Release 11g (11.1.1)
Part Number E18862-01
Contents
Previous
Next
| Oracle Fusion Middleware Data Modeling Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Publisher Release 11g (11.1.1) Part Number E18862-01 | Contents | Previous | Next |
| View PDF |
This chapter covers the following topics:
A data model is an object that contains a set of instructions for BI Publisher to retrieve and structure data for a report. Data models reside as separate objects in the catalog.
At the very simplest, a data model can be one data set retrieved from a single data source (for example, the data returned from the columns in the employees table). A data model can also be complex, including parameters, triggers, and bursting definitions as well as multiple data sets.
The data model editor is the tool for building your data models.
A data model supports the following components:
Data set
A data set contains the logic to retrieve data from a single data source. A data set can retrieve data from a variety of data sources (for example, a database, an existing data file, a Web service call to another application, or a URL/URI to an external data provider). A data model can have multiple data sets from multiple sources.
Event triggers
A trigger checks for an event. When the event occurs the trigger runs the PL/SQL code associated with it. The data model editor supports before data and after data triggers. Event triggers consist of a call to execute a set of functions defined in a PL/SQL package stored in an Oracle database.
Flexfields
A flexfield is a structure specific to Oracle Applications. The data model editor supports retrieving data from flexfield structures defined in your Oracle Application database tables.
Lists of values
A list of values is a menu of values from which report consumers can select parameter values to pass to the report.
Parameters
A parameter is a variable whose value can be set at runtime. The data model editor supports several parameter types.
Bursting Definitions
Bursting is a process of splitting data into blocks, generating documents for each data block, and delivering the documents to one or more destinations. A single bursting definition provides the instructions for splitting the report data, generating the document, and delivering the output to its specified destinations.
Use the data model editor to combine data from multiple data sets from different data sources, such as SQL, Excel files, Web services, HTTP feeds, and other applications into a single XML data structure. Data sets can either be unrelated or a relationship can be established between them using a data link.
The data model editor enables you to perform the following tasks:
Link data - define master-detail links between data sets to build a hierarchical data model.
Aggregate data - create group level totals and subtotals.
Transform data - modify source data to conform to business terms and reporting requirements.
Create calculations - compute data values that are required for your report that are not available in the underlying data sources.
BI Publisher supports a variety of data source types for creating data sets. These can be categorized into three general types:
The first type are data sets for which BI Publisher can retrieve metadata information from the source. For these data set types, the full range of data model editor functions is supported.
Submit a SQL query against Oracle BI Server, an Oracle database, or other supported databases. BI Publisher provides a Query Builder that enables you to build your SQL query graphically. For information on supported databases, see System Requirements and Certification.
Use data tables residing in a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. The Excel spreadsheet can be either stored in a file directory set up as a data source by your administrator; or you can upload it directly from a local source to the data model.
Issue a query against your LDAP repository to retrieve user data. You can report on this data directly, or join this to data retrieved from other sources.
Construct a multidimensional (MDX) query against an OLAP data source.
For the second type, BI Publisher can retrieve column names and data type information from the data source but it cannot process or structure the data. For these data set types, only a subset of the full range of data model editor functions is supported. These data set types are:
If you have integrated your BI Publisher installation with Oracle Business Intelligence Presentation Services, then you can use the data from an Oracle BI Analysis to create your report.
If BI Publisher is integrated with an application using Oracle Application Development Framework, you can use view objects associated with your Enterprise Java Bean data source to retrieve data.
For the third type, BI Publisher retrieves data that has been generated and structured at the source and no additional modifications can be applied by the data model editor:
Use an RSS feed off the Web that returns XML.
Supply the Web service WSDL to BI Publisher and then define the parameters in BI Publisher to use a Web service to return data for your report.
Use an existing XML data file stored in a directory that has been set up by your Administrator.
Following is the process overview for creating a data model:
| Step | Reference |
|---|---|
| Launch the Data Model Editor. | Launching the Data Model Editor |
| Set properties for the data model. (Optional) | Setting Data Model Properties |
| Create the data sets for the data model. | Creating Data Sets |
| Define the data output structure. (Optional) | Structuring Data |
| Define the parameters to pass to the query, and define lists of values for users to select parameter values. (Optional) | Adding Parameters and Lists of Values |
| Define Event Triggers. (Optional) | Defining Event Triggers |
| (Oracle Applications Only) Define Flexfields. (Optional) | Defining Flexfields |
| Test your data model and add sample data. | Testing Data Models and Generating Sample Data |
| Add a bursting definition. (Optional) | Adding Bursting Definitions |
Launch the Data Model Editor from the Home page or from the global header in one of the following ways:
On the global header:
Click New and then click Data Model to open the Data Model Editor.
From the Home page:
Under the Create region, click Data Model.
