.
Select Insert and click OK.
Click the Filter icon.
The Expression Builder dialog is displayed.
Enter the following expression in the Expression field:
$in.Sap05Collection/top:Sap05Collection/top:Sap05/top:operation='INSERT'
Click OK.
Click the Transformation icon next to the Using Transformation field.
The Request Transformation map dialog is displayed.
Select Create New Mapper File and enter SAP_TO_COMMON_INSERT.xsl.
Click OK.
A SAP_TO_COMMON_INSERT.xsl tab is displayed.
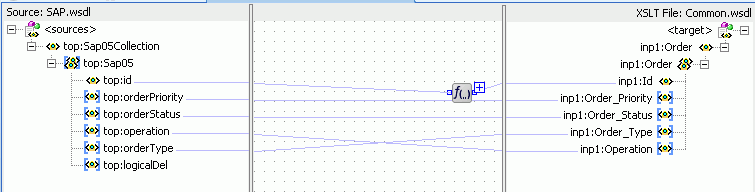
Drag and drop top:SAP05 source element to the inp1:Order target element.
The Auto Map Preferences dialog is displayed.
From the During Auto Map options, deselect Match Elements Considering their Ancestor Names.
Click OK.
The transformation is created as shown in Figure 47-52.
Figure 47-52 SAP_TO_COMMON_INSERT.xsl Transformation
From the Components Palette, select Advanced.
Select XREF Functions.
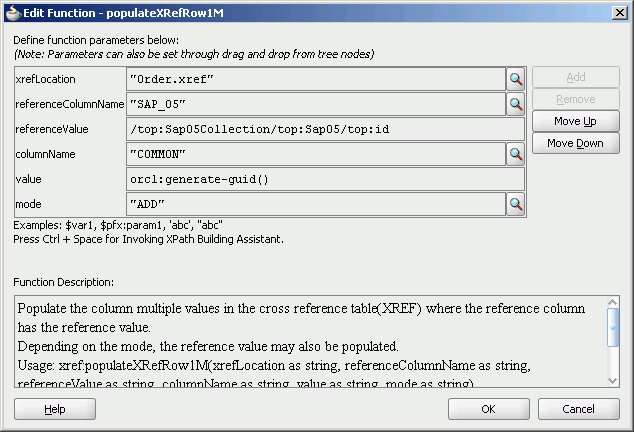
Drag and drop the populateXRefRow1M function from Components Palette to the line connecting top:id and inp1:id elements.
Double-click the populateXRefRow1M icon.
The Edit Function-populateXRefRow dialog is displayed.
Click Search to the right of xrefLocation field.
The SCA Resource Lookup dialog is displayed.
Select Order.xref and click OK.
In the referenceColumnName field, enter "SAP_05" or click Search to select the column name.
In the referenceValue column, enter /top:Sap05Collection/top:Sap05/top:id.
In the columnName field, enter "Common" or click Search to select the column name.
In the value field, enter orcl:generate-guid().
In the mode field, enter "Add" or click Search to select this mode.
Figure 47-53 shows populated Edit Function – populateXRefRow1M dialog.
Figure 47-53 Edit Function – populateXRefRow1M Dialog: XrefOrderApp Use Case
Click OK.
From the File menu, click Save All and close the SAP_TO_COMMON_INSERT.xsl tab.
The Routing Rules panel would appear as shown in Figure 47-54.
Figure 47-54 Routing Rules Panel with Insert Operation
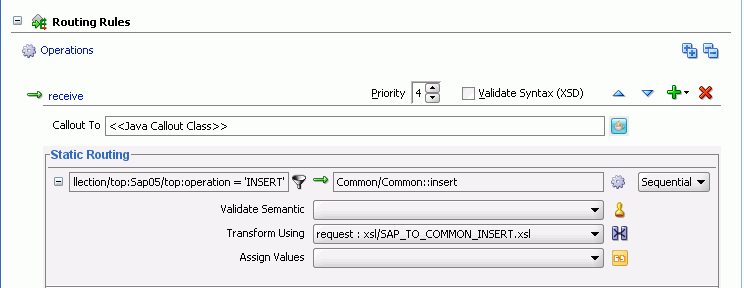
To create routing rules for update operation:
Perform the following tasks to create routing rules for Update operation:
In Routing Rules panel, click the Create a new Routing Rule icon.
