|
Oracle® Application Server 10g Administrator's Guide
10g (9.0.4) Part No. B10376-02 |
|
|
|
|
|
Oracle® Application Server 10g Administrator's Guide
10g (9.0.4) Part No. B10376-02 |
|
|
|
|
This chapter introduces the Oracle Application Server administration tools.
It contains the following topics:
About Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control
Monitoring and Diagnosing with the Application Server Control Console
Oracle realizes that the procedures you use to monitor and administer your application server components can vary, depending upon the size of your organization, the number of administrators you employ, and the types of components you manage. As a result, Oracle offers options for managing your Oracle Application Server installations.
These management options can be divided into the following categories:
Managing Oracle Application Server with Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g
Using Other Tools to Monitor the Built-In Performance Metrics
The primary tool for managing Oracle Application Server—as well as your entire Oracle environment—is Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g.
With Enterprise Manager, you can use your Web browser to:
Manage individual Oracle Application Server instances with Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control.
Centrally manage all the components of your network and your enterprise with Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Grid Control.
Application Server Control is installed with every instance of Oracle Application Server. As a result, you can immediately begin managing your application server and its components from your Web browser.
|
Note: If you select the Oracle Application Server Metadata Repository-only installation type, the Application Server Control is installed, but it is not configured or started automatically by the installation procedure. In fact, there is no need to start or use the Application Server Control Console for the Metadata Repository-only installation type.For information, see Section 2.5, "Managing the OracleAS Metadata Repository Database". |
From the Application Server Control Console, you can monitor and administer a single Oracle Application Server instance, a farm of application server instances, or an Oracle Application Server cluster.
Application Server Control Console organizes a wide variety of performance data and administrative functions into distinct, Web-based home pages for each application server component. The Enterprise Manager home pages make it easy to locate the most important monitoring data and the most commonly used administrative functions—all from your Web browser.
Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Grid Control is installed separately from the Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g installation CD-ROM. The Grid Control Console provides a wider view of your network so you can manage multiple Oracle Application Server instances. In addition, the Grid Control Console provides a robust feature set designed to help you manage all aspects of your enterprise, including your Oracle databases, hosts, listeners, and other components.
When used together, Application Server Control and Grid Control provide a complete set of efficient tools to reduce the cost and complexity of managing your enterprise.
Oracle Application Server also provides command-line interfaces to several key management technologies. After you become familiar with the architecture and components of your application server, command-line tools can help you automate your management procedures with scripts and custom utilities.
The two most important administration command-line tools are:
opmnctl, which provides a command-line interface to Oracle Process Management Notification (OPMN). You can use opmnctl to:
Start and stop components, instances, and OracleAS Clusters
Monitor processes
dcmctl, which provides a command-line interface to Distributed Configuration Management (DCM). You can use dcmctl to:
Create and remove OC4J instances and OracleAS Clusters
Deploy and undeploy OC4J applications
Archive and restore configuration information
Obtain configuration information
In addition to opmnctl and dcmctl, Oracle Application Server provides many other command-line tools for performing specific tasks.
After you install and start Oracle Application Server, the application server automatically begins gathering a set of built-in performance metrics. These built-in performance metrics are measured continuously using performance instrumentation inserted into the implementations of Oracle Application Server components.
The Application Server Control Console presents a subset of these performance metrics in an organized fashion on the application server component home pages. For example, the Oracle HTTP Server metrics are presented as a series of charts on the Performance property page, which is available from the Oracle HTTP Server home page.
Alternatively, you may want to view the complete set of built-in performance metrics, or you may need to monitor a specific set of application server component metrics. As a result, Oracle Application Server also provides a set of command-line and servlet-based tools to view the Oracle Application Server built-in performance metrics directly, outside of the Application Server Control Console.
Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control Console provides Web-based management capabilities designed specifically for Oracle Application Server. Using the Application Server Control Console, you can monitor, diagnose, and configure the components of your application server. You can deploy applications, manage security, and create and manage Oracle Application Server clusters.
The Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control consists of:
The Application Server Control Console and its Enterprise Manager home pages that you use to manage Oracle Application Server
These Web pages provide you with a high-level view of your Oracle Application Server environment. You can then drill down for more detailed performance and diagnostic information.
The underlying software technologies that keep track of your application server instances and components
These technologies automatically perform many of the management tasks as you select options and functions within the Application Server Control Console. For example, they discover the components of each application server instance, gather and process performance data, and provide access to application configuration information.
Oracle Application Server provides a wide variety of software solutions designed to help you run all aspects of your business. As a result, you will want to manage Oracle Application Server from different levels of detail.