The following figure shows the Properties pane of the data model editor interface:
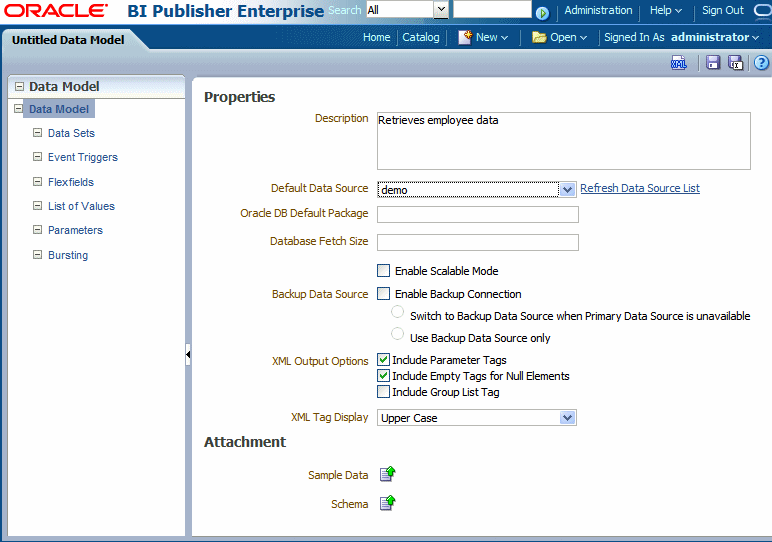
The Data Model Editor is designed with a component pane on the left and work pane on the right. Selecting a component on the left pane will launch the appropriate fields for the component in the work area.
The toolbar provides the following functions:
Launches the XML output page to run your data model definition and view or save the XML output.
Save / Save As
Choose Save to save your work in progress to the existing data model object or choose Save As to save the data model as a new object in the catalog.
Help
View online help for the data model editor.
Enter the following properties for your data model:
Description (optional) - the description you enter here displays in the catalog. This description is translatable.
Default Data Source - select the data source from the list. Data models can include multiple data sets from one or more data sources. The default data source you select here will be presented as the default for each new data set you define. Select Refresh Data Source List to see any new data sources added since your session was initiated.
Oracle DB Default Package - if you define a query against an Oracle database, you can include before or after data triggers (event triggers) in your data model. Event triggers make use of PL/SQL packages to execute RDBMS level functions. For data models that include event triggers or a PL/SQL group filter, you must enter a default PL/SQL package here. The package must exist on the default data source.
Database Fetch Size - sets the number of rows fetched at a time through the JDBC connection. This value will override the value set in the system properties. See Setting Server Configuration Properties, Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Publisher. If neither this value nor the server setting is defined, a default value of 300 will be used.
Enable Scalable Mode - processing large data sets requires the use of large amounts of RAM. To prevent running out of memory, activate scalable mode for the data engine. In scalable mode, the data engine takes advantage of disk space when it processes the data.
Backup Data Source - if you have set up a backup database for this data source, select Enable Backup Connection to enable the option; then select when you want BI Publisher to use the backup.
If you only want to use the backup data source when the primary is down, select Switch to Backup Data Source when Primary Data Source is unavailable.
If you want BI Publisher to always use the backup data source when executing this data model, select Use Backup Data Source Only. Using the backup database may enhance performance.
Note that this feature requires that a backup data source has been enabled for the selected data source. For more information see About Backup Data Sources, Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Publisher.
These options define characteristics of the XML data structure. Note that any changes to these options can impact layouts already built on the data model.
Include Parameter Tags - if you define parameters for your data model, select this box to include the parameter values in the XML output file. See Adding Parameters and Lists of Values for information on adding parameters to your data model. Enable this option when you want to use the parameter value in the report.
Include Empty Tags for Null Elements - select this box to include elements with null values in your output XML data. When you include a null element, then a requested element that contains no data in your data source will be included in your XML output as an empty XML tag as follows: <ELEMENT_ID\>. For example, if the element MANAGER_ID contained no data and you chose to include null elements, it would appear in your data as follows: <MANAGER_ID /> . If you do not select this option, no entry will appear for MANAGER_ID.
Include Group List Tag - (This property is for 10g backward compatibility and Oracle Report migration.) Select this box to include the rowset tags in your output XML data. If you include the group list tags, then the group list will appear as another hierarchy within your data.
XML Tag Display - choose whether to generate the XML data tags in upper case, in lower case, or to follow the definition you supplied in the data structure.
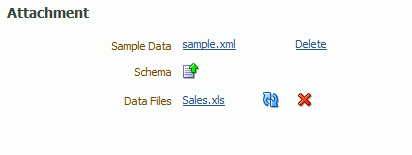
The Attachment region of the page displays data files that you have uploaded or attached to the data model.
After you build your data model, it is required that you attach a small, but representative set of sample data generated from your data model. The sample data will be used by BI Publisher's layout editing tools. Using a small sample file helps improve performance during the layout design phase.
The Data Model Editor provides an option to generate and attach the sample data. See Testing Data Models and Generating Sample XML Data.
The Data Model Editor enables you to attach sample schema to the data model definition. The schema file is not used by BI Publisher, but can be attached for developer reference. The Data Model Editor does not support schema generation.
If you have uploaded a local Microsoft Excel file as a data source for this report, the file will display here. Use the refresh button to refresh this file from the local source. For information on uploading an Excel file to use as a data source, see Defining a Microsoft Excel File as a Data Set Type.
The following figure shows the Attachments region with sample data and data files attached:
![]()
Copyright © 2010, 2011, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.