10g (9.0.4)
Part Number B10188-01
Home |
Solution Area |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle Application Server Wireless Administrator's Guide 10g (9.0.4) Part Number B10188-01 |
|
This chapter describes how to configure Wireless for voice and messaging communications through the following sections:
This section describes how to configure Wireless for PocketPCS, Palm, and WAP phone applications. Topics include:
This section describes the procedures for configuring Oracle Application Server Wireless to PocketPCS. Topics include:
To access the Wireless server from your Pocket PC device, connect the device to the network. If the Wireless server is on your corporate Intranet, then you must connect your device to your corporate Local Area Network (LAN). If the Wireless server is on the Internet, then you must connect to your Internet Service Provider (ISP). There are different ways to connect your Pocket PC device to your corporate LAN or to your ISP, and they are all documented in the Pocket PC Connection Manager tutorial at: http://www.microsoft.com/mobile/pocketpc/tutorials/connectionmanager/default.asp
To access the Wireless server using Internet Explorer:
Once connected to the main page on the Wireless server, you can make that page the Home Page for your Internet Explorer. Doing so saves from entering the URL every time.
There are two types of Palm devices for connecting to the Internet and Intranet:
If you have a device with built-in wireless Internet access, then you need only to activate your wireless service to connect your device to the Internet. Refer to http://www.palm.com/products/palmi705/wireless.html for more information about Wireless Connectivity with Palm.Net® Service.
If your device does not have built-in Internet access, then you need an ISP account and either a data-enabled phone or a Palm modem. (You can use a data-enabled phone or a Palm modem with Palm i705 as well.)
To configure the connection method:
To configure the ISP account.
If your handheld device supports more than one-way to connect to the Internet, you may choose your preferred method.
If you have a Palm device with built-in wireless Internet access and you have activated your wireless service, then you can use the Palm native web browser to access a wireless server.
To install Handspring's Blazer browser:
http://www.handspring.com/software/how_to.jhtml. (General instructions about installing software on Palm devices are available here: http://software.palm.com)
WAP devices use the WAP protocol for communication. Because the Wireless server does not support the WAP protocol directly, you need a WAP gateway to convert the WAP protocol to HTTP(S). If you connect to the Internet through your Wireless service provider, then the carrier must have already configured a WAP gateway for you. However, if you connect to the Internet or Intranet through a dial-up (PPP connection), then you must install and configure a WAP gateway.
Ensure that the WAP gateway you plan to install is a certified WAP gateway. The certified WAP gateways are listed at: http://www.otn.oracle.com. Go to the Mobile Tech Center.
Follow the installation instructions provided by your WAP gateway vendor.
Some gateways (WAPLite, for example) have a configuration parameter for the Default WML Home Page. Set this parameter to the Wireless server main page to save users from entering this parameter repeatedly.
The WAP phone configuration is specific to the phone model and to the wireless service provider. In general, the phone must be configured for a dial-up network connection (this is not applicable to GPRS phones), the WAP gateway, and the home URL for your WAP browser.
Generally, your phone is reconfigured by your wireless service provider to connect to their own WAP gateway. Some wireless service providers hide the phone settings to prevent the user from changing them. In most cases, you do not need to change the phone network settings; instead, to access the wireless server from a WAP phone, you need only enter the URL of the wireless server into the phone's WAP browser. (See the phone's user's manual for instructions on opening the WAP browser.)
Wireless serves requests from different devices, including Palm, Pocket PC, and WAP. These devices must be configured so that they can access the Wireless server. Requests from these devices to the wireless server come through an HTTP(S) protocol Protocol transformation gateway may be used in some cases to convert the device native network protocol to HTTP(S).
After Wireless has been installed and configured, the Oracle-hosted voice gateway enables you to immediately access both out-of-the-box applications and custom-built voice applications from voice devices. For more information, go to http://www.otn.oracle.com. Go to the Mobile Tech Center.
This section provides information on configuring your own voice gateway using the VoiceGenie developer studio as an example.
To configure voice access to Wireless, you must have access to an Oracle-accepted third-party VoiceXML gateway and the Voice.ear file (included with Wireless). Wireless has been tested against a number of VoiceXML gateways. The list of accepted gateways is located at: http://otn.oracle.com/tech/wireless/integration/content.html
Follow the third-party provider's instructions to properly install and configure your VoiceXML gateway.
If you do not have access to a VoiceXML gateway, a number of gateway providers have hosted gateways for developers that can be utilized, free of charge, for development and testing purposes. For example, VoiceGenie maintains a developer studio at http://developer.voicegenie.com, where users can sign up for a development account that provides them with 10 extensions into a voice gateway. From this Web site, users configure each of their extensions to point to different URLs. To configure voice access to Wireless, you must set up an extension to point to the URL outlined in Section 9.2.3.