At times, you may want to manage a single application server instance; or, you may find it efficient to combine multiple instances into an Oracle Application Server cluster. At other times, you will want to manage a specific application server component.
To support these multiple levels of management, Oracle introduces the Oracle Enterprise Manager home pages. Each home page provides the information you need to monitor the performance and availability of Oracle Application Server from a particular level of management detail. Selected home pages also provide tools for configuring your Oracle Application Server components.
From each home page, you can obtain high-level information or you can drill down to get more specific information about an instance, component, or application.
Consider the following home pages that are available when you use the Application Server Control Console:
Use the OracleAS Farm home page to view a set of related application server instances on your network and to create clusters that speed up the configuration and deployment of your Web applications. For more information, see Section 2.3.3, "Using the Oracle Application Server Farm Home Page".
Use the Application Server home page to manage all aspects of an individual application server instance. For more information, see Section 2.3.2, "Using the Application Server Home Page".
Drill down to a component home page to monitor or configure an individual component of the application server. For example, use the Oracle HTTP Server home page to monitor the performance of your Web server, or use the Oracle Containers for J2EE (OC4J) home page to deploy a custom Web-based application. For more information, see Section 2.3.4, "Using an Oracle Application Server Component Home Page".
The Application Server Control Console relies on various technologies to discover, monitor, and administer the Oracle Application Server environment. Table 2-1 provides a summary of the underlying technologies leveraged by the Application Server Control Console.
Table 2-1 Summary of the Application Server Control Underlying Technologies
| Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| Dynamic Monitoring Service (DMS) | The Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control Console uses DMS to gather performance data about your Oracle Application Server components.
For more information, see Oracle Application Server 10g Performance Guide. |
| Oracle Process Manager and Notification Server (OPMN) | OPMN manages Oracle HTTP Server, OC4J, and other Oracle Application Server processes. It channels all events from different component instances to all components interested in receiving them.
For more information, see Oracle Process Manager and Notification Server Administrator's Guide. |
| Distributed Configuration Management (DCM) | DCM manages configurations among application server instances that are associated with common Infrastructure Services (members of an Oracle Application Server Farm). It enables Oracle Application Server cluster-wide deployment so you can deploy an application to an entire cluster, or make a single host or instance configuration change applicable across all instances in a cluster. The Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control Console uses DCM to make configuration changes and to propagate configuration changes and deployed applications across the cluster.
For more information, see Distributed Configuration Management Reference Guide. |
| Oracle Management Agent | A local version of the Oracle Management Agent designed specifically to monitor and administer your application server components. |
| Oracle Management Watchdog Process | The Management Watchdog Process monitors the Management Agent and the Application Server Control Console to make sure both processes are running and available at all times. |
Previous versions of Oracle Application Server (specifically, Oracle9i Application Server 9.0.2 and 9.0.3) included the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web site, a Web-based tool that offers management capabilities similar to those provided by the Application Server Control Console.
In fact, you can still use the Enterprise Manager Web site to manage previous versions of Oracle9i Application Server after you begin deploying Oracle Application Server 10g (9.0.4) and its Application Server Control.
However, if you are familiar with the Enterprise Manager Web site and you plan to continue managing previous versions of Oracle Application Server, you should be aware of several differences between the Enterprise Manager Web site and the new Application Server Control. In particular, you should note the following:
Oracle9i Application Server (9.0.2) and Oracle9i Application Server (9.0.3) used one Enterprise Manager Web site to manage all the application server instances on a host.
You could navigate to individual Enterprise Manager home pages for each application server, but only one instance of the Enterprise Manager Web site was running on the host and you managed all the application server instances from one Enterprise Manager Web site URL. This approach to application server management was convenient, but it required all application server instances to be installed and managed by the same operating system user.
The current version of Oracle Application Server provides one Application Server Control for each application server instance on a host.
For example, if you install two application server instances on a single host, and you want to manage both instances, two separate instances of the Application Server Control—one for each application server instance—must be started on the host.
As a result, each application server instance provides a unique URL (specifically, a unique HTTP Server listening port number) for accessing the Application Server Control Console.
If you have Oracle9i Application Server (9.0.2 or 9.0.3) and Oracle Application Server 10g (9.0.4) instances on the same host, and you have to deinstall a 9.0.2 or 9.0.3 instance, you must apply a patch to ensure Oracle Enterprise Manager continues to work after the change. Refer to the section on deinstallation of 9.0.2 or 9.0.3 instances from a computer that also contains 10g (9.0.4) instances in Oracle Application Server 10g Installation Guide.
