|
Oracle® Application Server Web Cache Administrator's Guide
10g (9.0.4) Part No. B10401-02 |
|
|
|
|
|
Oracle® Application Server Web Cache Administrator's Guide
10g (9.0.4) Part No. B10401-02 |
|
|
|
|
This chapter introduces the various administration tools of OracleAS Web Cache. It discusses the main administration application and tells you how to launch it and navigate through it. It also introduces the command line tool.
This chapter contains these topics:
OracleAS Web Cache Manager is a graphical user interface tool that combines configuration and monitoring options to provide an integrated environment for configuring and managing OracleAS Web Cache and the Web sites for which it caches content. With OracleAS Web Cache Manager, you can easily:
Start, stop, and restart OracleAS Web Cache
Administer invalidation or rollover log files
Monitor performance and requests
Configure general properties of the cache
Configure log settings
Configure listening and operation port settings
Configure origin server settings
Configure site-specific settings
Configure caching rules
Associate caching rules with URLs
This section introduces you to the features of OracleAS Web Cache Manager. However, the primary documentation for using OracleAS Web Cache Manager is the accompanying online help. This section contains these topics:
To start OracleAS Web Cache Manager:
Start the admin server process with the following command:
opmnctl startproc ias-component=WebCache process-type=WebCacheAdmin
Point your browser to the following URL:
http://web_cache_hostname:4000/webcacheadmin
When prompted for the administrator user ID, enter either the Oracle Enterprise Manager user name, ias_admin, or the OracleAS Web Cache administrator user name, administrator, for the user name.
For the password, if you changed the password through OracleAS Web Cache Manager, enter that password. Otherwise, enter one of the following:
If you supplied a password during the installation, enter that password. (You are required to enter a password during the installation of Oracle Application Server.)
If you did not need to supply a password during the installation, as is the case with a standalone installation, enter administrator.
Note that changing the password for ias_admin through Oracle Enterprise Manager has no effect on the password for the OracleAS Web Cache.
|
Note: You can also point your browser tohttp://web_cache_hostname:4000 to link to OracleAS Web Cache Manager, information about examples, user documentation, and the Oracle Technology Network.
|
|
See Also:
|
The OracleAS Web Cache Manager interface includes:
Top frame containing Apply Changes and Cancel Changes buttons and OracleAS Web Cache status message
Navigator frame with configuration and monitoring menu items
Right frame with property sheet for selected menu item
Figure 6-1 shows the OracleAS Web Cache Manager interface.
The Apply Changes button applies submitted static and dynamic configuration changes to OracleAS Web Cache; the Cancel Changes button cancels submitted static and dynamic configuration changes to OracleAS Web Cache.
|
See Also: "Applying Static and Dynamic Configuration Changes" for further information about applying static and dynamic configuration changes |
Status messages appear beneath the Apply Changes and Cancel Changes buttons. Table 6-1 describes the possible status messages.
Table 6-1 OracleAS Web Cache Manager Status Messages
| Message | Description |
|---|---|
Web Cache running with current configuration.
|
This message appears if OracleAS Web Cache is running with an up-to-date configuration. |
Press "Apply Changes" to commit your modifications.
|
This message appears if Submit has been selected in some dialog box, but the Apply Changes button has not been chosen. |
Restart Web Cache to make configuration changes take effect
|
This message appears if OracleAS Web Cache is running with an older version of the configuration. This can happen when static configuration changes have been applied to webcache.xml, but OracleAS Web Cache was not restarted.
|
Dynamic Changes Applied. Restart Not Needed
|
This message appears if one or more dynamic configuration changes were applied.
See Also: "Applying Static and Dynamic Configuration Changes" |
| Retrieve configuration from remote cache | This message appears if the cache has been recently upgraded to the current version of OracleAS Web Cache but the configuration has not been copied to the local cache configuration file. |
In addition, information about any needed operation is displayed in the Cache Operations page.
The navigator frame provides a graphical tree view of configuration, administration, and performance monitoring capabilities for OracleAS Web Cache and its supported Web sites.
