10g (9.0.4)
Part Number B10425-01
Home | Contents |
Index |
| Oracle Application Server 10g Migrating from WebLogic 10g (9.0.4) Part Number B10425-01 |
|
This chapter provides the information you need to migrate Enterprise JavaBean components from WebLogic Server to Oracle Application Server. It addresses the migration of simple EJB JARs, as well as J2EE web applications in the form of EAR files or in an exploded directory format.
This chapter contains these topics:
Migrating Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) from WebLogic Server to Oracle Application Server is straightforward, requiring little or no code changes to the EJBs migrated. Both application servers support the EJB 2.0 specification.
All EJBs written and designed to the EJB 2.0 specifications should work correctly and require minimal migration effort. The primary effort goes into configuring and deploying the applications in the new environment. Only in cases where proprietary extensions are used will the migration effort get complex.
In this chapter we cover the migration of EJBs deployed in the form of EAR files or in an exploded directory format.
Since both WebLogic Server and Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE (OC4J) have implemented the same versions of the Enterprise JavaBeans specifications, there are no differences between the two in the core areas. The following table summarizes the EJB features available from both application servers:
There are two specific facts that reflect the significant performance advantages in using OC4J's container-managed persistence (CMP) implementation compared to WebLogic Server's implementation:
ejbStore only when necessary. WebLogic Server does not provide such automatic detection requiring a user to code is-modified methods which the WebLogic Server container uses to know whether or not to do the ejbStore operation.
where clause string in WebLogic Server and this results in doing unnecessary full table scans.
Application server clustering essentially means the use of a group of application servers that coordinate their actions in order to provide scalable, highly available services in a transparent manner.
From a comparative point of view, Oracle Application Server's J2EE container provides the following facilities:
In contrast, it is much more complex to configure WebLogic Server clusters with load balancing either with multiple instances on one machine or on multiple machines. For instance, if you indicate that your EJBs will be used in a cluster, then you need to specify it during the time the EJB stubs are created using ejbc, which then results in the creation of special cluster-aware classes that will be used for deployment. Overall, Oracle Application Server's J2EE container, together with other Oracle Application Server components, provide a more robust clustering architecture with better ease-of-use.
ejbStore(). The appropriate isolation mode will be selected, depending on whether the state of the bean can be updated by external systems, such as non-EJB applications using SQL.
WebLogic Server provides a similar set of features.
One of the key distinguishing features of OC4J is the seamless integration with Single Sign On (SSO) and Oracle Internet Directory (OID). This is achieved through Oracle's implementation of the Java Authentication and Authorization Service (JAAS) standard. See Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE User's Guide and Oracle Application Server 10g Security Guide.
The following are additional notes on the WebLogic Server EJB implementation:
weblogic-ejb-jar.xml. For OC4J, orion-ejb-jar.xml is created by the OC4J container for internal purposes. Developers have the ability to modify this file, if needed, but it is not necessary for developers to create this file. Hence, OC4J has a simpler process for deployment of EJBs.
One of the goals of the EJB initiative is to deliver component portability between different environments not only at source code level, but also at a binary level, to ensure portability of compiled, packaged components. While it is true that EJBs do offer portability, there are still a number of non portable, implementation-specific aspects that need to be addressed when migrating components from one platform to another. Typically, an EJB component requires low level interfaces with the container in the form of stub and skeleton classes that will need to stay implementation-specific. In effect, a clear partitioning between portable and non portable elements of an EJB component can be drawn.
Portable EJB elements include:
Implementation-specific elements include:
The tasks involved in migrating EJBs are best analyzed by looking at the steps required for deploying EJBs to an EJB container:
We can address the migration tasks along the same lines.
