| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Introducing Web Services 11g Release 1 (11.1.1) Part Number E14294-04 |
|
| View PDF |
| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Introducing Web Services 11g Release 1 (11.1.1) Part Number E14294-04 |
|
| View PDF |
Introducing Web Services
11g Release 1 (11.1.1)
E14294-04
January 2011
This document provides an overview of Web services in Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g. Sections include:
A Web service is a program that can be accessed remotely using different XML-based languages. What this program can do (that is, the functionality it implements) is described in a standard XML vocabulary called Web Services Description Language (WSDL). For example, a banking Web service may implement functions to check an account, print a statement, and deposit and withdraw funds. These functions are described in a WSDL file that any consumer can invoke to access the banking Web service. As a result, a consumer does not have to know anything more about a Web service than the WSDL file that describes what it can do.
A Web service consumer (such as, a desktop application or a Java Platform, Enterprise Edition client such as a portlet) invokes a Web service by submitting a request in the form of an XML document to a Web service provider. The Web service provider processes the request and returns the result to the Web service consumer in an XML document as shown in the example below.

In this example, the Web service consumer sends a request in the form of a Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) message (SOAP is an XML messaging framework designed to allow heterogeneous applications to exchange structured information in a distributed environment). The Web service provider (www.xmethods.com) processes the request and returns the response, in this case the stock quote for Oracle. In the example above, the Web service provider may have asked for credentials to access the service, for example a username and a password. Also, the Web service provider may have encrypted the response (the value of the stock).
You can also develop Representational State Transfer (REST) Web services, or "RESTful" Web services. REST describes any simple interface that transmits data over a standardized interface (such as HTTP) without an additional messaging layer, such as SOAP. REST provides a set of design rules for creating stateless services that are viewed as resources, or sources of specific information, and can be identified by their unique URIs. A client accesses the resource using the URI, a standardized fixed set of methods, and a representation of the resource is returned. The client is said to transfer state with each new resource representation.
In summary, Web services are loosely coupled, distributed environments that allow companies to integrate heterogeneous applications within the enterprise or expose business functions to their customers and partners over the Internet.
Web services are characterized by three factors:
What they do (the business functionality they expose),
Where they are (the web site which exposes that functionality),
How they can be accessed (the set of published interfaces necessary to use the exposed functionality).
Web services rely on XML-based industry standards:
Extensible Markup Language (XML)—A data format that allows uniform communication between Web services consumers and Web services providers.
XML Schema—A framework that describes XML vocabularies used in business transactions.
SOAP—A protocol for exchanging structured information in the implementation of Web services.
WSDL—An XML-based language providing a model for describing Web services.
WS-Policy—The WS-Policy framework provides a flexible and extensible grammar for describing the capabilities, requirements, and general characteristics of Web services using policies.
Universal Description, Discovery, and Integration (UDDI)—A framework to publish and look up Web services on the Internet.
The following illustration shows common interactions between Oracle Fusion Middleware Web services and clients, and identifies Web service policy support at each interaction point.
The Oracle Web Services Manager (WSM) Policy Manager is the security and management policy lynchpin for Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g Web services. For more information about how the Oracle WSM Policy Manager provides the policy framework for managing policies, see "Understanding Oracle WSM Policy Framework" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services.
Figure 1 Web Services in Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g
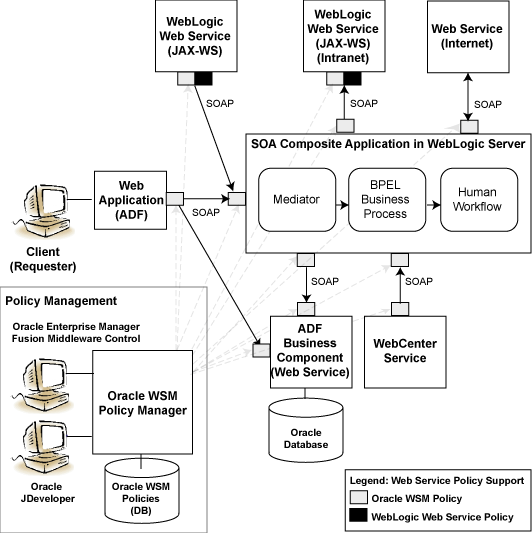
The following sections provide more detail about the Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g Web services architecture and each of the Web service components shown in the previous figure:
For a complete roadmap of all Web service development, security, and administration tasks, see "Roadmap for Implementing Oracle Fusion Middleware Web Services".
In Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g, there are two categories of Web services:
Oracle Infrastructure Web services—SOA, ADF, and WebCenter services
WebLogic Web services (Java EE Web services)
The following figure illustrates the two Web services categories.
Figure 2 Web Services in Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g
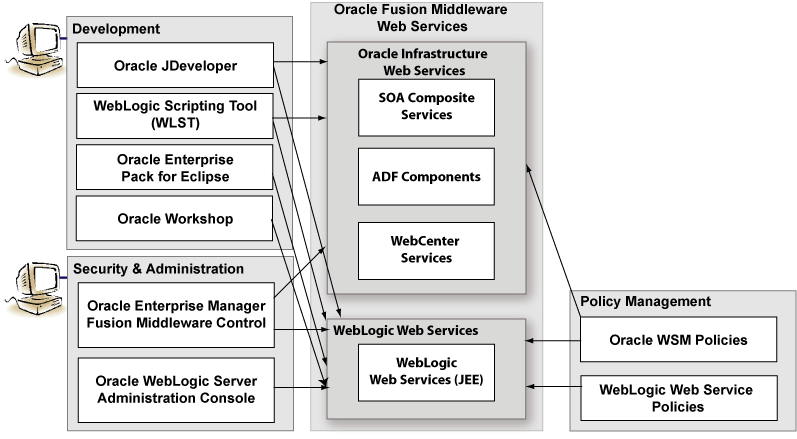
Table 1 summarizes the types of Web services supported in Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g.
Note:
All Web services and clients can be deployed to an Oracle Fusion Middleware environment that runs on Oracle WebLogic Server. Oracle WebLogic Web services can be deployed to a standalone Oracle WebLogic Server, as well.Table 1 Oracle Fusion Middleware Web Services
| Web Service | Description |
|---|---|
|
WebLogic Web service (Java EE) |
WebLogic Web services are implemented according to the Web services for Java EE specification, available at For more information about developing WebLogic Web services, see:
You can deploy WebLogic Web services to any Oracle WebLogic Server environment, including a standalone environment. |
|
SOA service components |
SOA composite applications include SOA service components. SOA service components are the basic building blocks of SOA applications, implementing a part of the overall business logic functionality. The following SOA service components can be managed using Oracle WSM:
For more information about developing SOA service components, see Developer's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite. You can deploy SOA service components to the Oracle Fusion Middleware environment. |
|
SOA service binding components |
SOA Service binding components provide the outside world with an entry point to the SOA composite application. The WSDL file of the service advertises its capabilities to external applications. These capabilities are used for contacting the SOA composite application components. For more information, see Developer's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite. |
|
ADF Business Components |
ADF Business Components simplify the development, delivery, and customization of business applications for the Java EE platform by providing a library of reusable components and supporting design time facilities in Oracle JDeveloper. Using ADF Business Components, developers are not required to write the application infrastructure code required by the typical Java EE application to perform the following tasks:
Additionally, Oracle JDeveloper facilities expose ADF Business Component application modules that encapsulate built-in data manipulation operations and custom methods as Web services so that a service-enabled application module can be consumed across modules of the deploy Fusion Web application. For more information, see "Integrating Service-Enabled Application Modules" in Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework. |
|
WebCenter services |
WebCenter services expose Web 2.0 technologies for social networking and personal productivity, such as Wiki, RSS, and blogs. WebCenter provides a set of features and services (for example, portlets, customization, and content integration) that you can selectively add to your application. For more information about integrating WebCenter services, see Developer's Guide for Oracle WebCenter. |
Table 2 summarizes the types of Web service clients supported in Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g.
Table 2 Oracle Fusion Middleware Web Service Clients
| Web Service Client | Description |
|---|---|
|
Web service clients |
Client applications that invoke WebLogic Web services can be written using any technology: Java, Microsoft .NET, and so on. There are two types of client applications:
For more information about developing WebLogic Web service clients, see:
|
|
SOA reference binding components |
SOA reference binding components connect the SOA composite application to external partners. For more information about developing SOA reference binding components, see Developer's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite. |
|
ADF Web applications |
ADF Web applications can invoke a service, such as a WebLogic Web service, a SOA composite application, or a service-enabled ADF application module. For more information, see Developer's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite. In addition, ADF Web applications can work with Web services in the user interface using a Web service data control. For more information about generating service-enabled application modules, calling a Web service from an ADF application module, or creating Web service data controls, see Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework. |
|
WebCenter portlets |
WebCenter portlets enable you to surface WebCenter services. For more information about developing WebCenter portlets, see Developer's Guide for Oracle WebCenter. |
As shown in Figure 2, there are two types of policies that can be attached to Web services.