The navigator frame contains the following major categories:
Operations: This category contains pages that enable you to:
Start, stop, and restart OracleAS Web Cache
Invalidate documents in the cache
Rollover log files
Monitoring: This category contains pages that enable you to:
Monitor the performance of OracleAS Web Cache
Monitor the performance of origin servers
View the contents of a cache
Analyze the performance of pages configured for end-user performance monitoring
Properties: This category contains pages that enable you to:
Configure security settings such as usernames and passwords for administrators and invalidation users
Specify the process identity for OracleAS Web Cache processes
Specify settings for the auto-restart mechanism
Specify network time-outs
Specify the size of the cache and the number of connections
Configure a cache cluster
Logging and Diagnostics: This category contains pages that enable you to:
Configure event logging settings
Configure access logging settings
Configure end-user performance monitoring
Configure diagnostic information
Ports: This category contains pages that enable you to:
Configure OracleAS Web Cache listening ports
Configure listening ports for administration, statistics, and invalidation requests
Origin Servers, Sites, and Load Balancing: This category contains pages that enable you to:
Specify origin servers
Configure site definitions
Map site definitions to origin servers
Configure error pages
Configure session binding
Specify the location of the wallet used for communication to an origin server
Rules for Caching, Personalization, and Compression: This category contains pages that enable you to:
Configure caching rules
Specify expiration policies
Configure session definitions
Configure cookie definitions
Rules Association: This category contains pages that enable you to associate caching rules with:
Compression
Expiration policies
Session policies
Cookies
HTTP request headers
HTTP errors
ESI propagation policies
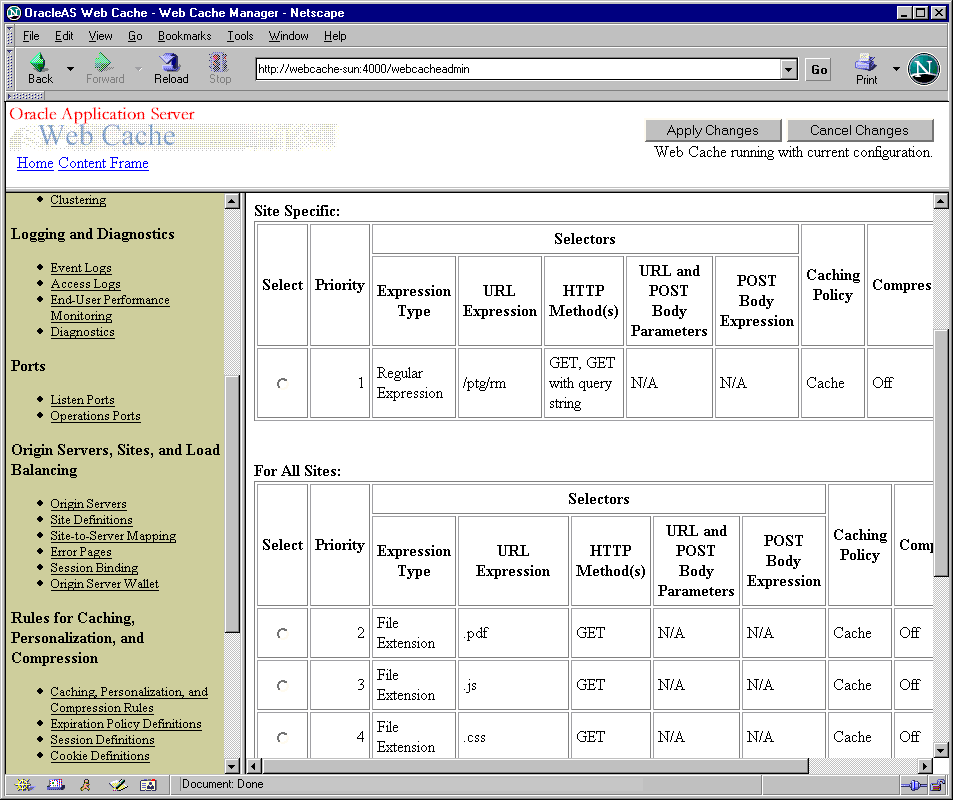
The right frame contains property sheets that enable you to configure and administer OracleAS Web Cache. Figure 6-2 shows the Caching, Personalization, and Compression Rules page used for viewing caching rules.
Figure 6-2 Caching, Personalization, and Compression Rules Page
The Cache Operations page, shown in Figure 6-1, of OracleAS Web Cache Manager (Operations > Cache Operations) provides information about the status of a cache and what operations are needed. From this page, you can start, stop, or restart a cache.
If the cache is part of a cache cluster, all caches in the cluster are listed on the Cache Operations page. In addition to starting, stopping, and restarting a cache, you can propagate the configuration to other cluster members from this page. You can perform the operations on a selected cache or on all caches in the cluster. To minimize disruption in your Web site, you can specify an interval to stagger the times that the operations begin on the caches.
|
See Also: "Starting and Stopping OracleAS Web Cache" for further information about using the Cache Operations page |
Using the following menus in the navigator frame, you can change the configuration for OracleAS Web Cache:
Properties
Logging and Diagnostics
Ports
Origin Servers, Sites, and Load Balancing
Rules for Caching, Personalization, and Compression
Rule Association
Configuration changes are saved in a temporary configuration file, before they are applied to the webcache.xml file in the $ORACLE_HOME/webcache directory on UNIX or ORACLE_HOME\webcache directory on Windows.
Most configuration changes are static. When static changes are applied with Apply Changes, OracleAS Web Cache saves the temporary configuration file to the webcache.xml file. You must restart OracleAS Web Cache to apply changes.