The deployment process starts with a JAR file or a J2EE standard deployment directory that contains the compiled EJB interfaces and implementation classes created by the EJB provider. There should also be an EJB-compliant ejb-jar.xml file that describes the bundled EJB(s). The ejb-jar.xml file and other required XML deployment files, typically the vendor-specific deployment descriptors, must reside in a top level META-INF directory of the JAR file or deployment directory as follows:
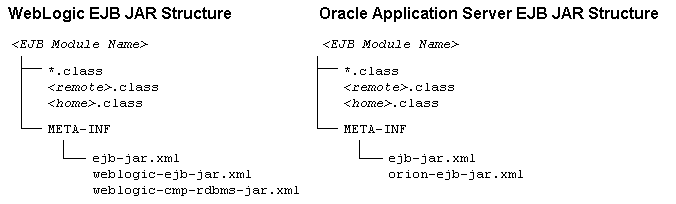
You would have first created and configured the WebLogic Server-specific and mandatory deployment descriptor, weblogic-ejb-jar.xml, and then added the file to the deployment file or directory. The weblogic-ejb-jar.xml file is used for specifying caching, clustering, and performance behavior.
If you were deploying an entity EJB that used container managed persistence, you would have also included an additional deployment file for specifying the O-R mapping details, or, in other words, the RDBMS-based persistence services in a file called weblogic-cmp-rdbms-jar.xml. A separate file would have been required for each bean that used RDBMS persistence.
In the case of OC4J, only one file is required. Via Application Server Control, the OC4J-specific and mandatory deployment descriptor, orion-ejb-jar.xml, is created and added to the deployment file or directory. The orion-ejb-jar.xml file is used for defining caching, clustering, and performance behavior. The details on O-R mapping or the RDBMS-based persistence services are also specified in the orion-ejb-jar.xml file. This is different from WebLogic Server where two separate files were required.
The next step after compiling the EJB classes and adding the required XML deployment descriptors (the J2EE deployment descriptor as well as the vendor-specific deployment descriptors) is generation of the container classes that are used to access the EJB. The container classes include implementation of the external interfaces (home and remote) that clients use, as well as the classes that the application server uses, for the internal representation of the EJBs.
In WebLogic Server, you would have used the ejbc compiler to generate container classes according to the deployment properties specified in the WebLogic Server-specific XML deployment files. For example, if you indicate that your EJBs are to be used in a cluster, ejbc creates special cluster-aware classes that will be used for deployment. You can also use ejbc directly from the command line by supplying the required options and arguments.
Once the container classes have been generated, you need to package the classes into a JAR or EAR file and deploy the classes using the console GUI.
For OC4J, explicit compilation is not required. The EJB JAR file is packaged into a EAR file (together with a WAR file, if any). Then, you can use the Application Server Control GUI to specify the EAR file for deployment. The container classes are generated for OC4J and any J2EE Web application in the EAR file is bound to the OC4J container. In lieu of the Application Server Control, you can also use the dcmctl command to deploy the EAR file. Refer to Distributed Configuration Management Reference Guide for more information.
The final step in deploying an EJB involves loading the generated container classes into WebLogic Server. However, you can prompt WebLogic Server to automatically load EJB classes by starting WebLogic Server. This places the EJB in the deployment directory where it is automatically deployed when the server is started.
Similarly, you can specify classes belonging to an application to be loaded when OC4J starts by specifying the auto-start="true" parameter in the <application> tag in server.xml.
EAR and JAR files containing EJBs which are deployed in WebLogic Server can be migrated to Oracle Application Server. However, you should unarchive and rearchive the EAR file to ensure its contents are complete and that the XML descriptors have the correct entries. Use the following points as a guideline:
web.xml. If the client is standalone, the names should be specified in application-client.xml.
application-client.jar, should be archived into a JAR file, which in turn should be archived into the EAR file where the EJBs are.
application.xml.
dcmctl.
ejbc, rmic, or other such facilities into the client application. The OC4J EJB container generates EJB stubs on demand as it needs them.
EJB applications can also be deployed as a collection of files that use a standard directory structure defined in the J2EE specification. This type of deployment deploys applications in an exploded directory format. Deploying an EJB application in exploded directory format is done most often whilst developing your application and only for standalone OC4J instances. This is because the exploded directory format is more suitable for developers to modify source files and test the application quickly. In Oracle Application Server production environments, however, the application should be packaged in a EAR file and deployed using Application Server Control or dcmctl.