At any time while using the Application Server Control Console, you can click Help at the top of the page to get more information. In most cases, the Help window displays a help topic about the current page. Click Help Contents in the Help window to browse the list of help topics or to search for a particular word or phrase.
Use the following sections to get started with the Application Server Control Console and become familiar with the Enterprise Manager home pages within the Application Server Control Console:
The following sections describe how to display the Application Server Control Console and introduce you to the initial home pages you should see when you display the Application Server Control Console for the first time:
Displaying the Application Server Control Console from the Welcome Page
Understanding the Initial Application Server Control Console Home Page
The URL for the Application Server Control Console is included in the text file that displays at the end of the Oracle Application Server installation procedure. This text file is saved in the following location after you install the application server:
(UNIX) ORACLE_HOME/install/setupinfo.txt (Windows) ORACLE_HOME\install\setupinfo.txt
The Application Server Control Console URL typically includes the name of the host computer and the port number assigned to the Application Server Control Console during the installation. For example:
http://mgmthost1.acme.com:1810
|
Note: The default port for the Application Server Control Console is usually 1810; however, if that port is in use, the installation procedure will assign another port. Refer to thesetupinfo.txt file for the exact port for your installation of Oracle Application Server.
|
To view the Application Server Control Console from the Oracle Application Server Welcome Page:
Display the Oracle Application Server Welcome Page by entering the following URL in your Web browser:
http://hostname.domain:port
For example, if you installed Oracle Application Server on a host called sys42, you would enter the following address in your Web browser:
http://sys42.acme.com:7777
|
Note: The default port for Oracle HTTP Server (and, as a result, the Welcome page) is described in the text file (setupinfo.txt) that is generated and displayed at the end of the Oracle Application Server installation.
|
Click Log on to the Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control Console.
Enterprise Manager displays the administrator logon dialog box.
Enter the Oracle Application Server administrator user name and password and click OK.
The user name for the administrator user is ias_admin. The password is the one you supplied during the installation of Oracle Application Server.
When you first display the Application Server Control Console, the initial home page you see varies depending upon whether or not the instance uses an OracleAS Metadata Repository (belongs to a farm).
|
See Also: Oracle Application Server 10g Installation Guide for your platform |
Table 2-2 describes the Enterprise Manager home pages that might be used as a starting point when you first browse to the Application Server Control Console.
Table 2-2 Enterprise Manager Home Pages for Managing Oracle Application Server
| Enterprise Manager Home Page | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Server home page | Use this home page to monitor and configure a single application server instance.
For more information, see Section 2.3.2, "Using the Application Server Home Page". The Application Server home page is the first page you see if you have installed a single application server instance that is not using an OracleAS Metadata Repository. |
| OracleAS Farm home page | Use this home page to view a list of all the application server instances that use a common OracleAS Metadata Repository.
For more information, see Section 2.3.3, "Using the Oracle Application Server Farm Home Page". The Farm home page is the first page you see if you have installed one or more application server instances that use a common set of Infrastructure Services—or more specifically, a common metadata repository. |
From the Application Server home page (Figure 2-1), you can start and stop the application server instance, monitor the overall performance of the server, and review the components of the server. You can also drill down and examine the performance of a particular component and configure the component.
If you scroll down the page, the home page provides a table that lists the components of the application server. From this table, you can also get a snapshot of how each individual component is performing.
From the System Components table, you can display a home page for each component of the application server.
You can perform the following management functions from the Instance home page:
Click Logs at the top of the page to locate and search the various Oracle Application Server log files, as well as the Oracle Application Server Log Repository.
Click J2EE Applications to display a list of the applications deployed on this instance of Oracle Application Server.
Click Ports to view a list of all the ports currently in use by the various Oracle Application Server components. You can also modify many of the port assignments when necessary.
Click Infrastructure to use Identity Management, Central Management, or the cluster capabilities of Oracle Application Server.
Click Enable/Disable Components to control whether or not the selected components are started automatically or affected by server-wide actions, such as Start All or Restart All. When a component is disabled, you can always enable it later.
For more information, click Help after selecting an option on the Application Server home page.
If your application server instance uses an OracleAS Metadata Repository, your start page for the Application Server Control Console is the OracleAS Farm home page (Figure 2-2).
|
See Also: Oracle Application Server 10g Installation Guide for your platform information about installing an OracleAS Metadata Repository |
The Farm home page displays a list of the standalone application server instances and Oracle Application Server clusters associated with your Infrastructure Services. Standalone instances are application server instances that are not part of an Oracle Application Server cluster.
You can configure your application server instance to use Infrastructure Services by clicking Infrastructure on the Application Server home page. For more information, see the Enterprise Manager online help.