Table 3 Types of Web Service Policies
| Type of Policy | Description |
|---|---|
|
Oracle Web Services Manager (WSM) Policy |
Policy provided by the Oracle WSM. For more information about the Oracle WSM and the predefined policies, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services. You can attach Oracle WSM policies to Oracle Infrastructure Web services. You can only attach Oracle WSM security policies to WebLogic JAX-WS Web services. You manage Oracle WSM policies from Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control. |
|
WebLogic Web Service Policy |
Policy provided by WebLogic Server. For more information about the WebLogic Web service policies, see Securing WebLogic Web Services for Oracle WebLogic Server. A subset of WebLogic Web service policies interoperate with Oracle WSM policies. For more information, see "Interoperability with Oracle WebLogic Server 11g Web Service Security Environments" in the Interoperability Guide for Oracle Web Services Manager. You manage WebLogic Web service policies from WebLogic Administration Console. |
Note:
It is recommended that you use Oracle WSM policies over WebLogic Web services whenever possible. You cannot mix your use of Oracle WSM and WebLogic Web service policies on the same Web service.To develop Web services, you can use the tools described in the following table, or your favorite IDE.
Table 4 Tools for Web Service Development
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
|
Oracle JDeveloper |
Provides powerful tools that help you discover and use existing Web services, and develop and deploy new Web services. For more information, see the Oracle JDeveloper online help. |
|
Ant |
Uses XML-based configuration files (called build.xml by default) to execute tasks written in Java. Ant is a Java-based build tool, similar to the make command but much more powerful. For more information, see "Ant Task Reference" in WebLogic Web Services Reference for Oracle WebLogic Server. |
|
WebLogic Server Scripting Tool (WLST) |
Enables administrators to view and configure Web services, and manage Web service policies from the command line. For more information, see WebLogic Scripting Tool Command Reference. |
|
Oracle Enterprise Pack for Eclipse (OEPE) |
Provides a collection of plug-ins to the Eclipse IDE platform that facilitate development of WebLogic Web services. For more information, see the Eclipse IDE platform online help. |
|
Oracle Workshop |
Provides a collection plug-ins to the Eclipse IDE platform that facilitate development of WebLogic Web services. For more information, see
NOTE: Oracle Workshop is deprecated, and is being replaced by OEPE, described above. |
To secure and administer Web services, the tools that you use vary depending on the Web service type.
Table 5 Tools for Web Service Security and Administration
| To secure and administer . . . | Use. . . |
|---|---|
|
Oracle Infrastructure Web Services |
|
|
WebLogic Web Services |
|
The following sections provide roadmaps of common tasks for developing, securing, and administering Oracle Fusion Middleware Web services. Roadmaps are presented for each Web service category shown in Figure 2:
The following sections provides roadmaps of common tasks for developing, securing, and administering Oracle Infrastructure Web services:
Table 6 summarizes the roadmap for implementing SOA composite services and clients.
Table 6 Roadmap for Implementing SOA Composite Services and Clients
| Task | More Information |
|---|---|
|
Develop SOA composite Web services and clients |
|
|
Deploy Web services |
|
|
Administer Web services |
Part II: "Basic Administration" and Part III "Advanced Adminstration" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services |
|
Create policies |
"Managing Web Service Policies" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services |
|
Create custom assertions |
"Creating Custom Assertions" in Extensibility Guide for Oracle Web Services Manager |
|
Attach policies (development time—Oracle JDeveloper) |
"Managing Policies" in Developer's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite |
|
Attach policies (deployment time—Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control) |
|
|
Configure policies |
|
|
Test Web services |
"Testing Web Services" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services |
|
Monitor Web service performance |
"Monitoring the Performance of Web Services" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services |
|
Manage application migration between environments |
"Managing Application Migration Between Environments" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services |
|
Diagnose problems |
"Diagnosing Problems" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services |
|
Interoperate with:
|
Table 7 summarizes how to implement ADF components and clients.
