10g (9.0.4)
Part Number B10322-01
Home |
Solution Area |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE User's Guide 10g (9.0.4) Part Number B10322-01 |
|
Chapter 2, "Configuration and Deployment", discusses basic configuration, development, and deployment of a J2EE application. This chapter discusses both global J2EE service configuration and advanced J2EE application configuration.
This chapter discusses the following topics:
You can configure J2EE services, J2EE applications, and Oracle Application Server clusters with Oracle Enterprise Manager. Some aspects are configured at the OC4J instance level; thus, they provide a global configuration for all deployed applications in the instance. Other aspects are configured at the application level; thus, this type of configuration is local and applicable only to the application.
The following sections provide you with an overview of advanced configuration within Oracle Enterprise Manager for OC4J:
Off of the OC4J Home page, you can configure global services that apply to all applications by drilling down to the Administration page, which allows you to configure the following:
To configure OC4J properties, scroll down to the Instance Properties section and select Server Properties. The General section of this page contains the following fields:

Text description of the illustration general.gif
The following information about the default server properties is displayed in the upper half of the page.
application.xml, which is separate from the application.xml included with each EAR file. This application.xml file is known as the global application.xml file. It defines properties that are used across all deployed applications within this OC4J instance.
In this section, you can modify OC4J server defaults. These are listed below:
global-web-application.xml. If you want it to refer to another XML file, you can change the pointer to this file here. However, this file must conform to the DTD that Oracle specifies. The directory is relative to j2ee/home/config.
If you want to actually modify elements contained within this file, update entries in either the Web Site Properties or Advanced Properties section. These are discussed more in "Configure a Web Site" and "Modifying XML Files Included in the Deployed Application EAR File".
/applications directory. The default directory is where OC4J places modified module deployment descriptors with added defaults. Currently, this location is in the /application-deployments directory. You can change the locations of the default directories in these fields. The directory is relative to j2ee/home/config. See "What Happens When You Deploy?" for more information on the usage of these directories.
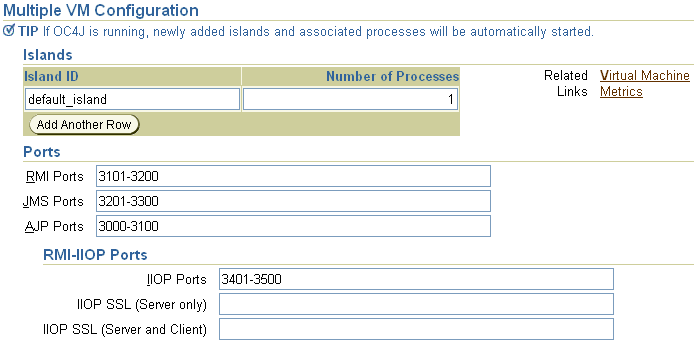
The next section, Multiple VM Configuration, is dedicated as part of the cluster configuration. The following details what each field means; however, the context of how to configure clusters using this section is discussed fully in Chapter 8, "OC4J Clustering".
javac
java'
See "OC4J Command-Line Options and System Properties" for a list of command-line options and system properties.
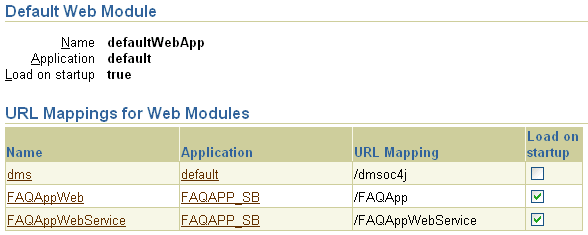
To configure your Web site, select Website Properties in the Instance Properties column on the Administration page.
The Web site page has two sections. In the first section, you can see what is the default Web application. In the second section--URL Mappings for Web Modules--you can specify whether each Web application is to be loaded upon startup. These parameters are discussed in more detail in the Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Servlet Developer's Guide and are stored in the default-web-site.xml file.
You can configure global JSP Container parameters. These apply to all JSPs deployed in this OC4J instance. To configure JSP Container parameters, select JSP Container Properties in the Instance Properties column on the Administration page. This brings you to the following page:
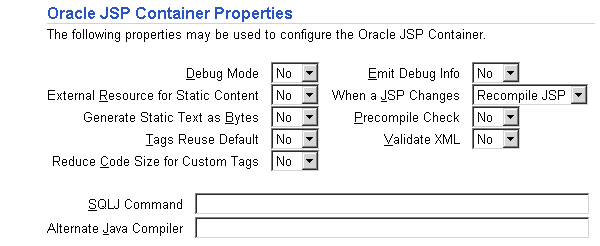
Most of the properties indicated here are described in Chapter 3 of the Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Support for JavaServer Pages Developer's Guide. These properties can be included within the global-web-application.xml file within the <servlet> element.
For clustering servlet or EJBs, you may need to configure replication parameters. See "OC4J Instance Configuration" for details.
In OC4J version 1.0.2.2, you configured the OC4J server and all deployed application parameters through XML files. Since the OC4J server existed on a single node and did not need high availability and clustering management, this worked well. However, with the integration of OC4J with Oracle Application Server, increased enterprise management abilities with clustering and high availability options, all configuration must be accomplished through Oracle Enterprise Manager.
When you select Advanced Properties off of the Administration page, you can modify the OC4J Server XML files. These include the XML files that configure the server and its services. The files that are in this group are server.xml, global-web-application.xml, rmi.xml, jms.xml, and default-web-site.xml. Modify any of these XML files in the Advanced Properties page off of the OC4J Home Page.
Other XML configuration files can be modified in other areas of the Application Server Control.
application.xml, data-sources.xml, the security XML file and oc4j-connectors.xml. To modify these XML files, select Applications off of the OC4J Home Page. On the Applications page, select default. On the default application page, scroll down to the Administration section and choose Advanced Properties.
data-sources.xml, orion-application.xml, and security XML files. To modify these files, drill down to the specific application from the Deployed Applications section on the Applications page. On the specified application screen, scroll down to the Administration section and choose Advanced Properties.
web.xml, orion-web.xml, ejb-jar.xml, and orion-ejb-jar.xml. You can modify parameters only in the OC4J-specific (orion-xxx.xml) XML files. You cannot modify the J2EE XML files, such as web.xml or ejb-jar.xml. For more information on modifying these XML files, see "Modifying XML Files Included in the Deployed Application EAR File".
As an example, the server.xml page is shown. Notice that you can hand edit the XML elements.