However, OracleAS Web Cache recognizes some changes as dynamic. OracleAS Web Cache Manager provides dynamic configuration for the following features:
Setting buffering and verbosity detail level in the Event Logs page (Logging and Diagnostics > Event Logs)
Setting buffering in the Access Logs page (Logging and Diagnostics > Access Logs)
Enabling and disabling of diagnostics information in the HTML response body of a document in the Diagnostics page (Logging and Diagnostics > Diagnostics)
Setting routing to origin servers in the Origin Servers page (Origin Servers, Sites, and Load Balancing > Origin Servers)
OracleAS Web Cache Manager displays the icon, shown in Figure 6-3, to distinguish dynamic configuration from static configuration changes.
Figure 6-3 OracleAS Web Cache Manager Dynamic Configuration Icon
When dynamic changes are applied with Apply Changes, OracleAS Web Cache immediately applies the configuration changes and saves the temporary configuration file to the webcache.xml file. No restart is needed.
If you use OracleAS Web Cache Manager to apply both a dynamic and static configuration change, you must restart OracleAS Web Cache.
|
See Also: "Starting and Stopping OracleAS Web Cache" for further information about restarting OracleAS Web Cache |
Oracle Enterprise Manager is the primary tool for administering Oracle Application Server. It is a complete management solution for administering, configuring, and monitoring the application server and its components.
The Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control Console enables you manage an Oracle Application Server instance.
For OracleAS Web Cache, you can use the Application Server Control Console to start, stop, or restart the cache, as well as monitor cache and origin server status.
The Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Grid Control Console enables you view historical metrics for multiple Oracle Application Server targets.
For OracleAS Web Cache, you can use the Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Grid Control Console to view the overall status of OracleAS Web Cache and view OracleAS Web Cache performance metrics.
Based on the metrics, you can make changes to the configuration with OracleAS Web Cache Manager. Later, you can use Enterprise Manager to monitor how configuration changes affect the performance of the OracleAS Web Cache.
|
See Also: Oracle Application Server 10g Administrator's Guide and Oracle Enterprise Manager Advanced Configuration for further information about using Oracle Enterprise Manager to monitor OracleAS Web Cache |
Oracle Process Manager and Notification (OPMN) Server manages Oracle Application Server processes, including Oracle HTTP Server, OC4J, and OracleAS Web Cache processes, and channels all notifications from different components instances to all interested in receiving them.
With OPMN, you can administer the OracleAS Web Cache processes, including the admin server process and cache server process:
The executable used for managing these process is webcached, which resides in $ORACLE_HOME/webcache directory on UNIX and the ORACLE_HOME\bin directory on Windows.
In addition, if auto-restart is enabled for the cache, OPMN monitors the cache server process. If the cache server process fails, OPMN restarts the process. The executable used for managing auto-restart is webcachemon, which resides in $ORACLE_HOME/webcache directory on UNIX and the ORACLE_HOME\bin directory on Windows.
To use OPMN, you use the opmnctl utility. First, you must start OPMN, using the following command:
opmnctl start
Then, you use OPMN to control OracleAS Web Cache. The following shows the format of the opmnctl commands:
opmnctl command [parameter=value] [parameter=value]
Table 6-2 shows the commands of the opmnctl utility that are applicable to OracleAS Web Cache.
Table 6-2 Commands of the opmnctl Utility
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
startproc
|
Starts the specified process or component. |
stopproc
|
Stops the specified process or component. If used to stop the cache server process, this command also clears the cache of all content and all statistics. It waits for all currently accepted requests to be served, or until the user-specified timeout, before stopping the cache.
To stop the specified process immediately, use the |
restartproc
|
Stops, then restarts the specified process or component. |
startall
|
Starts all processes controlled by OPMN. |
stopall
|
Stops all processes controlled by OPMN. |
status
|
Shows the status of the processes controlled by OPMN. For more information about the options for the status command, at the command line, enter:
opmnctl status -help |
Table 6-3 shows the parameters for the opmnctl utility. It also shows the valid values that are applicable for OracleAS Web Cache. Unless otherwise noted, you can use any parameter with any command, except for status, listed in Table 6-2.
Table 6-3 Parameters for the opmnctl Utility
The opmn executable is located in the $ORACLE_HOME/opmn/bin directory on UNIX and the ORACLE_HOME\bin directory on Windows.
|
Note: If you are running OracleAS Web Cache in a standalone environment (that is, you installed OracleAS Web Cache from a kit that included only this product; you did not install OracleAS Web Cache as part of an Oracle Application Server installation), you must use thewebcachectl utility to administer OracleAS Web Cache processes.