The Target Type dialog is displayed.
Select Service.
The Target Services dialog is displayed.
Navigate to XrefOrderApp, Mediators, Common, Services, Common.
Select Update and click OK.
Click the Filter icon.
The Expression Builder dialog is displayed.
Enter the following expression in the Expression field:
$in.Sap05Collection/top:Sap05Collection/top:Sap05/top:operation='UPDATE'
Click OK.
Click the Transformation icon next to the Transform Using field.
The Request Transformation map dialog is displayed.
Select Create New Mapper File and enter SAP_TO_COMMON_UPDATE.xsl.
Click OK.
A SAP_TO_COMMON_UPDATE.xsl tab is displayed.
Drag and drop the top:Sap05 source element to the inp1:Order target element.
The Auto Map Preferences dialog is displayed.
Click OK.
From the Components Palette, select Advanced.
Select XREF Functions.
Drag and drop the lookupXRef function from Components Palette to the line connecting top:id and inp1:id elements.
Double-click the lookupXRef icon.
The Edit Function-lookupXRef dialog is displayed.
Click Search to the right of xrefLocation field.
The SCA Resource Lookup dialog is displayed.
Select customer.xref and click OK.
In the referenceColumnName field, enter "SAP_05" or click Search to select the column name.
In the referenceValue column, enter /top:Sap05Collection/top:Sap05/top:id.
In the columnName field, enter "COMMON" or click Search to select the column name.
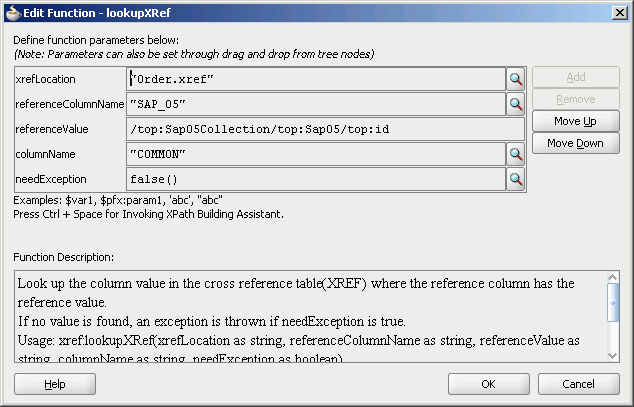
In the needException field, enter true() or click Search to select this mode.
Figure 47-55 shows populated Edit Function – looupXRef dialog.
Figure 47-55 Edit Function – looupXRef Dialog: XRefOrderApp Use Case
Click OK.
From the File menu, click Save All and close the SAP_TO_COMMON_UPDATE.xsl tab.
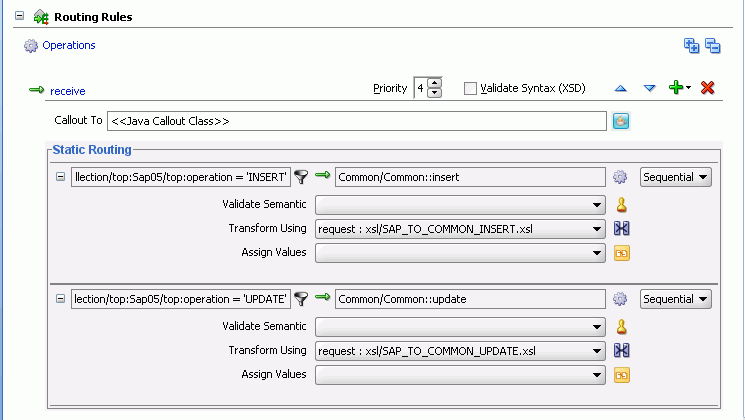
The Routing Rules panel would appear as shown in Figure 47-56.
Figure 47-56 Insert Operation and Update Operation
You must specify routing rules for following operations of Common Mediator:
Insert
Update
To create routing rules for insert operation:
Double-click Common Mediator.
The Mediator Editor is displayed.