If you do not understand the OC4J XML files, see "Overview of OC4J and J2EE XML Files" for a discussion of these files and their relation to each other. Other books in the OC4J documentation set describe the elements within each of these files.
You can configure global or local data sources. A global data source is available to all deployed applications in this OC4J instance. A local data source is configured within the deployed application and can only be used by that application.
See Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Services Guide for a full explanation of how to configure a data source and the elements within the data-sources.xml file.
To configure global data sources, select one of the following off of the OC4J Home Page:
data-sources.xml file.
data-sources.xml on this page. This allows you to add data sources using the XML definitions. This is useful if you have been provided the XML. You can just copy in the already configured data sources.
To configure local data sources, you perform the same selection off of the application page. You drill down to the particular application to which this data source is local. On the application page, choose Data Source under the Resources column. It displays the same data source field page that is discussed in "Data Source Field Page".
To configure a new Data Source, click Add Data Source. This brings you to a page where you can enter all configuration details about the data source. This page is divided up into four sections.
Figure 3-7 shows the General section.
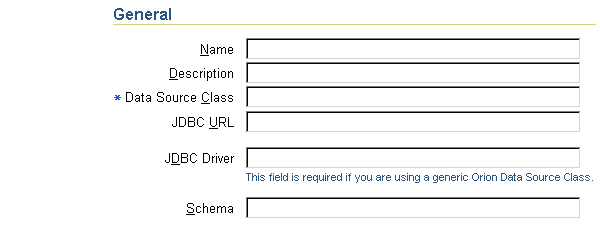
The General section enables you to define the following aspects about a data source:
com.evermind.sql.DriverManagerDataSource, that the data source is instantiated as.
jdbc:oracle:thin:@my-lap:1521:SID.
oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver.
Figure 3-8 shows the username and password.

Username/Password--The username and password used to authenticate to the database that this data source represents. The password can either be entered as clear text, or you can provide a username for an indirect password. For details, see the Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Services Guide.
Figure 3-9 shows the JNDI Locations section.

The JNDI Locations section enables you to define the JNDI location string that the data source is bound with. This JNDI location is used within the JNDI lookup for retrieving this data source.
Figure 3-10 shows the Connection Attributes section.
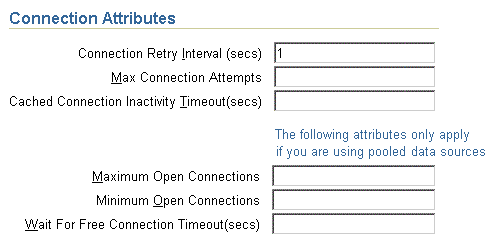
This section enables you to modify connection tuning parameters, including the retry interval, pooling parameters, timeout parameters, and maximum attempt parameter.
Figure 3-11 shows the Properties section for the data source.

If your data source is a third party data source, you may need to set certain properties. These properties would be defined in the third-party documentation. In addition, properties must be set for JTA transactions for the two-phase commit coordinator.
The user manager, employing the user name and password, verifies the user's identity based on information in the user repository. The user manager defines what type of authentication you will be using. It contains your definitions for users, groups, or roles. The default user manager is the JAZNUserManager. You can define a user manager for all applications or for specific applications.
See the Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Security Guide for a full description of OC4J security, including user managers.
JMS can be configured either within the JMS section or directly within the jms.xml file, as follows:
To add Oracle JMS or third-party JMS providers, select JMS Providers under the Application Defaults column on the Administration page. This brings you to the following page:
Click the Add new JMS Provider button to configure each JMS provider, which brings up the following page:
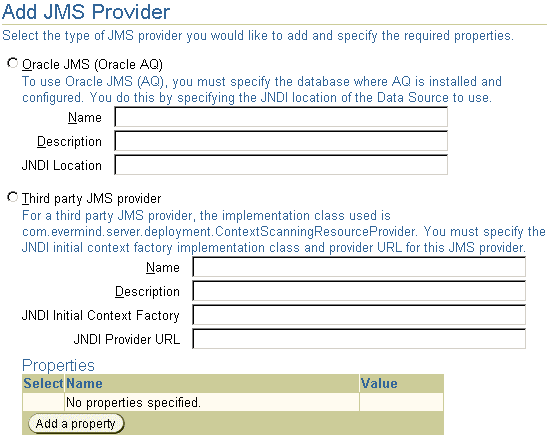
This page enables you to configure either Oracle JMS or a third-party JMS provider. OC4J JMS is always provided and preconfigured, except for the topics and queues, with the OC4J installation.
Once you choose the typs of JMS provider, you must provide the following:
java.naming.factory.initial and java.naming.provider.url, click Add a property. A row is added where you can add the name for each JNDI property and its value.
This only configures the providers; it does not configure the Destination objects (topic, queue, and subscription). See the Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Services Guide or more information on JMS providers.
To configure a JMS provider that is only for a specific application, select the application from the Applications page, scroll down to the Resources column, and select JMS Providers. The screens that appear are the same as for the default JMS provider.
To add queues and topics for OC4J JMS, you can edit the jms.xml file directly as follows: select the Advanced Server Properties section under the Instance Properties column on the Administration page. In this section, choose jms.xml to modify the straight XML file. See the Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Services Guide or descriptions of the elements in the jms.xml file.
To configure Web parameters that apply to all deployed Web applications, select Global Web Module in the Application Defaults column on the Administration page. This brings you to the following page:
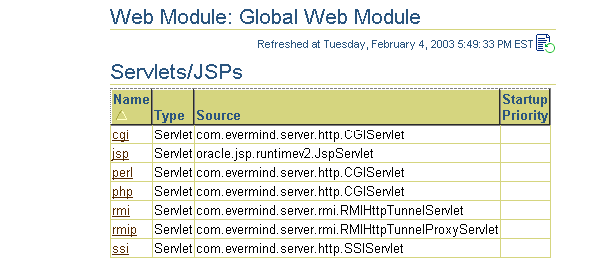
The type of parameters that you can define for Web modules concern mappings, filtering, chaining, environment, and security. Drill down into each of the provided links under the Properties and Security columns to modify these parameters. Each of these parameters are discussed in detail in the Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Servlet Developer's Guide. These parameters are stored in the global-web-application.xml and orion-web.xml files. This guide discusses the elements in these files.
RMI can only be defined within an XML definition. To edit the rmi.xml file, select Advanced Properties under the Instance Properties column on the Administration page. In this section, choose rmi.xml to modify the XML file. See the Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Services Guide for descriptions of the elements in the rmi.xml file.