Table 7 Roadmap for Implementing ADF Components and Clients
| Task | More Information |
|---|---|
|
Develop ADF components and clients |
|
|
Deploy Web services |
|
|
Administer Web services |
Part II: "Basic Administration" and Part III "Advanced Adminstration" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services |
|
Create policies |
"Managing Web Service Policies" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services |
|
Create custom assertions |
"Creating Custom Assertions" in Extensibility Guide for Oracle Web Services Manager |
|
Attach policies (development time—Oracle JDeveloper) |
"Securing Web Service Data Controls" in Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework |
|
Attach policies (deployment time—Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control) |
"Attaching Policies to Web Services" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services |
|
Configure policies |
|
|
Test Web services |
"Testing Web Services" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services |
|
Monitor Web service performance |
"Monitoring the Performance of Web Services" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services |
|
Manage application migration between environments |
"Managing Application Migration Between Environments" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services |
|
Diagnose problems |
"Diagnosing Problems" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services |
|
Interoperate with:
|
Table 8 summarizes the roadmap for implementing WebCenter services and clients.
Table 8 Roadmap for Implementing WebCenter Services and Clients
| Task | More Information |
|---|---|
|
Develop WebCenter services and clients |
|
|
Deploy WebCenter services |
|
|
Administer WebCenter services |
Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle WebCenter |
|
Create policies |
"Managing Web Service Policies" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services |
|
Create custom assertions |
"Creating Custom Assertions" in Extensibility Guide for Oracle Web Services Manager |
|
Attach policies (deployment time—Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control) |
|
|
Configure policies |
|
|
Test WebCenter services |
"Testing and Deploying Your WebCenter Application" in Developer's Guide for Oracle WebCenter |
|
Monitor WebCenter service performance |
Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle WebCenter |
|
Manage application migration between environments |
"Managing Application Migration Between Environments" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services |
|
Diagnose problems |
"Diagnosing Problems" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services |
|
Interoperate with:
|
The following table provides a roadmap of common tasks for developing, securing, and administering WebLogic (Java EE) Web services.
Table 9 Roadmap for Implementing WebLogic (Java EE) Web Services
| Task | More Information |
|---|---|
|
Develop WebLogic Web services and clients |
|
|
Deploy Web services |
|
|
Administer Web services |
"Web Services" in WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help |
|
Create Oracle WSM policies |
"Managing Web Service Policies" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services |
|
Create WebLogic Web service policies |
|
|
Configure Oracle WSM policies |
|
|
Configure WebLogic Web service policies |
|
|
Create custom Oracle WSM policy file |
"Creating Custom Assertions" in Extensibility Guide for Oracle Web Services Manager |
|
Create custom WebLogic Web service policy file |
"Creating and Using a Custom Policy File" in Securing WebLogic Web Services for Oracle WebLogic Server |
|
Attach Oracle WSM policies (development time—Oracle JDeveloper) |
|
|
Attach WebLogic Web service policies (development time—Oracle JDeveloper) |
|
|
Attach Oracle WSM policies (deployment time) |
"Attaching Policies to Web Services" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services |
|
Attach WebLogic Web service policies (deployment time) |
"Associate a WS-Policy file with a Web Service" in WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help |
|
Test Web services |
|
|
Monitor Web service performance |
|
|
Interoperate WebLogic and Oracle WSM Web service policies |
The following table summarizes the documentation that is related to Web services development, security, and administration.