Obtain a VoiceGenie developer account by visiting http://developer.voicegenie.com. Follow directions at that site.
The Wireless server provides pre-configured voice portal which contains the following mobile applications.
These user-friendly applications have an enhanced voice user interface.
The voice portal is comprised of the Main Menu master application. Table 9-1 describes the input parameters of the Main Menu master application.
| Parameter | Default Value |
|---|---|
|
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MESSAGE_ INPUT_ENCODING |
UTF-8 |
|
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MAIL_PROTOCOL |
IMAP |
|
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MAIL_SERVER_NAME |
The name of your email server (localhost). |
|
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MAIL_SERVER_PORT |
The email server port. For IMAP, the value is 143; for POP, the value is 110. |
|
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MAIL_SMTP_SERVER_NAME |
The name of the SMTP server. |
|
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MAIL_AUTODOMAIN |
The domain of your organization (for example, oracle.com). |
|
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MAIL_FOLDER_INBOX |
Inbox (or the name of the folder that loads during startup). |
|
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MAIL_FOLDER_SENT |
Sent (or the name of the folder that receives saved messages). |
|
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MAIL_DEFAULT_EMAILDOMAIN |
The default email domain (for example, oracle.com). |
|
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MAIL_MSGFETCH_SETSIZE |
200 |
|
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MAIL_SERVER_CONNECT_TIMEOUT |
2000 |
|
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MAIL_AUDIO_TMP_DIR |
The UNIX directory for the audio files. Note: This parameter must be designated as Modifiable. |
|
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MAIL_AUDIO_TMP_URL |
The URL pointing to the UNIX directory of the audio files. |
|
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MAIL_MAIL_CONFIG_CLASS |
oracle.panama.module.pim.mail.util.Config |
|
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_CALENDAR_SERVER_NAME |
scheduler:cal:suncal01.us.oracle.com:1522:GMCAL:flows:oo:gmmail.oraclecorp.com:143 |
|
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_CALENDAR_DOMAIN |
OracleDomain |
|
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MAIL_OID |
The OID (object ID) of the Mail application as displayed in the browsing screen of the Content Manager. See Section 9.2.3.2.1 for more information on retrieving this value. |
|
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_CALENDAR_OID |
The OID (object ID) of the Calendar application as displayed in the browsing screen of the Content Manager. See Section 9.2.3.2.1 for more information on retrieving this value. |
This application is the template for the Voice Main Menu application link (an alias to the Main Menu application, which can be customized and distributed to user groups).
The Voice Main Menu application, which you access from the Content Manager (one of the Wireless Tools), also has these input values; however, the input value names and values cannot be changed unless the Application Developer designates them as Modifiable in the Main Menu master application, which is accessed through the Service Manager tool. For information about the Voice Main Menu application, see Section 9.2.3.2.
For more information on application links, see Chapter 5, "Managing Content". For more information on creating a master application, see the Oracle Application Server Wireless Developer's Guide.
To enable voice access, you provision a voice gateway phone number to the following URL:
<server-name>:<port>/ptg/rm?PAlogin=true&PAlocale=<locale>
Where the port is the WebCache listening port number 7777 (the default port number) and the port number range is 7777 to 7877.
You must specify the locale for a language other than English; if the locale is English, however, then you do not need the PAlocale attribute. You specify the locale using the two-letter Java locale format (the two-letter Java country code is optional). For example, to define the PAlocale attribute as French-Canadian, you enter fr_CA (fr is the Java locale, CA is the country code).
This provisioning scheme contacts the voice login service for the Wireless server. After users login, a main menu displays, which lists all of the applications that they can access.
Use the PAoid=<oid> attribute to enable users to log into a particular application, such as the Voice Main Menu. For the Voice Main Menu to execute the playlist items (the number of new email messages and appointments), use the start=true attribute.
When provisioning Mobile Studio for voice access, point the VoiceXML gateway to a URL for a start or login page in the Wireless and Voice Portal in the form of
http://<hostname>/ptg/rm
In addition to regular voice access, Oracle Application Server Wireless also provides a voice portal that plays the number of new messages and appointments for the user and contains links to such PIM applications as mail, calendar, address book, files, and directory.
This section includes a discussion on how to use the Content Manager, one of the Oracle Application Server Wireless Tools, to enable applications to return to the Voice Main Menu application and how to optimize the loading of the mail application to improve user performance. For more information on using the Content Manager, see Chapter 5, "Managing Content".
To access the Content Manager, you must be granted either the Super User or Content Manager roles. For more information on user roles, see Section 4.1.1 in Chapter 4, "Managing Users". For information on logging into the Oracle Application Server Wireless Tools (including the Content Manager), see Section 2.3 in Chapter 2, "Verifying the Wireless Installation".