You can deploy, redeploy, or undeploy a J2EE application that exists in an EAR or WAR file archival format. To deploy an application, click the Deploy EAR File or Deploy WAR File buttons to deploy in the Deployed Applications section on the Applications page.
This starts the deployment wizard that is covered in "Deploying Applications". If you deploy an EAR file, it must contain an application.xml that describes the application modules; if you deploy a WAR file, the application.xml file is created for you automatically.
To undeploy, click the Select radio button for the application and then click the Undeploy button.
To redeploy, click the Select radio button for the application and then click the Redeploy button.
|
Note: You can also deploy, undeploy, or redeploy simple applications with the DCM command. See the Distributed Configuration Management Reference Guide for directions. |
Once you have deployed your application, you can modify most of the parameters for this application. To configure application-specific parameters, do the following:
This page is the initiating point for changing general application configuration as well as configuration specific to a certain part of your deployed application, such as a WAR file.
The following sections provide a brief overview of these configuration options:
If you drill down to the application, scroll down to the Properties column and select the General link, you can configure a multitude of application details, as follows:
As described in "Configure Data Sources" and "Configure Security", you can configure data sources and security either for all deployed applications (global) or only for a specific application (local). See these sections for directions on how to configure your J2EE services for your application.
You can modify only the OC4J-specific XML files of your application after deployment. This includes orion-ejb-jar.xml, orion-web.xml, and orion-application-client.xml. You cannot modify the J2EE XML files, such as web.xml, ejb-jar.xml, and application-client.xml.
In order to modify the OC4J-specific XML files, do the following:
orion-ejb-jar.xml, orion-web.xml, and orion-application-client.xml.
This section contains the following topics:
Each XML file within OC4J exists to satisfy a certain role; thus, if you have need of that role, you will understand which XML file to modify and maintain.
Figure 3-15 illustrates all the OC4J XML files and their respective roles.
These files configure the OC4J server and point to other key configuration files. The settings in the OC4J configuration files are not related to the deployed J2EE applications directly, but to the server itself.
orion-" prefix. In addition, the following are global configuration files for all components in the application:
application.xml as the global application configuration file that contains common settings for all applications in this OC4J instance.
orion-application.xml file contains OC4J-specific global application information for all applications in this OC4J instance.
global-web-application.xml file contains OC4J-specific global Web application configuration information that contains common settings for all Web modules in this OC4J instance.
oc4j-connectors.xml file contains global connector configuration information.
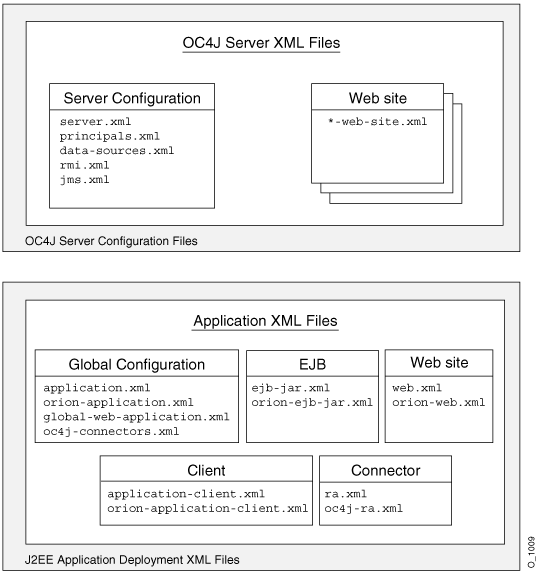
Table 3-1 describes the role and function for each XML file that was displayed in the preceding figure.
Some of these XML files are interrelated. That is, some of these XML files reference other XML files--both OC4J configuration and J2EE application (see Figure 3-17).
Here are the interrelated files:
server.xml--contains references to the following:
*-web-site.xml files for each Web site for this OC4J server, including the default default-web-site.xml file.
jazn-data.xml and data-sources.xml which are defined in the global application.xml, shown in Figure 3-15
application.xml file for each J2EE application that has been deployed in OC4J
default-web-site.xml--references applications by name, as defined in the server.xml file. And this file references an application-specific EAR file.
application.xml--contains references to the jazn-data.xml and data-sources.xml files.
The server.xml file is the keystone that contains references to most of the files used within the OC4J server. Figure 3-16 shows the XML files that can be referenced in the server.xml file:
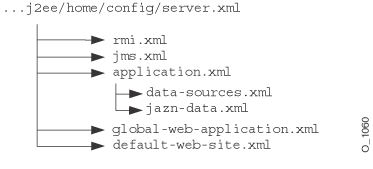
Figure 3-17 demonstrates how the server.xml points to other XML configuration files. For each XML file, the location can be the full path or a path relative to the location of where the server.xml file exists. In addition, the name of the XML file can be any name, as long as the contents of the file conform to the appropriate DTD.
<rmi-config> tag denotes the name and location of the rmi.xml file.
<jms-config> tag denotes the name and location of the jms.xml file.
<global-application> tag denotes the name and location of the global application.xml file.
<global-web-app-config> tag denotes the name and location of the global-web-application.xml file.
<web-site> tag denotes the name and location of one *-web-site.xml file. Since you can have multiple Web sites, you can have multiple <web-site> entries.
In addition to pointing to the OC4J server configuration files, the server.xml file describes the applications that have been deployed to this OC4J server. Each deployed application is denoted by the <application> tag.
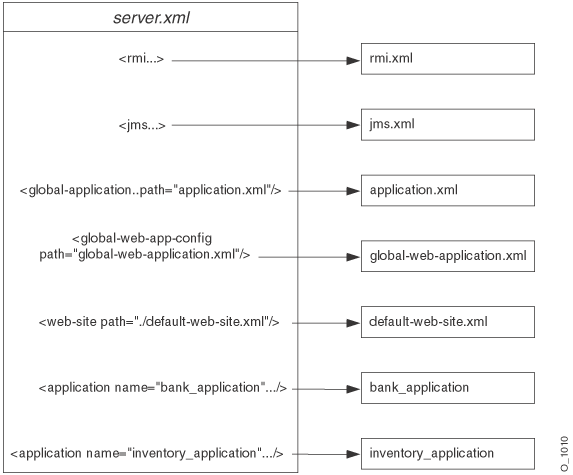
Other tags for server.xml are described in "Elements in the server.xml File".