Using the Farm home page, you can perform the following tasks:
Manage multiple application server instances on multiple hosts
Drill down to the Application Server home page for each instance
Create and manage Oracle Application Server clusters
|
See Also: Oracle Application Server 10g High Availability Guide for more information about using Oracle Application Server clusters |
Component home pages vary from one component to another because each component has different monitoring and configuration requirements. However, most of the component home pages have the following common elements:
A general information section that includes an icon to indicate the current state of the component and buttons for starting and stopping the component (if applicable)
Status information, including CPU and memory usage information, so you can get a snapshot of how the component is performing
Component-specific information, such as a virtual hosts tab on the HTTP Server home page or a list of deployed applications on the OC4J home page
Links to administrative functions where appropriate, so you can modify the configuration of selected components. In many cases, this means you can use a graphical user interface to modify complex configuration files.
The Application Server Control Console is designed to encourage a top-down approach to your monitoring and diagnostic activities. For example, you can start by reviewing the basic characteristics of your application server on the Application Server home page and then drill down to examine the performance of individual components of the server.
The following sections provide an outline of this monitoring methodology:
The Application Server home page provides general information about the status of your server, including the name, location, and application server availability. The home page also provides high-level information about CPU and Memory usage. When reviewing the home page, review the CPU Usage and Memory Usage charts for excessive CPU or Memory usage by the application server (Figure 2-3).
Figure 2-3 General Section of the Application Server Home Page
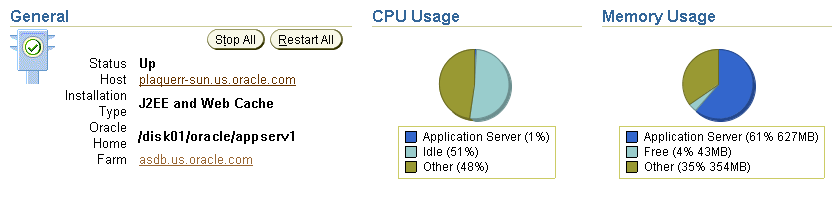
If you suspect that the application server is using too many resources, review the list of components to confirm that each component is up and running and to review the resource usage by each component (Figure 2-4).
Figure 2-4 System Components Table on the Application Server Home Page
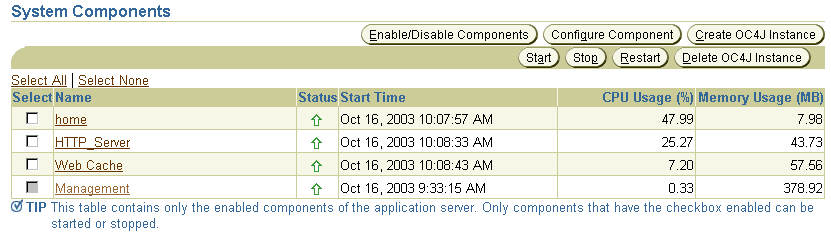
Consider disabling any components that you are not currently using as part of this application server instance. Disabled components are not started when you start the application server and as a result do not consume system resources.You can always enable a disabled application server component at a later time.
|
See Also: 'Disabling and Enabling Components" in the Enterprise Manager online help |
Many performance or configuration issues are directly related to a lack of available resources on the host. Before you drill down to analyze the performance and resource usage of the individual application server components, review the resources and characteristics of the application server host.
Click the host name in the General section of the Application Server home page to display the Host home page. The Host home page provides a summary of the operating system, memory, and disk capacity. The Load section of the page provides a CPU chart that breaks down the CPU usage into categories of usage; the load metrics beneath the chart provide details about system memory usage (Figure 2-5).
|
See Also: "About Memory Usage" in the Enterprise Manager online help for information about how Enterprise Manager calculates the memory usage for your application server. |
Figure 2-5 General Information and Load Statistics on the Host Home Page
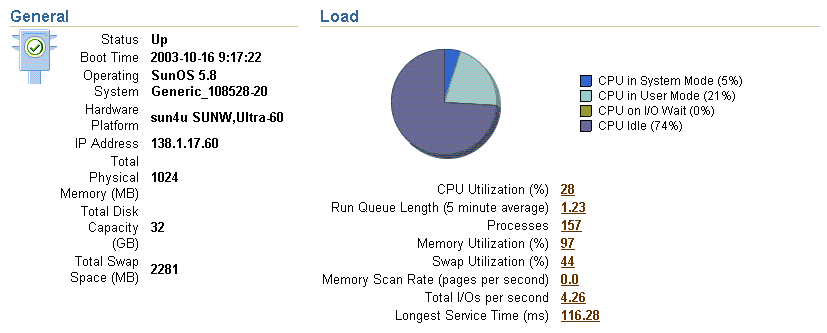
Scroll to the bottom of the page to view a set of links to real-time performance metrics. If you are concerned about the CPU and Memory usage on the system, click Top Processes to display tables listing the processes that are using the most resources on the host.