To set up the voice portal, provision a telephone number to:
http://<server-name>:<server-port>/ptg/rm?PAlogin=true&PAoid=<oid of Voice Main Menu>&start=true"
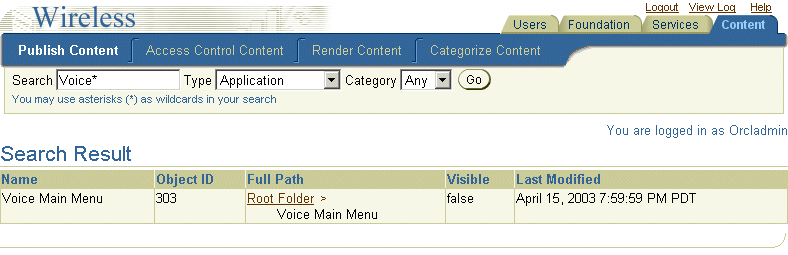
You define the PAOID attribute using the OID (Object ID in the Wireless Repository) of the Voice Main Menu application, which is listed in the Object OID column of the browsing and search result tables of the Content Manager. (For example, the Object ID for the Voice Main Menu application is noted as 303 in Figure 9-1.)
To find this number, you first log into the Wireless Tools and then select the Content Manager (the Content tab, as illustrated in Table 9-1). The Content Manager defaults to the Publish Content subtab, displaying the browsing screen. From the table listing application links, find the Voice Main Menu application. Its OID is listed on the same row in the Object ID column.
You can also use the Content Manager's search functions to retrieve the Voice Main Menu application. For more information on searching for an application link in the Content Manager, see Section 5.3.1 in Chapter 5, "Managing Content".
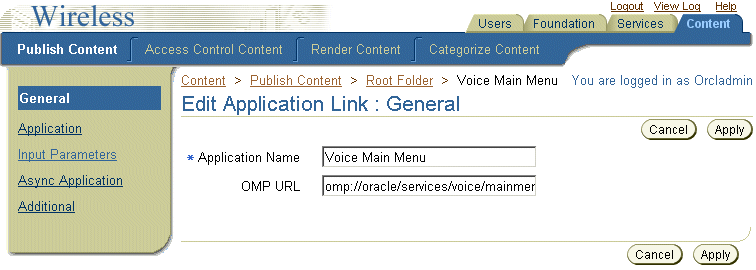
To ensure that applications return to the Voice Main Menu after a user says "main menu", you edit the application by entering the following Oracle Mobile Protocol (OMP) URL that points to the Voice Main Menu:
omp://oracle/services/voice/mainmenu
Use the Content Manager's application link editing functions to add this URL as follows:
To use the Mail, Address Book, Voice Mail, Calendar, or Files applications, users must save their login credentials through the Wireless Customization Portal or from the Wireless and Voice Portal. For the portal, users must enter their user account credentials for the Mail, Address Book, Voice Mail, Calendar, and Files applications and click Save Password.
By default, the Mail, Address Book, Voice Mail, Calendar, and Files applications are configured out-of-the-box with the installation of Oracle Application Server. If you do not use Oracle Application Server, however, then you must configure the input parameters of these applications using the Content Manager as described in Steps 1 through 4 in Section 9.2.3.2.2.
The online help invoked from the Content Manager provides you with instructions on editing the input parameters.
When editing the input parameters of the Mail application:
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MAIL_AUDIO_MAIL_AUDIO_TMP_URL.
Click Apply to save your changes.
You can configure the Voice Main Menu application so that it can prefetch the mail application, enabling it to load more quickly and thus improve the user experience.
To configure the Voice Main Menu application to prefetch the mail application:
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MAIL_AUDIO_MAIL_AUDIO_TMP_URL.
Click Apply to save your changes. The mail application now loads faster.
See Chapter 5, "Managing Content" for more information on editing application links.
The configuration for the Voicemail application link is the same as the configuration for the email application, except that the value for ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MAIL_FILTERMODE parameter must be defined as voicemail. For example:
ORACLE_SERVICES_PIM_MAIL_FILTERMODE=voicemail
The Voicemail application filters email messages based on the x-orcl-messagetype=voice-message header.
To access the voice-enabled applications for testing, you must first dial the provisioned phone number. You then create a user account with the User Manager. Once the account has been created, (that is, after you have entered both the PIN and a Primary Phone Number), the Voice Main Menu plays. For more information on creating a user account, see Section 4.5.).
This section details the following
The commands described in Table 9-2 must always take you to the appropriate place in the voice portal:
Depending on the setup of the voice portal, users can access any application at any point by saying the name of the application. The following applications are available out of the box:
Users must be able to access this applications at all times. To add more commands to the global grammar, modify the following file for links between module applications:
Modify the following file for the My Oracle main menu, or another .JSP for a personalized menu:
The Email application reads an email message on any configured IMAP or POP3 server. By default, the application begins reading the messages from the Inbox folder. The application reads a bucket of New Messages before reading from the Old Messages bucket. The application reads the messages continually until the user commands it to stop.