When deploying an exploded directory structure to WebLogic Server, you would have copied the top level directory containing an EJB application in exploded directory format into the mydomain/config/applications/ directory of your WebLogic Server distribution (where mydomain is the name of your WebLogic Server domain). Once copied, WebLogic Server automatically deploys the EJB application.
For OC4J, copy the top level directory containing the EJB application in exploded directory format into the following directory in your OC4J installation:
UNIX:
<ORACLE_HOME>/j2ee/home/applications/
Windows:
<ORACLE_HOME>\j2ee\home\applications\
Then, modify the default J2EE application deployment descriptor, server.xml, located in the <ORACLE_HOME>/j2ee/home/config/ directory in UNIX, or <ORACLE_HOME>\j2ee\home\config\ in Windows, to include your EJB module.
In WebLogic Server, if a file is modified using the administration console, or otherwise, it requires a server restart before the updated configuration is picked up. In the case of OC4J, the timestamp change for server.xml will cause OC4J to effect the changes in the XML file.
There are two deployment descriptors that are used to configure and deploy EJBs. The first deployment descriptor, ejb-jar.xml, is defined in the EJB specifications and provides a standardized format that describes an EJB application. The second deployment descriptor is a vendor-specific deployment descriptor that maps resources defined in the ejb-jar.xml file to resources in the application server. It is also used to define other aspects of the EJB container such as EJB behavior, caching, and vendor-specific features.
The WebLogic Server specific deployment descriptors are weblogic-ejb-jar.xml and weblogic-cmp-rdbms-jar.xml, and the OC4J-specific deployment descriptor is orion-ejb-jar.xml.
A typical J2EE application directory structure would look like this:

The WebLogic Server-specific deployment descriptor, weblogic-ejb-jar.xml, defines EJB deployment descriptor DTDs which are unique to WebLogic Server. The DTD for weblogic-ejb-jar.xml includes elements for enabling stateful session EJB replication, configuring entity EJB locking behavior, and assigning JMS Queue and Topic names for message-driven beans.
Elements configured in the EJB weblogic-ejb-jar.xml include:
The WebLogic Server-specific deployment descriptor, weblogic-cmp-rdbms-jar.xml, defines deployment properties for an entity EJB that uses WebLogic Server RDBMS-based persistence services.
Each weblogic-cmp-rdbms-jar.xml defines the following persistence options:
The OC4J-specific deployment descriptor, orion-ejb-jar.xml, contains extended deployment information for session beans, entity beans, message driven beans, and security.
An entity EJB can save its state in any transactional or non transactional persistent storage (bean-managed persistence), or it can ask the container to save its non-transient instance variables automatically (container-managed persistence). WebLogic Server and OC4J allow both choices and a mixture of the two.
In the case of an EJB that uses container-managed persistence, the weblogic-ejb-jar.xml or the orion-ejb-jar.xml deployment descriptor file specifies the type of persistence services that an EJB uses. In the case of WebLogic Server, the automatic persistence services requires the use of additional deployment files to specify their deployment descriptors, and to define entity EJB finder methods. WebLogic Server RDBMS-based persistence services obtain deployment descriptors and finder definitions from a particular bean using the bean's weblogic-cmp-rdbms-jar.xml file. This configuration file must be referenced in the weblogic-ejb-jar.xml file. In the case of OC4J, the type of persistence service as well as the details regarding the RDBMS-based persistence services are configured and obtained from the same deployment descriptor - orion-ejb-jar.xml.
Some of the attributes such as Development Mode are unique to OC4J.
For EJBs that use RDBMS persistence, WebLogic Server provides a way to write dynamic finders. The EJB provider writes the method signature of a finder in the EJBHome interface, and defines the finder's query expressions in the ejb-jar.xml deployment file. The ejbc compiler creates implementations of the finder methods at deployment time, using the queries in ejb-jar.xml.