In Routing Rules panel, click the Create a new Routing Rule icon.
The Target Type dialog is displayed.
Select Service.
The Target Services dialog is displayed.
Navigate to XrefOrderApp, References, EBS.
Select EBS and click OK.
Click the Transformation icon next to the Transform Using field.
The Request Transformation map dialog is displayed.
Select Create New Mapper File and enter COMMON_TO_EBS_INSERT.xsl.
Click OK.
A COMMON_TO_EBS_INSERT.xsl tab is displayed.
Drag and drop inp1:Order source element to the db:InputParameters target element.
The Auto Map Preferences dialog is displayed.
Set the value of the db:X_APP_INSTANCE node on the right side to EBS_i75.
Click OK.
The transformation is created as shown in Figure 47-57.
Figure 47-57 COMMON_TO_EBS_INSERT.xsl Transformation

From the File menu, click Save All and close the COMMON_TO_EBS_INSERT.xsl window.
In the Synchronous Reply panel, click Browse for target service operations.
The Target Type dialog is displayed.
Select Service.
The Target Services dialog is displayed.
Navigate to XrefOrderApp, References, Logger.
Select Write and click OK.
Click the Transformation icon next to the Transform Using field.
The Reply Transformation map dialog is displayed.
Select Create New Mapper File and enter EBS_TO_COMMON_INSERT.xsl.
Select Include Request in the Reply Payload.
Click OK.
AN EBS_TO_COMMON_INSERT.xsl window is displayed.
Connect inp1:Order source element to the db:X:APP_ID.
Drag and drop the populateXRefRow function from Components Palette to the connecting line.
Double-click the populateXRefRow icon.
The Edit Function-populateXRefRow dialog is displayed.
Enter the information in the following fields:
xrefLocation: "order.xref"
referenceColumnName: "Common"
referenceValue: $initial.Customers/inp1:Customers/inp1:Order/inp1:Id
columnName:"EBS_75"
value:/db:OutputParameters/db:X_APP_ID
mode:"LINK"
Click OK.
The EBS_TO_COMMON_INSERT.xsl would appear as shown in Figure 47-58.
Figure 47-58 EBS_TO_COMMON_INSERT.xsl Transformation
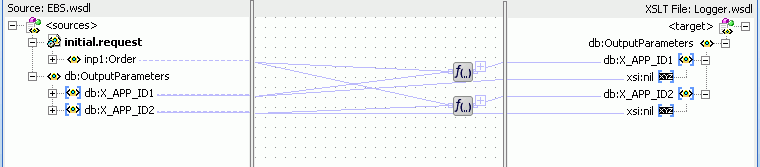
From the File menu, click Save All and close the EBS_TO_COMMON_INSERT.xsl tab.
In the Synchronous Reply panel, click the Assign Values icon.
The Assign Values dialog is displayed.
Click Add.
The Assign Value dialog is displayed.
In the From section, select Expression.
Click the Invoke Expression Builder icon.
The Expression Builder dialog is displayed.
Enter the following expression in the Expression field and click OK.
concat('INSERT-',$in.OutputParameters/db:OutputParameters/db:X_APP_ID,'.xml')
In the To section, select Property.
Select jca.file.FileName property and click OK.
Click OK.
The insert operation panel would appear as shown in Figure 47-59.
Figure 47-59 Insert Operation with EBS Target Service
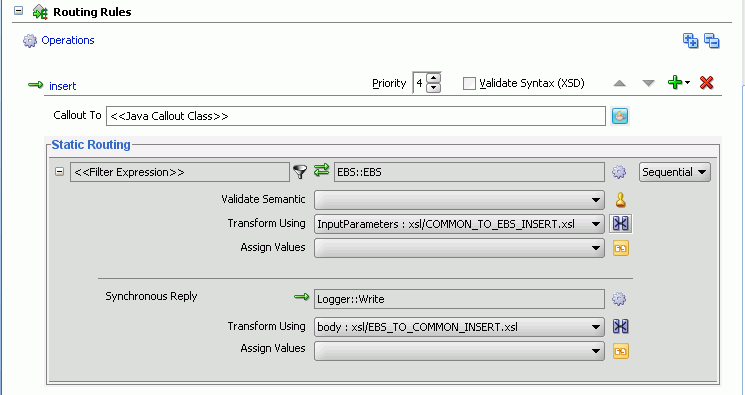
From the File menu, click Save All.