Table 10 Related Documentation
| Document | Description |
|---|---|
|
Introducing Web Services |
This document. Provides an introduction to Web services for Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g. |
|
Describes how to secure and administer Oracle Infrastructure Web services. |
|
|
Describes how to build custom assertions for Oracle Web Services Manager (Oracle WSM). |
|
|
Describes how to implement the most common Oracle WSM interoperability scenarios. |
|
|
Introduces concepts that are relevant to Oracle Infrastructure Web services. |
|
|
Introducing WebLogic Web Services for Oracle WebLogic Server |
Introduces WebLogic Web services, the standards that are supported, interoperability information, and relevant samples and documentation. |
|
Getting Started With JAX-WS Web Services for Oracle WebLogic Server |
Provides the basic knowledge and tasks required to program a simple WebLogic Web service using JAX-WS. The guide includes use cases and examples, iterative development procedures, typical JWS programming steps, data type information, and how to invoke a Web service. |
|
Programming Advanced Features of JAX-WS Web Services for Oracle WebLogic Server |
Describes how to program more advanced features using JAX-WS, such as callbacks, XML Catalog, and SOAP message handlers. |
|
Getting Started With JAX-RPC Web Services for Oracle WebLogic Server |
Provides the basic knowledge and tasks required to program a simple WebLogic Web service using JAX-RPC. The guide includes use cases and examples, iterative development procedures, typical JWS programming steps, data type information, and how to invoke a Web service. |
|
Programming Advanced Features of JAX-RPC Web Services for Oracle WebLogic Server |
Describes how to program more advanced features using JAX-RPC, such as Web service reliable messaging, callbacks, conversational Web services, use of JMS transport to invoke a Web service, and SOAP message handlers. |
|
Describes how to program and configure message-level (digital signatures and encryption), transport-level, and access control security for a Web service. |
|
|
Provides reference information on JWS annotations, Ant tasks, reliable messaging WS-Policy assertions, security WS-Policy assertions, and deployment descriptors. |
|
|
Describes how to develop SOA composite services. |
|
|
Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework |
Describes how to develop ADF components. |
|
Describes how to develop WebCenter services. |
|
|
"Developing with Web Services" in the Oracle JDeveloper online help |
Describes how to develop Web services and attach policies using Oracle JDeveloper. |
|
Explains how to use Workshop to write and manage source code and design with sophisticated visual tools and Java frameworks. NOTE: Oracle Workshop is deprecated, and is being replaced by OEPE, described above. |
Our goal is to make Oracle products, services, and supporting documentation accessible to all users, including users that are disabled. To that end, our documentation includes features that make information available to users of assistive technology. This documentation is available in HTML format, and contains markup to facilitate access by the disabled community. Accessibility standards will continue to evolve over time, and Oracle is actively engaged with other market-leading technology vendors to address technical obstacles so that our documentation can be accessible to all of our customers. For more information, visit the Oracle Accessibility Program Web site at http://www.oracle.com/accessibility/.
Accessibility of Code Examples in Documentation
Screen readers may not always correctly read the code examples in this document. The conventions for writing code require that closing braces should appear on an otherwise empty line; however, some screen readers may not always read a line of text that consists solely of a bracket or brace.
Accessibility of Links to External Web Sites in Documentation
This documentation may contain links to Web sites of other companies or organizations that Oracle does not own or control. Oracle neither evaluates nor makes any representations regarding the accessibility of these Web sites.
Access to Oracle Support
Oracle customers have access to electronic support through My Oracle Support. For information, visit http://www.oracle.com/support/contact.html or visit http://www.oracle.com/accessibility/support.html if you are hearing impaired.
Oracle Fusion Middleware Introducing Web Services, 11g Release 1 (11.1.1)
E14294-04
Copyright © 2007, 2011, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
This software and related documentation are provided under a license agreement containing restrictions on use and disclosure and are protected by intellectual property laws. Except as expressly permitted in your license agreement or allowed by law, you may not use, copy, reproduce, translate, broadcast, modify, license, transmit, distribute, exhibit, perform, publish, or display any part, in any form, or by any means. Reverse engineering, disassembly, or decompilation of this software, unless required by law for interoperability, is prohibited.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice and is not warranted to be error-free. If you find any errors, please report them to us in writing.
If this software or related documentation is delivered to the U.S. Government or anyone licensing it on behalf of the U.S. Government, the following notice is applicable:
U.S. GOVERNMENT RIGHTS Programs, software, databases, and related documentation and technical data delivered to U.S. Government customers are "commercial computer software" or "commercial technical data" pursuant to the applicable Federal Acquisition Regulation and agency-specific supplemental regulations. As such, the use, duplication, disclosure, modification, and adaptation shall be subject to the restrictions and license terms set forth in the applicable Government contract, and, to the extent applicable by the terms of the Government contract, the additional rights set forth in FAR 52.227-19, Commercial Computer Software License (December 2007). Oracle USA, Inc., 500 Oracle Parkway, Redwood City, CA 94065.
This software is developed for general use in a variety of information management applications. It is not developed or intended for use in any inherently dangerous applications, including applications which may create a risk of personal injury. If you use this software in dangerous applications, then you shall be responsible to take all appropriate fail-safe, backup, redundancy, and other measures to ensure the safe use of this software. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates disclaim any liability for any damages caused by use of this software in dangerous applications.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
This software and documentation may provide access to or information on content, products, and services from third parties. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates are not responsible for and expressly disclaim all warranties of any kind with respect to third-party content, products, and services. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates will not be responsible for any loss, costs, or damages incurred due to your access to or use of third-party content, products, or services.