When you become more proficient with OC4J and deploying applications, you should acquaint yourself with what OC4J does for you. The following sections help you understand these tasks:
When you deploy your application, the following occurs:
OC4J opens the EAR file and reads the descriptors.
application.xml that exists in the EAR file. The application.xml file lists all of the modules contained within the EAR file. OC4J notes these modules and initializes the EAR environment.
application-deployments/ directory. These are the descriptors that OC4J uses when starting and restarting your application. But do not modify these descriptors. Always change your deployment descriptors in the "master" location.
applications/ directory. You can change the "master" directory in the Server Properties page off of the OC4J Home Page. In the General section, modify the Application Directory field to the new location of the "master" directory. The location of the directory is relative to /j2ee/home/config.
server.xml file with the notation that this application has been deployed.
After deployment, you can see your application configuration in the server.xml and default-web-site.xml files, as follows:
server.xml, each existing application contains a line with an <application name=... path=... auto-start="true" /> entry. The auto-start attribute designates that you want this application automatically started when OC4J starts. The path is either the location of the EAR file to be deployed or the exploded directory where the applicatoin has been built. See "Basic Deployment" or "Building and Deploying Within a Directory" for more information.
default-web-site.xml, a <web-app...> entry exists for each Web application that is bound to the Web site upon OC4J startup. Because the name attribute is the WAR filename (without the .WAR extension), there is one line for each WAR file included in your J2EE application.
For each Web application binding included in a WAR file, the following line has been added:
<web-app application="myapp" name="myapp-web" root="/myapp" />
application attribute is the name provided in the server.xml as the application name.
name attribute is the name of the WAR file, without the .WAR extension.
root attribute defines the root context for the application off of the Web site. For example, if you defined your Web site as "http://<ohs_host>:7777/j2ee", then to initiate the application, point your browser at "http://<ohs_host>:7777/j2ee/myapp".
If you have libraries that you want to share among applications, add a <library> element in the global application.xml file, indicating the directory where you are placing the libraries, as follows:
Windows:
<library path="d:\oc4j\j2ee\home\applib\"/>
UNIX:
<library path="/private/oc4j/j2ee/home/applib/"/>
For each directory to be included, use a separate <library> element on a separate line, as follows:
<library path="/private/oc4j/j2ee/home/applib/"/> <library path="/private/oc4j/j2ee/home/mylibrary/"/>
As a default, a <library> element exists in the global application.xml file with the j2ee/home/applib directory. Instead of modifying the <library> element to contain other directories, you could move your libraries into the applib directory. However, note that adding libraries to this directory increases the size of OC4J and effects the performance as all libraries are searched for unknown classes. Use this with discretion.
If you can, you should keep your shared libraries local to the application through the orion-application.xml file deployed with the application. You can add <library> elements in the orion-application.xml file for the application to indicate where the libraries are located, which are used only within the application.
Incoming client requests use one of three protocols: AJP, HTTP, or RMI. AJP and HTTP are used for HTTP requests. AJP is used between the OHS and OC4J components. HTTP is used for HTTP requests directed past OHS to OC4J. RMI is used for incoming EJB requests.
All HTTP requests, whether through OHS or directly to OC4J, must have a listener configured in an OC4J Web site. You can have two Web sites for each OC4J instance: one for each protocol type. That is, one Web site is only for AJP requests and the other is for HTTP requests. You cannot have one Web site listen for both types of protocols. Thus, OC4J provides two Web site configuration files:
default-web-site.xml--This is the AJP protocol listener and the default for most HTTP requests that use Oracle Application Server. After installation, the Oracle HTTP Server front-end forwards incoming HTTP requests over the AJP port. The OC4J Web server configuration file (default-web-site.xml) indicates the AJP listener port. The default-web-site.xml file defines the default AJP port as zero. This enables OC4J and the Oracle HTTP Server to negotiate a port upon startup. The range of port values that the AJP port can be is configured in the OPMN configuration. See the High Availability chapter in the Oracle Application Server 10g Administrator's Guide for more information on OPMN.
The following shows the entry in the default-web-site.xml for the default AJP listener:
<web-site host="oc4j_host" port="0" protocol="ajp13"
display-name="Default OC4J WebSite">
You can configure the AJP default Web site protocol in two places: Website Properties or Advanced Properties off of the OC4J Home Page.
http-web-site.xml--This is the HTTP protocol listener. If you want to bypass OHS and go directly to OC4J, you use the port number defined in this file. However, you must be careful. The AJP port is chosen at random every time OC4J is started. If it chooses the same port number that is hard-coded in this XML file, there will be a conflict. If you use this method for incoming requests, verify that the port number you choose is outside of the range for AJP port numbers, which is defined in the OPMN configuration.
The default HTTP port is 7777. The following shows the entry in the http-web-site.xml for an HTTP listener with a port number of 7777:
<web-site host="oc4j_host" port="7777" protocol="http"
display-name="HTTP OC4J WebSite">
You access the http-web-site.xml file only in the Advanced Properties on the OC4J Home Page.
The RMI protocol listener is set up by OPMN in the RMI configuration--rmi.xml. It is separate from the Web site configuration. EJB clients and the OC4J tools access the OC4J server through a configured RMI port. OPMN designates a range of ports that the RMI listener could be using. When you use the "opmn:ormi://" string in the lookup, the client retrieves automatically the assigned RMI port. See "Accessing the EJB" in the EJB Primer chapter in Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Enterprise JavaBeans Developer's Guide.
The mod_oc4j module in the Oracle HTTP Server is configured at install time to direct all j2ee/ context bound applications to the OC4J server. If you want to use a different context, such as pubs/, you can add another mount for this context in the mod_oc4j.conf configuration file.
To modify this file, drill down to the Oracle HTTP Server Page and select mod_oc4j.conf. The file is presented for edits in the right-hand frame.
Oc4jMount /j2ee/* OC4Jworker
OC4Jworker, then both lines would be as follows:
Oc4jMount /j2ee/* OC4Jworker Oc4jMount /pubs/* OC4Jworker
Then all incoming requests for the pubs/ context will be directed to the OC4J server. Note that when you deploy an application using the deployment wizard, the wizard automatically adds a mount point as described here for your URL mapping.
See the Oracle HTTP Server Administrator's Guide for complete details on the mod_oc4j module configuration.
When developing applications, you want to quickly modify, compile, and execute your classes. OC4J can automatically deploy your applications as you are developing them within an expanded directory format. OC4J automatically deploys applications if the timestamp of the top directory, noted by <appname> in Figure 3-18, changes. This is the directory that server.xml knows as the "master" location.
The application must be placed in the "master" directory in the same hierarchical format as necessary for JAR, WAR, and EAR files. For example, if <appname> is the directory where your J2EE application resides, Figure 3-18 displays the necessary directory structure.