To create routing rules for update operation:
Perform the following tasks to create routing rules for Update operation:
In Routing Rules panel, click the Create a new Routing Rule icon.
The Target Type dialog is displayed.
Select Service.
The Target Services dialog is displayed.
Navigate to XrefOrderApp, References, EBS.
Select EBS and click OK.
Click the Transformation icon next to the Transform Using field.
The Request Transformation map dialog is displayed.
Select Create New Mapper File and enter COMMON_TO_EBS_UPDATE.xsl.
Click OK.
A COMMON_TO_EBS_UPDATE.xsl tab is displayed.
Drag and drop inp1:Orders source element to the db:InputParameters target element.
The Auto Map Preferences dialog is displayed.
Click OK.
The transformation is created as shown in Figure 47-37.
Drag and drop the lookupXRef function from Components Palette to the line connecting inp1:id and db:X_APP_ID.
Double-click the lookupXRef icon.
The Edit Function: lookupXRef dialog is displayed.
Enter the information in the following fields:
xrefLocation: "order.xref"
referenceColumnName: "Common"
referenceValue: /inp1:Customers/inp1:Order/inp1:Id
columnName:"EBS_i75"
needException:true()
Click OK.
From the File menu, click Save All and close the COMMON_TO_EBS_UPDATE.xsl window.
In the Synchronous Reply panel, click Browse for target service operations.
The Target Type dialog is displayed.
Select Service.
The Target Services dialog is displayed.
Navigate to XrefOrderApp, References, Logger.
Select Write and click OK.
Click the Transformation icon next to the Transform Using field.
The Reply Transformation map dialog is displayed.
Select Create New Mapper File and enter EBS_TO_COMMON_UPDATE.xsl.
Click OK.
A EBS_TO_COMMON_UPDATE.xsl window is displayed.
Connect db:X:APP_ID source element to the db:X:APP_ID.
From the File menu, click Save All and close the EBS_TO_COMMON_UPDATE.xsl tab.
In the Synchronous Reply panel, click the Assign Values icon.
The Assign Values dialog is displayed.
Click Add.
The Assign Value dialog is displayed.
In the From section, select Expression.
Click the Invoke Expression Builder icon.
The Expression Builder dialog is displayed.
Enter following expression in the Expression field and click OK.
concat('UPDATE-',$in.OutputParameters/db:OutputParameters/db:X_APP_ID,'.xml')
In the To section, select Property.
Select jca.file.FileName property and click OK.
Click OK.
The update operation panel would appear as shown in Figure 47-60.
Figure 47-60 Update Operation with EBS Target Service
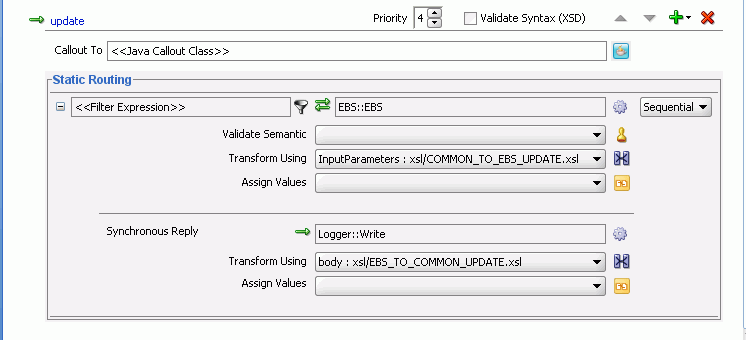
From the File menu, click Save All.
An Oracle Application Server connection is required for deploying your SOA composite application. For information on creating Oracle Application Server connection, refer to Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Technology Adapters.
Deploying the XrefOrderApp composite application to Oracle Application Server consists of following steps:
Creating an Application Deployment Profile
Deploying the Application to Oracle Application Server
For detailed information about these steps, see Section 43.2, "Deploying a Single SOA Composite in Oracle JDeveloper".