The key components of a finder for RDBMS persistence are:
EJBHome
ejb-jar.xml
weblogic-cmp-rdbms-jar.xml
OC4J simplifies the whole process by automatically generating the finder methods.
Specifying the findByPrimaryKey method is easy to do in OC4J. All the fields for defining a simple or complex primary key are specified within the ejb-jar.xml deployment descriptor. To define other finder methods in a CMP entity bean, do the following:
orion-ejb-jar.xml file
In WebLogic Server 5.1 and 6.0, each finder query stanza in the weblogic-cmp-rdbms-jar.xml file had to include a WLQL string that defines the query used to return EJBs. These releases of WebLogic Server implemented an EJB 1.1 container and did not support standardized EJB QL.
With the emergence of EJB Query Language, which is a standard based on the EJB 2.0 specification, use of WLQL is deprecated. With WebLogic Server 7.0, its EJB container is EJB 2.0 compliant and supports EJB QL. This EJB container additionally provides a WLQL extension to EJB QL. This extension is proprietary to WebLogic Server.
Oracle Application Server provides complete support for EJB QL including the following features:
For more information on EJB QL in Oracle Application Server, refer to Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Enterprise JavaBeans Developer's Guide.
In WebLogic Server, in addition to the new ejb-jar.xml elements, the weblogic-ejb-jar.xml file includes only one new message-driven-descriptor stanza to associate the message-driven bean with an actual destination in WebLogic Server. The XML element is destination-jndi-name.
In OC4J, to create a message-driven bean, you perform the following steps:
Destination type (queue or topic) in the OC4J JMS XML file, jms.xml.
Destination type to the message-driven bean in the OC4J-specific deployment descriptor, orion-ejb-jar.xml
data-sources.xml.
application.xml file, create an EAR file, and deploy the EJB in OC4J.
Security can be handled by the application server, or it can be incorporated programmatically into your EJB classes. Both WebLogic Server and OC4J provide similar support for security such as authentication, authorization, and digital certificates.
Oracle Application Server provides clustering features that are superior to WebLogic Server in performance as well as ease of use. Further, migrating cluster-aware applications from WebLogic Server to OC4J is straightforward.
The WebLogic Server EJB container can replicate the state of an EJB across clustered WebLogic Server instances.
Replication support for stateful session EJBs is transparent to clients of the EJB. When a stateful session EJB is deployed, WebLogic Server creates a cluster-aware EJBHome stub and a replica-aware EJBObject stub for the stateful session EJB. The EJBObject stub maintains a list of the primary WebLogic Server instance on which the EJB instance runs and the name of a secondary WebLogic Server to use for replicating the bean's state.
Each time a client of the EJB commits a transaction that modifies the EJB's state, WebLogic Server replicates the bean's state to the secondary server instance. Replication of the bean's state occurs directly in memory, for best performance in a clustered environment.
Should the primary server instance fail, the client's next method invocation is automatically transferred to the EJB instance on the secondary server. The secondary server becomes the primary WebLogic Server for the EJB instance, and a new secondary server is used to account for the possibility of additional failovers. Should the EJB's secondary server fail, WebLogic Server enlists a new secondary server instance from the cluster.
By replicating the state of a stateful session EJB, clients are generally guaranteed to have the last committed state of the EJB, even if the primary WebLogic Server instance fails. However, in certain rare failover scenarios, the last committed state may not be available. This can happen when:
EJBHome stub and restart the transaction.
To replicate the state of a stateful session EJB in a WebLogic Server cluster, ensure that the cluster is homogeneous for the EJB class. In other words, deploy the same EJB class to every WebLogic Server instance in the cluster, using the same deployment descriptors. In-memory replication is not supported for heterogeneous clusters.