See Appendix C for information on using the |
|
See Also:
|
For UNIX operating systems, you can use the webcache_setuser.sh script to set the file permissions according to the mode in which in you need to run OracleAS Web Cache. The file webcache_setuser.sh is located in the directory $ORACLE_HOME/webcache/bin.
Prior to running the webcache_setuser.sh script, stop both the cache and admin server processes, using the OPMN utility command:
opmnctl stopproc ias-compononent=WebCache
You cannot use the options in the Cache Operations page to stop or start the admin server process. See "Starting and Stopping OracleAS Web Cache" for more information on starting and stopping OracleAS Web Cache.
The following shows the format of the webcache_setuser.sh syntax:
webcache_setuser.sh command user_ID
Table 6-4 describes the commands.
Table 6-4 Commands of the webcache_setuser.sh Script
The parameter user_ID is the user ID associated with the OracleAS Web Cache processes. (By default, that user ID is the ID of the user that performed the installation.) For setroot and revert modes, the user ID must be the ID of the user that performed the installation. The user ID must match the user ID specified in the Process Identity page (Properties > Process Identity) of OracleAS Web Cache Manager.
|
See Also: "Task 2: Modify Security Settings " and "Running webcached with Root Privilege" for further information about when running thewebcache_setuser.sh script is necessary
|
OracleAS Web Cache configuration and administration tasks are described throughout this guide and in the OracleAS Web Cache Manager online help system. Table 6-5 lists the common tasks, and points you to the topic in this guide that describes the task.
Table 6-5 Common Administrative Tasks for OracleAS Web Cache
| Task | See |
|---|---|
| Configuring OracleAS Web Cache Basics | |
Change the administrator or invalidator password.
|
"Task 2: Modify Security Settings "
|
| Configure the auto-restart mechanism. | "Task 3: Configure Auto-Restart Settings "
|
| Modify the network time-outs for OracleAS Web Cache. | "Task 4: Configure Network Time Outs"
|
| Set the maximum cache size limit. | "Task 5: Set Resource Limits"
|
| Configure OracleAS Web Cache with listening ports. | "Task 6: Configure OracleAS Web Cache with Listening Ports for Incoming Browser Requests"
|
| Configure listening ports for administration, invalidation, and statistics monitoring requests. | "Task 8: Configure OracleAS Web Cache with Operations Ports"
|
| Specify the settings for origin servers. | "Task 9: Configure Origin Server, Load Balancing, and Failover Settings "
|
| Configure Web site definitions and map the site to origin servers. | "Task 10: Configure Web Site Settings "
|
| Configure error pages. | "Configure Error Pages "
|
| Bind a session to an origin server. | "Bind a Session to an Origin Server "
|
| Configuring OracleAS Web Cache for Specialized Configurations | |
| Configure a cache hierarchy. | "Configuring a Hierarchy of Caches "
|
| Configure a cache cluster. | "Configuring a Cache Cluster "
|
| Configuring Logging and Diagnostics Settings | |
| Configure event log settings. | "Configuring Event Logs"
|
| Configure access log settings. | "Configuring Access Logs"
|
| Configure end-user performance monitoring. | "Configuring End-User Performance Monitoring"
|
| Configuring Support for HTTPS Requests | |
| Create a wallet. | "Task 1: Create Wallets"
|
| Configure OracleAS Web Cache with an HTTPS listening port. | "Task 2: Configure HTTPS Listening Ports and Wallet Location for the Cache"
|
| Configure HTTPS listening ports for administration, invalidation, and statistics monitoring requests. | "Task 3: Configure HTTPS Operations Ports for the Cache"
|
| Configure the origin server with an HTTPS listening port. | "Task 5: Configure HTTPS Port and Wallet Location for the Origin Server"
|
| Administering OracleAS Web Cache | |
| Start and stop OracleAS Web Cache | "Starting and Stopping OracleAS Web Cache"
|
| Invalidate documents in the cache. | Chapter 11, " Sending Invalidation Requests "
|
| Propagate configuration changes to cache cluster members. | "Propagating Configuration Changes to Cache Cluster Members"
|
| List the URLs of the documents in the cache. | "Listing Popular Requests and Cache Contents"
|
| Rollover log files. | "Rolling Over Event and Access Logs "
|
| Monitoring Performance | |
| Monitor overall OracleAS Web Cache health. | "Monitoring OracleAS Web Cache Health"
|
| Monitor OracleAS Web Cache performance. | "Gathering OracleAS Web Cache Performance Statistics"
|
| Monitor origin server performance. | "Gathering Origin Server Performance Statistics"
|
|
Note: Except for those tasks listed under the Administering OracleAS Web Cache and Monitoring Performance rows, most tasks require stopping and then restarting OracleAS Web Cache. See "Applying Static and Dynamic Configuration Changes" for exceptions, and "Starting and Stopping OracleAS Web Cache" for further information about restarting OracleAS Web Cache. |