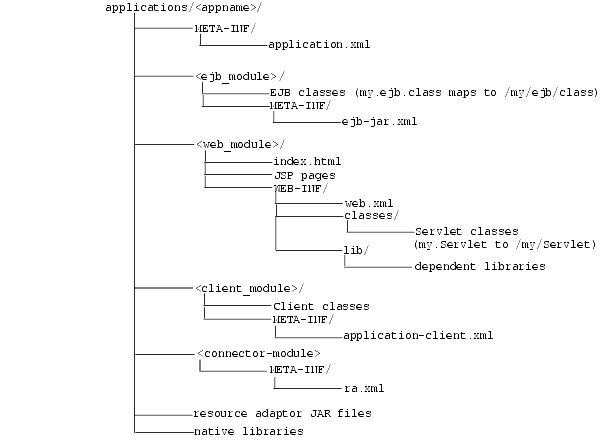
To deploy EJB or complex J2EE applications in an expanded directory format, complete the following steps:
j2ee/home/applications/<appname>/. The directory structure below <appname> is similar to that used within an EAR file, as follows:
<ejb_module>/, <web_module>/, <client_module>/, and <connector_module>/.
server.xml, application.xml, and *-web-site.xml files. The server.xml and *-web-site.xml files are located in j2ee/home/config directory, while the application.xml is under j2ee/home/applications/<appname>/META-INF directory. Modify these files as follows:
server.xml, add a new or modify the existing <application name=... path=... auto-start="true" /> element for each J2EE application. The path points to the "master" application directory. In Figure 3-18, this is j2ee/home/applications/<appname>/.
You can specify the path in one of two manners:
In the example in Figure 3-18, if <appname> is "myapp", then the fully-qualified path is as follows:
<application_name="myapp" path="/private/j2ee/home/applications/myapp" auto-start="true" />
server.xml file exists to where the parent directory lives.
In the example in Figure 3-18, if <appname> is "myapp", then the relative path is as follows:
<application_name="myapp" path="../applications/myapp" auto-start="true" />
application.xml, modify the <module> elements to contain the directory names for each module--not JAR or WAR files. You must modify the <web-uri>, the <ejb>, and the <client> elements in the application.xml file to designate the directories where these modules exist. The path included in these elements should be relative to the "master" directory and the parent of the WEB-INF or META-INF directories in each of these application types.
For example, if the <web_module>/ directory in Figure 3-18 was "myapp-web/", then the following example designates this as the Web module directory within the <web-uri> element as follows:
<module> <web> <web-uri>myapp-web</web-uri> </web> </module>
*-web-site.xml file, add a <web-app...> element for each Web application. This is important, because it binds the Web application within the Web site. The application attribute value should be the same value as that provided in the server.xml file. The name attribute should be the directory for the Web application. Note that the directory path given in the name element follows the same rules as for the path in the <web-uri> element in the application.xml file.
To bind the"myapp" Web application, add the following:
<web-app application="myapp" name="myapp-web" root="/myapp" />
mod_oc4j.conf configuration file. Based on the root="/myapp" in this example, the mod_oc4j.conf should be updated to contain the following lines:
Oc4jMount /myapp home Oc4jMount /myapp/* home
You can develop classes that are called after OC4J initializes or before OC4J terminates. Startup classes can start services and perform functions after OC4J initiates; shutdown classes can terminate these services and perform functions before OC4J terminates. The oc4j.jar must be in the Java CLASSPATH when you compile these classes.
OC4J deploys and executes the OC4J startup and shutdown classes based on configuration of these classes in the server.xml file.
Startup classes are executed only once after OC4J initializes. They are not re-executed everytime the server.xml file is touched. Your startup class implements the com.evermind.server.OC4JStartup interface that contains two methods--preDeploy and postDeploy--in which you can implement code for starting services or performing other initialization routines.
preDeploy method executes before any OC4J application initialization.
postDeploy method executes after all OC4J applications initialize.
Each method requires two arguments--a Hashtable that is populated from the configuration and a JNDI Context to which you can bind to process values contained within the Context. Both methods return a String, which is currently ignored.
Once created, you must configure the startup class within the <startup-classes> element in the server.xml file. You access this file by selecting Advanced Properties on the OC4J home page. Each OC4JStartup class is defined in a single <startup-class> element within the <startup-classes> element. Each <startup-class> defines the following:
com.evermind.server.OC4JStartup interface.
String, which OC4J takes, which are provided within the input Hashtable argument. The names for the key-value pairs must be unique, as JNDI is used to bind each value to its name.
In the <init-library path="../[xxx]" /> element in the server.xml file, configure the directory where the startup class resides, or the directory and JAR filename where the class is archived. The path attribute can be fully-qualified or relative to j2ee/home/config.
The configuration for the TestStartup class is contained within a <startup-class> element in the server.xml file. The configuration defines the following:
failure-is-fatal attribute is true, so that an exception causes OC4J to exit.
execution-order is 0, so that this is the first startup class to execute.
String, which will be populated in the Hashtable, of the following:
"oracle.test.startup" "true" "startup.oracle.year" "2002"
Thus, configure the following in the server.xml file to define the TestStartup class:
<startup-classes> <startup-class classname="TestStartup" failure-is-fatal="true"> <execution-order>0</execution-order> <init-param> <param-name>oracle.test.startup</param-name> <param-value>true</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>startup.oracle.year</param-name> <param-value>2002</param-value> </init-param> </startup-class> </startup-classes>
The container provides the two initialization kay-value pairs within the input Hashtable parameter to the startup class.
The following example shows TestStartup, which implements the com.evermind.server.OC4JStartup interface. The preDeploy method retrieves the key-value pairs from the Hashtable and prints them out. The postDeploy method is a null method. The oc4j.jar must be in the Java CLASSPATH when you compile TestStartup.
import com.evermind.server.OC4JStartup; import javax.naming.*; import java.util.*; public class TestStartup implements OC4JStartup { public String preDeploy(Hashtable args, Context context) throws Exception { // bind each argument using its name Enumeration keys = args.keys(); while(keys.hasMoreElements()) { String key = (String)keys.nextElement(); String value = (String)args.get(key); System.out.println("prop: " + key + " value: " + args.get(key)); context.bind(key, value); } return "ok"; } public String postDeploy(Hashtable args, Context context) throws Exception { return null; } }
Assuming that the TestStartup class is archived in "../app1/startup.jar", modify the <init-library> element in the server.xml file as follows:
<init-library path="../app1/startup.jar" />
When you start OC4J, the preDeploy method is executed before any application is initialized. OC4J populates the JNDI context with the values from the Hashtable. If TestStartup throws an exception, then OC4J exits since the failure-is-fatal attribute was set to TRUE.