By default, WebLogic Server does not replicate the state of stateful session EJB instances in a cluster. To enable replication, set the replication type deployment parameter to InMemory in the weblogic-ejb-jar.xml deployment file. For example:
<stateful-session-clustering> ... ... ... <replication-type>InMemory</replication-type> </stateful-session-clustering>
EJB clustering in Oracle Application Server provides EJB load balancing and failover. For Oracle Application Server, the mechanisms used to achieve these are different from HTTP session load balancing and failover. For EJBs, load balancing redirection is performed by the EJB client stubs and state replication for failover is done without using cluster islands (a future release of Oracle Application Server will implement cluster islands for EJBs).
To create an EJB cluster, you need to specify which OC4J nodes are part of the cluster and configure each of them with the same multicast address, username, and password. The EJBs to be clustered can then be deployed to each of these nodes. Configuring all nodes in the cluster with the same multicast username and password allows authentication to all nodes with a single username/password combination. If you use a different username/password combination with the same multicast address, another cluster is actually defined. The Application Server Control provides a user interface to specify the multicast username and password.
Load balancing for EJBs is performed at the EJB client end. The client stubs obtain the addresses of nodes in the cluster in one of two ways: static discovery or dynamic discovery. Once all nodes in the same cluster are known, a client stub selects one at random. Load balancing is performed using a random methodology.
Static and dynamic discovery is performed as follows:
At lookup time, the JNDI addresses of all nodes in the cluster are provided in the lookup URL property. This requires knowledge of the node name and ormi port for each node. For example:
java.naming.provider.url = ormi://serverA:23791/ejb, ormi://serverB:23792/ejb, ormi://serverC:23791/ejb;
For dynamic discovery, at the first lookup made, the first node that is contacted communicates with the other nodes with the same multicast address and username/password. The ormi addresses of these nodes are retrieved and returned to the client stubs, which select one of the addresses at random. To enable dynamic discovery, "lookup:" is inserted before the ormi URL:
ic.lookup("lookup:ormi://serverA:23791/ejb");
Depending on the type of EJB that is clustered, failover in an EJB cluster is achieved by request redirection and state replication.
Load balancing and failover for stateless session EJBs is performed by EJB client stubs by redirecting requests to randomly picked nodes after the nodes have been discovered statically or dynamically. Because of the stateless nature of the EJBs, replication of bean state is not required.
Load balancing for stateful session EJBs is the same as for stateless session EJBs. For failover, state replication is required, and by default, is replicated to all nodes in the cluster at the end of every method call to each EJB instance. Though reliable, this obviously incurs a significant amount of CPU overhead in all the nodes and degrades performance. Hence, two more replication modes are provided to allow replication without compromising performance significantly: JVM termination and stateful session context replication modes.
The JVM termination mode replicates the state of all stateful session EJBs to one other node when the JVM executing these EJBs terminates gracefully. The replication logic uses JDK termination hooks (JDK 1.3 or later is required). This mode is the most performant among all because replication is done only once. However, reliability is not the best as it is dependent on the JVM's ability to shutdown properly.
Stateful session context mode replicates state programatically. An OC4J-proprietary class, com.evermind.server.ejb.statefulSessionContext, is provided to allow you to specify the information to be replicated. By setting this information as parameters for the setAttribute method, this information can be replicated to all nodes in the EJB cluster. Hence, EJB providers have more control on when and what to replicate.
Replication for entity EJBs allows EJB state to be stored in a database. Each time the state of an entity EJB changes, it is updated in the database. The entity EJB that changes the state notifies the other nodes in the cluster that their equivalent entity EJBs are out-of-date. If the node hosting the "up-to-date" EJB fails, the client stub redirects to another node and the out-of-date entity EJB in that node resynchronizes its state with the information in the database.
When EJB clustering is enabled, JNDI namespace replication is also enabled between the OC4J instances that have a role in the EJB cluster. New bindings to the JNDI namespace in one OC4J instance are propagated to other OC4J instances that are participating in the EJB cluster. Rebindings and unbindings are not replicated.
JNDI replication is completed outside the scope of OC4J islands. In other words, multiple islands in an OC4J instance have visibility into the same replicated JNDI namespace. For more information see the Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Services Guide.
|
|
 Copyright © 2003 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|