| Oracle® Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Business Process Management 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.4.0) Part Number E15175-03 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Business Process Management 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.4.0) Part Number E15175-03 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter contains these topics:
Standard dashboards are the graphs and drill-downs based on data previously computed in a process cube schema. They reflect the standard metrics gathered during the execution of a process.
In each of the standard dashboards, clicking a bar graph in the left pane causes data to be displayed graphically in the right pane. Clicking an item in the right pane displays certain data in the lower pane. This section explains how each type of dashboard operates.
This section contains these topics:
Two types of standard participant dashboards enable you to analyze:
The workload of participants
The performance of participants
Figure 6-1 shows an example of a participant workload dashboard.
Figure 6-1 Participant Workload Dashboard
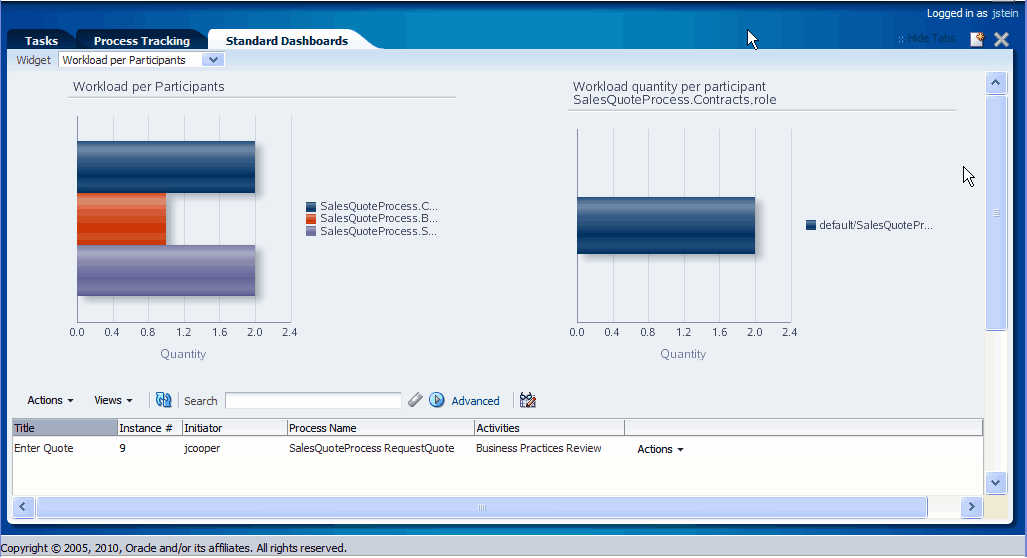
The left panel of a participant workload dashboard displays the total number of active instances waiting for completion for each participant across all processes. When you drill down into the chart for a specific participant, the right panel displays the total number of active instances waiting for completion by process for either the selected participant or the selected role. The last drill-down displays the active instances waiting for completion for either the selected participant or the selected role and process.
Note:
In this release, participant information in a workload dashboard is for the physical role corresponding to the swimlane for the task. When the swimlane role is not defined, the corresponding participant information is null.Figure 6-2 shows a participant performance dashboard.
The left panel of a participant performance dashboard displays the average time taken by participants across all processes. When you drill down into the chart for a specific participant, the right panel displays the average time taken to complete instances by process for the selected participant. The last drill-down displays the list of completed instances for either the selected participant or the selected role and process.
Note:
In this release, for processes that have user tasks with multiple users, user information is captured only for the last user that updated the task.Two types of standard process dashboards enable you to analyze:
The number of process instances waiting for completion
The average time taken per process
Figure 6-3 shows a process workload dashboard.
The left panel in the process workload dashboard displays the total number of active instances waiting for completion per process. When you drill down into a specific process, the right panel displays the total number of active instances waiting for completion for activities in the selected process. The last drill-down displays the active instances waiting for completion for the selected activity and process.
The left panel in the process performance dashboard displays the average time taken per process. When you drill down into a specific process, the right panel displays the average time taken to complete by activities in the selected process. The last drill-down displays the completed instances for the selected activity and process.
Figure 6-4 shows a process performance dashboard.
As with standard dashboards, custom dashboards are the graphs and drill-downs based on data previously computed in a process cube schema. They reflect the standard and user-defined metrics gathered during the execution of the process. They enable you to define new graphs using both standard metrics and user-defined metrics specified by using business indicators.
For instructions about adding a custom dashboard, see Section 5.1.1, "How to Create a Custom Page".
Graph content is specified by defining a data source. Figure 6-5 shows an example of the Data Sources dialog box.
For information about invoking the data source dialog box, see Section 5.1.3, "How to Add a Dashboards Panel to a Customized Page."
In the Data Sources dialog box, specify the following:
Name: Provide a data source identifier
Title: Provide the title used while displaying the data source
Graph Type: Select one of the following list of graph types:
Area
Percent Area
Stacked Area
Horizontal Bar
Horizontal Percent Bar
Horizontal Stacked Bar
Bar
Percent Bar
Stacked Bar
Line
Percent Line
Stacked Line
Pie
Pie Bar
Multiple Pie
Process: Select the process from the list. All business indicators associated with the selected process become available for the data source definition.
Data Type: Select one of the following supported data types:
Workload
Activity and Measurement Sampling
Process Level Sampling
Dimensions
Series: Specify the dimension.
Use Range: Select to use ranges for dimensions with ranges.
Group: Specify the dimension used to group the dimensions used in a series.
Use Range: Select to use ranges for dimensions with ranges.
Drilldown to Series
Use Range: Select to use ranges for dimensions with ranges.
Table 6-1 summarizes the standard dimensions available based on the Data Type selection. Additionally, all the process specific dimensions are available.
Table 6-1 Standard Dimensions Available
| Workload | Activity and Measurement Sampling | Process Sampling | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Dimension: Series |
Revision Role Activities Participant |
Revision Role Activities Participant Completion Date |
Revision Completion Date |
|
Dimension: Group |
Participant |
Participant Completion Date |
Completion Date |
Measure
Variable: Specify the measurement
Table 6-2 summarizes list of standard measurements available based on the Data Type selection. Additionally, all the process-specific measurements are available.
Operation Type: Specify the aggregation functions to be applied on the measurement variables selected.
Table 6-3 summarizes the operation types that can be used with various Data Type selections.
Value Type: Select one of the following values: Value, Day(s), Hours, Minutes, Seconds, Percentage
Note:
If a new process is deployed while you have a dashboards page open, the new process will not be listed in the Data Sources dialog box until you log out of Process Workspace and then log back in.Filters
You can add filter conditions based on the measure variables, series, and groups. You can add the filter condition only if a process is selected from the Process list. If "All" is selected in the Process list, then the Filters section is disabled.
Note:
If you add a filter for business indicators, that filter filters out the values initially based on the condition given. Aggregation—either the sum or the average—then applies to the resulting set of items.For example, if the user tries to compute the average of all business indicator values greater than 1000, the user will set a filter for this—for example: BI <Greater or equals> 1000 and set Operation type as "avg". The result is that the business indicator values greater than 1000 are collected first, and then the computation for the average calculation takes place.