Shutdown classes are executed before OC4J terminates. Your shutdown class implements the com.evermind.server.OC4JShutdown interface that contains two methods--preUndeploy and postUndeploy--in which you can implement code for shutting down services or perform other termination routines.
preUndeploy method executes before any OC4J application terminates.
postUndeploy method executes after all OC4J applications terminates.
Each method requires two arguments--a Hashtable that is populated from the configuration and a JNDI Context to which you can bind to process values contained within the Context.
The implementation and configuration is identical to the shutdown classes as described in "OC4J Startup Classes" with the exception that the configuration is defined within the <shutdown-classes> and <shutdown-class> elements and there is no failure-is-fatal attribute. Thus, the configuration for a TestShutdown class would be as follows:
<shutdown-classes> <shutdown-class classname="TestShutdown"> <execution-order>0</execution-order> <init-param> <param-name>oracle.test.shutdown</param-name> <param-value>true</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>shutdown.oracle.year</param-name> <param-value>2002</param-value> </init-param> </shutdown-class> </shutdown-classes>
Assuming that the TestShutdown class is archived in "../app1/shutdown.jar", add another <init-library> element in the server.xml file as follows:
<init-library path="../app1/shutdown.jar" />
Most performance settings are discussed in the Oracle Application Server 10g Performance Guide.
You can manage these performance settings yourself from either the OC4J command-line option or by editing the appropriate XML file element.
Each -D command-line option, except for the dedicated.rmicontext option, defaults to the recommended setting. However, you can modify these options by providing each -D command-line option as an OC4J option. See the"OC4J Command-Line Options and System Properties" for an example.
dedicated.rmicontext=true/false. The default value is false. This replaces the deprecated dedicated.connection setting. When two or more clients in the same process retrieve an InitialContext, OC4J returns a cached context. Thus, each client receives the same InitialContext, which is assigned to the process. Server lookup, which results in server load balancing, happens only if the client retrieves its own InitialContext. If you set dedicated.rmicontext=true, then each client receives its own InitialContext instead of a shared context. When each client has its own InitialContext, then the clients can be load balanced.
This parameter is for the client. You can also set this in the JNDI properties.
oracle.dms.sensors=[none, normal, heavy, all]. You can set the value for Oracle Application Server built-in performance metrics to the following: None (off), normal (medium amount of metrics), heavy (high number of metrics), or all (all possible metrics). The default is normal.This parameter should be set on the OC4J server. The previous method for turning on these performance metrics, oracle.dms.gate=true/false, is replaced by the oracle.dms.sensors variable. However, if you still use oracle.dms.gate, then setting this variable to false is equivalent to setting oracle.dms.sensors=none.
DefineColumnType=true/false. The default is false. Set this to true if you are using an Oracle JDBC driver that is prior to 9.2. For these drivers, setting this variable to true avoids a round-trip when executing a select over the Oracle JDBC driver. This parameter should be set on the OC4J server.
When you change the value of this option and restart OC4J, it is only valid for applications deployed after the change. Any applications deployed before the change are not affected.
When true, the DefineColumnType extension saves a round trip to the database that would otherwise be necessary to describe the table. When the Oracle JDBC driver performs a query, it first uses a round trip to a database to determine the types that it should use for the columns of the result set. Then, when JDBC receives data from the query, it converts the data, as necessary, as it populates the result set. When you specify column types for a query with the DefineColumnType extension set to true, you avoid the first round trip to the Oracle database. The server, which is optimized to do so, performs any necessary type conversions.
You can specify an unbounded, one, or two thread pools for an OC4J process through the <global-thread-pool> element in the server.xml file. If you do not specify this element, then an infinite number of threads can be created, which is the unbounded option.
There are two types of threads in OC4J:
ApplicationServerThreadPool.
ConnectionThreadPool.
OC4J always maintains a certain amount of worker threads, so that any client connection traffic bursts can be handled.
If you specify a single thread pool, then both short and long lived threads exist in this pool. The risk is that all the available threads in the pool are one type of thread. Then, performance can be poor because of a lack of resources for the other type of thread. However, OC4J always guarantees a certain amount of worker threads, which are normally mapped to short lived threads. If a need for a worker thread arises and no short lived thread is available, the work is handled by a long lived thread.
If you specify two thread pools, then each pool contains one type of thread.
To create a single pool, configure the min, max, queue, and keepAlive attributes. To create two pools, configure the min, max, queue, and keepAlive attributes for the first pool and the cx-min, cx-max, cx-queue, and cx-keepAlive attributes for the second pool. In order to activate two thread pools, you must configure all the attributes for the first thread pool, which includes min, max, queue, and keepAlive. If any of these attributes is not configured, you cannot configure the second pool. Instead, you will receive the following error message:
Error initializing server: Invalid Thread Pool parameter: null
The global-thread-pool element provides the following attributes:
Recommendations:
queue attributes should be at least twice the size of the maximum number of threads.
cx-min and cx-max sets the thread pool size for the connection threads; thus, they are relative to the number of the physical connections you have at any point in time. The cx-queue handles burst in connection traffic.
keepAlive attribute to negative one.
The following example initializes two thread pools for the OC4J process. Each contains at minimum 10 threads and maximum of 100 threads. The number of requests outstanding in each queue can be 200 requests. Also, idle threads are kept alive for 700 seconds. The thread pool information is printed at startup.
<application-server ...> ... <global-thread-pool min="10" max="100" queue="200" keepAlive="700000" cx-min="10" cx-max="100" cx-queue="200" cx-keepAlive="700000" debug="true"/> ... </application-server>
You can cache database statements, which prevents the overhead of repeated cursor creation and repeated statement parsing and creation. In the DataSource configuration, you enable JDBC statement caching, which caches executable statements that are used repeatedly. A JDBC statement cache is associated with a particular physical connection. See Oracle9i JDBC Developer's Guide and Reference for more information on statement caching.
You can dynamically enable and disable statement caching programmatically through the setStmtCacheSize() method of your connection object or through the stmt-cache-size XML attribute in the DataSource configuration. An integer value is expected with the size of the cache. The cache size you specify is the maximum number of statements in the cache. The user determines how many distinct statements the application issues to the database. Then, the user sets the size of the cache to this number.
If you do not specify this attribute or set it to zero, this cache is disabled.