The application orders the New Messages from the oldest unread message to the newest unread message. The application orders the Old Messages from the newest read message to the oldest read message.
The email application responds to voice commands described in Table 9-3.
You must test email using different types of messages to ensure that each message type functions. Populate the Inbox with the following types of messages:
The calendar application enables users to listen to, and create, calendar appointments. The application reads the appointments for the current day first. Table 9-4 describes the Interrupt commands, which enable a user to interrupt the playback of appointments at any point (even after the playback of an appointment has completed).
The voice version of the Oracle Files application enables users to browse directories, listen to the descriptions of the file names, and then either fax or delete the file.
Table 9-5 describes the voice commands used when browsing folders:
The Directory application enables users to search for other users in a corporate directory by spelling the name of the user.
In the first dialog, user select the type of search they want to perform. For example, users can select Search by Name or Search by Email. If only one type of search is available, then this dialog is skipped.
The second dialog asks users to spell the name of the person they are searching for. In addition to providing letters, users can also use the commands for searching corporate directories, which are described in Table 9-6.
In the results dialog,
The Address Book application enables users to listen to the details of contact in the address book, or to call or email someone. A natural interface is also available for this application, which enables quick calling or emailing.
Users retrieve the contact details by saying the name of the person, or by pressing the appropriate key tone when prompted. Users hear a list of contacts by saying "List".
The contact details dialog enables The Address Book application responds to the voice commands described in Table 9-7.
Async-enabled Wireless applications can be accessed using such messaging devices as an SMS phone (two-way text message capable), two-way pagers and email. Async-related terms in Wireless include the following:
See the Oracle Application Server Wireless Developer's Guide for more information on Async features.
To configure email-based access:
Each pre-configured Async-enabled application is assigned a short name so the service is addressable to device users. In other words, a shortname is the keyword that device users use to identify which service they intend to invoke. You use the Content Manager to create and edit short names. For more information, see Section 5.3.4. in Chapter 5, "Managing Content".
This section discuses configuring email, SMS, pagers, fax and voice for notifications.
Oracle Application Server Wireless features a messaging component that handles sending and receiving messages to and from devices. Typically, Wireless must be configured to connect to an external server to deliver messages (such as SMS or email).
Wireless is pre-configured to send SMS, Voice, Email and Fax messages without configuration, by connecting to and utilizing the Oracle-hosted online Push Service.
If you do not to use the Oracle-hosted online Push Service, you must set up the necessary communications channels. Wireless includes a set of drivers that you can use to configure your network capability (such as SMS, Voice, or email). This may involve working with network providers (carriers) -- depending on your network type -- to set up the kind of connection the drivers to which drivers can connect for message delivery.
The Wireless messaging system is pre-configured to connect to the Oracle-hosted online Push Service, which is capable of sending messages to SMS phones, pagers, voice and faxes. No configuration is required. Once the pre-seeded Messaging Sever is started, you can send messages. The PushClient driver is configured to communicate with the Oracle-hosted online Push Service running at the following URL:
http://messenger.oracle.com/push/webservices
Wireless ships with pre-built network drivers that support major protocols that have been accepted as industry standards. The pre-built drivers handle communications protocols such as SMS (short message for phone), email (paging or desktop), voice and fax.
To enable those network channels, you must configure the pre-built drivers to work with their corresponding network servers:
Remove the pre-configured PushClient driver and its corresponding instances if they are not used.
To configure the email and paging services:
To deliver SMS messages to phones, you must set up a communication channel to the SMS carrier. To do this, you must contract with a carrier having a network used for sending and receiving of SMS messages through the UCP or SMPP protocols.
Alternatively, you can use a network aggregator, such as Mobileway, who acts as an intermediary between the SMS carriers and the enterprise. This may be beneficial when supporting messaging on which multiple carriers are required. See the following URL for vendors whose protocols are certified to work with Wireless:
http://otn.oracle.com/products/iaswe/integration/content.html
Configure the corresponding SMS drivers (for example: UCP, SMPP) and driver instances.
For this release, RightFax (a product of Captaris, Inc.) is the supported product. Customers must acquire the RightFax product and follow its instructions to set up a fax server.
The location of client API .jar files from RightFax must be added to the classpath in ORACLE_HOME/wireless/sample/runpanamaserver.sh. Configure the fax driver and driver instance as specified in the common tasks.
The voice driver implements the outbound telephony calls through a VoiceGenie VoiceXML Gateway. To configure the voice driver, provide the URL to the VoiceGenie Outbound Call servlet. The remaining configuration of the voice driver and driver instance can be performed as described in the common tasks.
|
|
 Copyright © 2003 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|