The following XML sets the statement cache size to 200 statements.
<data-source> ... stmt-cache-size="200" </data-source>
The task manager is a background process that performs cleanup. However, the task manager can be expensive. You can manage when the task manager performs its duties through the taskmanager-granularity attribute in server.xml. This attribute sets how often the task manager is kicked off for cleanup. Value is in milliseconds. Default is 1000 milliseconds.
<application-server ... taskmanager-granularity="60000" ...>
OC4J logs messages both to standard error, standard out, and several log files for OC4J services and deployed applications.
Also, OC4J supports Jakarta
Note:
log4j. See the "Open Source Frameworks and Utilities" appendix in the Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Servlet Developer's Guide.
Each OC4J process included in the Oracle Application Server environment has a set of log files, as shown in Table 3-3. If there are multiple processes running for an OC4J instance, there is a multiple set of log files.
There are two types of log files:
The ODL log entries are each written out in XML format in its respective log file. Each XML message can be read through the Oracle Enterprise Manager GUI or through your own XML reader. The advantages for ODL logging is that the log files and the directory have a maximum limit. When the limit is reached, the log files are overwritten.
When you enable ODL logging, each new message goes into the current log file, named log.xml. When the log file is full--that is, the log file size maximum is reached--then it is copied to an archival log file, named logN.xml, where N is a number starting at one. When the last log file is full, the following occurs:
log.xml file is written to the latest logN.xml file, where N increments by one over the most recent log file.
Thus, your log files are constantly rolling over and do not encroach on your disk space.
Within each XML file listed in Table 3-3, you enable ODL logging by uncommenting the ODL configuration line, as follows:
<odl> element within the <log> element in all XML files listed in Table 3-3, except for the default-web-site.xml file.
<odl-access-log> element in the default-web-site.xml file.
The attributes that you can configure are:
path: Path and folder name of the log folder for this area. You can use an absolute path or a path relative to where the configuration XML file exists, which is normally in the j2ee/home/config directory. This denotes where the log files will reside for the feature that the XML configuration file is concerned with. For example, modifying this element in the server.xml file denotes where the server log files are written.
max-file-size: The maximum size in KB of each individual log file.
max-directory-size: The maximum size of the directory in KB.
New files are created within the directory, until the maximum directory size is reached. Each log file is equal to or less than the maximum specified in the attributes.
Thus, to specify log files of 1000 KB and a maximum of 10,000 KB for the directory in the ORACLE_HOME/j2ee/log/server directory in the server.xml file, configure the following:
<log> <odl path="../log/server/" max-file-size="1000" max-directory-size="10000" /> </log>
When OC4J is executing, all log messages that are server oriented are logged in the ORACLE_HOME/j2ee/log/server directory.
The XML message that is logged is of the following format:
<MESSAGE> <HEADER> <TSTZ_ORIGINATING>2002-11-12T15:02:07.051-08:00</TSTZ_ORIGINATING> <COMPONENT_ID>oc4j</COMPONENT_ID> <MSG_TYPE TYPE="ERROR"></MSG_TYPE> <MSG_LEVEL>1</MSG_LEVEL> <HOST_ID>myhost</HOST_ID> <HOST_NWADDR>001.11.22.33</HOST_NWADDR> <PROCESS_ID>null-Thread[Orion Launcher,5,main]</PROCESS_ID> <USER_ID>dpda</USER_ID> </HEADER> <PAYLOAD> <MSG_TEXT>java.lang.NullPointerException at com.evermind.server.ApplicationServer.setConfig(ApplicationServer.java:1070) at com.evermind.server.ApplicationServerLauncher.run (ApplicationServerLauncher.java:93) at java.lang.Thread.run(Unknown Source) </MSG_TEXT> </PAYLOAD> </MESSAGE/>
You can have both the ODL and text logging turned on. To save on disk space, you should turn off one of these options. If you decide to enable ODL logging, turn off the text logging functionality by commenting out the <file> subelement of the <log> element for all XML files except the default-web-site.xml file. For the default-web-site.xml file, turn off the text logging by commenting out the <access-log> element.
You can view ODL log files by performing the following:
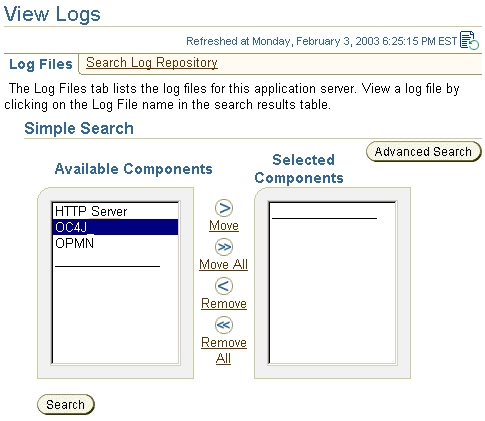
|
See Also:
"Managing Log Files" chapter in the Oracle Application Server 10g Administrator's Guide |
Full text logging is still available in OC4J. Primarily, you should use text logging within OC4J standalone. It is easier to read within any editor, as it is not in XML format.
The text logging facility separates messages out in alignment with the XML files. However, instead of writing to multiple log files of the same size, all messages for that component are written into a single file. The text logging does not have any imposed limits or log rollover. Instead, the log files will continue to grow, unless you stop OC4J, remove the file, and restart OC4J to start the log files over. You can overrun your disk space if you do not monitor your log files. This is only feasible in a standalone, development environment.
Text messaging is the default and is configured in the same XML files as listed for ODL logging in Table 3-3. Text messaging is enabled in the <file> subelement the <log> element of the XML files, except the default-web-site.xml file. For the default-web-site.xml file, the text messaging is enabled with the <access-log> element. To turn off text messaging, eliminate or comment out the <file> or <access-log> element. If you do not remove this line and enable ODL logging, you will have both logging facilities turned on. The location and filename for text messaging does have defaults, as shown in Table 3-4, but you can specify the location and filename within the path attribute of the <log> or <access-log> elements.
The following table shows the default location directory for text messaging log files of an OC4J process.
The location of all of the above log files can be specified, except the web-access.log file, using the <log> element in the respective configuration files. You can specify either absolute paths or paths relative to the j2ee/home/config directory. For example, specify the server log file in the server.xml configuration file, as follows:
<log> <file path="../log/my-server.log" /> </log>
You can also specify an absolute path for the location of the log file, as follows:
<log> <file path="d:\log-files\my-server.log" /> </log>
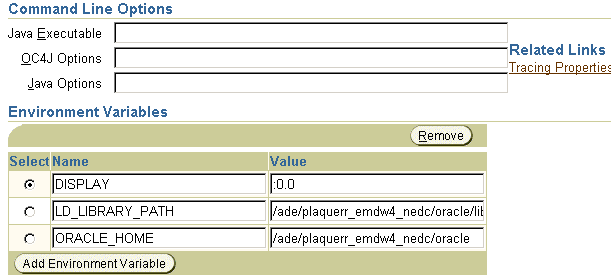
In an Oracle Application Server environment, the standard output and standard errors for OC4J are routed to the OPMN log for the OC4J instance. For example, if you have an OC4J instance called OC4J_Demos, and it has an island called default_island, and there is only one process in the island, the file that will contain the STDOUT and STDERR streams is $ORACLE_HOME/opmn/logs/OC4J_Demos.default_island.1
Figure 3-20 shows how you specify the -out and -err parameters in the OC4J command-line options for your OC4J Instance. When you specify these parameters without specifying a specific directory, the log files are created in the $J2EE_HOME/<OC4JInstanceName>_<IslandName>_<Process#> file. For example, if you have an OC4J instance called OC4J_Demos and it has an island called default_island, then the log file will be created in the $J2EE_HOME/OC4J_Demos_default_island_1.
In the Application Server Control, select Server Properties on the Administration page, which will bring you to the screen in Figure 3-20.
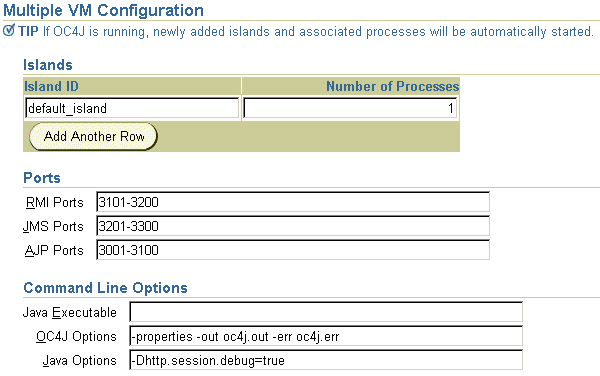
OC4J properties are configuration switches that can be set on the command-line. As shown in Figure 3-20, the properties are prefaced with a -D in the Java Options line. OC4J provides several debug properties for generating additional information on the operations performed by the various sub-systems of OC4J. These debug properties can be set for a particular sub-system while starting up OC4J.
OC4J is started and managed by OPMN. You have to specify the Java system properties for your OC4J instance using Oracle Enterprise Manager as shown in Figure 3-20. The supplied properties are saved in the OPMN configuration file. OPMN starts OC4J with these supplied properties when you shutdown and restart your OC4J Instance. See "OC4J Command-Line Options and System Properties" for OC4J general properties.
By default, the debug information is written to the OPMN log file for the OC4J Instance, which resides in the $ORACLE_HOME/opmn/logs/ directory. For example, you have a OC4J instance named OC4J_DEMOS and there is only one island and the island has only process for this OC4J instance, then the debug information is logged in $ORACLE_HOME/opmn/logs/OC4J_Demos.default_island.1. However, if there is -out and -err command-line options specified with OC4J, then the debug information is redirected to the appropriate files.
The following tables provide useful debug options that available with OC4J. These debug options have two states either true or false. By default these are set to false. For a complete list of debug properties, see "OC4J Command-Line Options and System Properties".
| EJB Debugging | Description of Options |
|---|---|
|
|
Turns on EJB clustering debug messages |
| RMI Debugging | Description of Options |
|---|---|
|
|
Prints RMI debug information |
|
|
Provides very verbose information on RMI calls |
| OracleAS Web Services Debugging | Description of Options |
|---|---|
|
|
Turns on Web Services debugging |
In addition to the specific sub-system switches, you can also start OC4J with a supplied verbosity level. The verbosity level is an integer between 1 and 10. The higher the verbosity level, the more information that is printed in the console. You specify the verbosity level with the -verbosity OC4J option in the Oracle Enterprise Manager in the OC4J command-line options section. The following examples show the output with and without verbosity:
D:\oc4j903\j2ee\home>java -jar oc4j.jar Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE initialized
D:\oc4j903\j2ee\home>java -jar oc4j.jar -verbosity 10 Application default (default) initialized... Binding EJB work.ejb.WorkHours to work.ejb.WorkHours... Application work (work) initialized... Application serv23 (Servlet 2.3 New Features Demo) initialized... Web-App default:defaultWebApp (0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0:8888) started... Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE initialized
You deployed a Web application to OC4J that is having some problems with servlets. You are losing the client session when you use a pre-configured data source to make database connection. You want to know what OC4J is doing when the servlet is accessing the data source. In order to generate the debug information on HTTP Session and data source usage, you must set two debug options - http.session.debug and datasource.verbose to true.
Perform the following tasks
-Dhttp.session.debug=true -Ddatasource.verbose=true
After the OC4J Instance is restarted, you re-execute your servlet and see the following type of debug information in the standard output for the OC4J Instance:
DataSource logwriter activated... jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:DEBU: Started jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:DEBU: Started Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE initialized Created session with id '4fa5eb1b9a564869a426e8544963754f' at Tue APR 23 16:22:56 PDT 2002, secure-only: false Created new physical connection: XA XA Orion Pooled jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:DEBU null: Connection XA XA Orion Pooled jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:DEBU allocated (Pool size: 0) jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:DEBU: Opened connection Created new physical connection: Pooled oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleConnection@5f18 Pooled jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:DEBU: Connection Pooled oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleConnection@5f1832 allocated (Pool size: 0) Pooled jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:DEBU: Releasing connection Pooled oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleConnection@5f1832 to pool (Pool size: 1) null: Releasing connection XA XA Orion Pooled jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:DEBU to pool (Pool size: 1) Orion Pooled jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:DEBU: Cache timeout, closing connection (Pool size: 0) com.evermind.sql.OrionCMTDataSource/default/jdbc/OracleDS: Cache timeout, closing connection (Pool size: 0)
You can remotely debug your applications deployed in OC4J using any Java debugging facility that supports the JPDA (Java Platform Debugging Architecture). With OC4J embedded directly inside of the Oracle JDeveloper IDE, debugging both locally deployed and remote J2EE applications is simple. For more details, please see the Oracle JDeveloper documentation or read the "Remote Debugging How-To" document that is posted on OTN.
|
|
 Copyright © 2002, 2003 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|