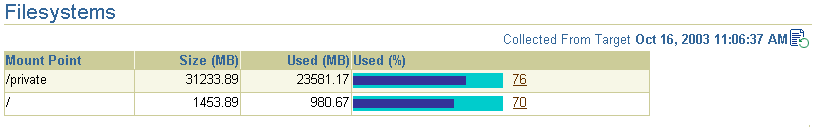
Click Filesystems to display a bar chart that reveals the amount of disk space available on the application server host (Figure 2-6).
Figure 2-6 Disk Space Usage Chart Available from the Host Home Page
After you review the high-level performance metrics and the resources available on the application server host computer, you can then begin to look for potential issues within the individual application server components.
To diagnose problems with individual application server components, click the component name in the System Components table on the Application Server home page. This technique of "drilling down" to obtain more detail can help you isolate problems in a particular component or area of the application server.
The J2EE applications you deploy and maintain with Oracle Application Server represent the most important aspects of your application server deployments. As a result, Enterprise Manager also provides a shortcut you can use to review the performance of your J2EE applications. Simply click J2EE Applications on the Application Server home page to display a list of the applications deployed from this application server instance (Figure 2-7).
Figure 2-7 List of Applications on the J2EE Applications Page
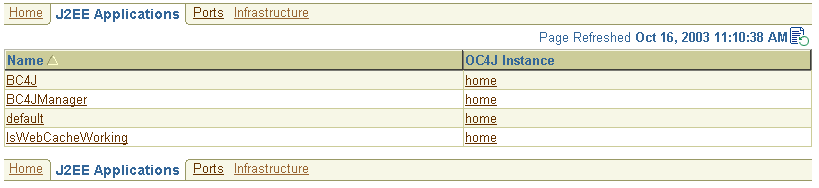
From this list of J2EE applications, you can navigate quickly to the OC4J instance or application page for information on the performance and availability of each application you have deployed.
For more complete information about monitoring Oracle Application Server, refer to the Application Server Control Console online help and the Oracle Application Server 10g Performance Guide.
Many features of Oracle Application Server depend upon OracleAS Infrastructure 10g, which uses an Oracle database to contain the OracleAS Metadata Repository. When you install the OracleAS Metadata Repository, you can choose to install a preconfigured Oracle9i database for the OracleAS Metadata Repository.
|
See Also: Oracle Application Server 10g Installation Guide for your platform |
If you have installed and deployed Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Grid Control, you can use the Grid Control Console to manage the OracleAS Metadata Repository.
However, if you are not centrally managing your environment with Grid Control, the Oracle9i database that is installed as part of OracleAS Infrastructure 10g comes with its own management tools.
Specifically, the OracleAS Metadata Repository database comes with the Enterprise Manager Java-based Console, which is part of the Enterprise Manager software provided with all Oracle9i databases.
However, this version of the Java-based Console is designed specifically to manage the OracleAS Metadata Repository database; as a result, it does not include all of the related Enterprise Manager framework components, such as the Oracle Management Server, the Management Repository, or the Intelligent Agent.
|
See Also: Oracle Enterprise Manager Concepts in the Oracle9i documentation library for more information about the Enterprise Manager framework components and architecture |
When you use the Enterprise Manager Console without a Management Server or Management Repository, you are using the Console in standalone mode.
To launch the Enterprise Manager Console in standalone mode:
Enter the following command in the Oracle home directory of your OracleAS Infrastructure 10g installation:
(UNIX) ORACLE_HOME/bin/oemapp console (Windows) ORACLE_HOME\bin\oemapp console
Enterprise Manager displays the Console login dialog box.
Select Launch Standalone and click OK.
Enterprise Manager launches the Console.
When the Console window appears, expand the Databases folder in the Navigator frame.
The OracleAS Metadata Repository database appears as an available database.
Click the plus sign (+) next to the database name.
Enterprise Manager displays the Database Connect Information dialog box.
Enter the credentials for the OracleAS Metadata Repository database and click OK.
These are the credentials you specified for the database during the OracleAS Metadata Repository installation.
When you connect to the database, a set of database objects appear in the Navigator. Objects within the Navigator can be managed via context-sensitive menus. For example, you can perform many administration tasks from the Navigator, such as creating, editing, or dropping tablespaces.
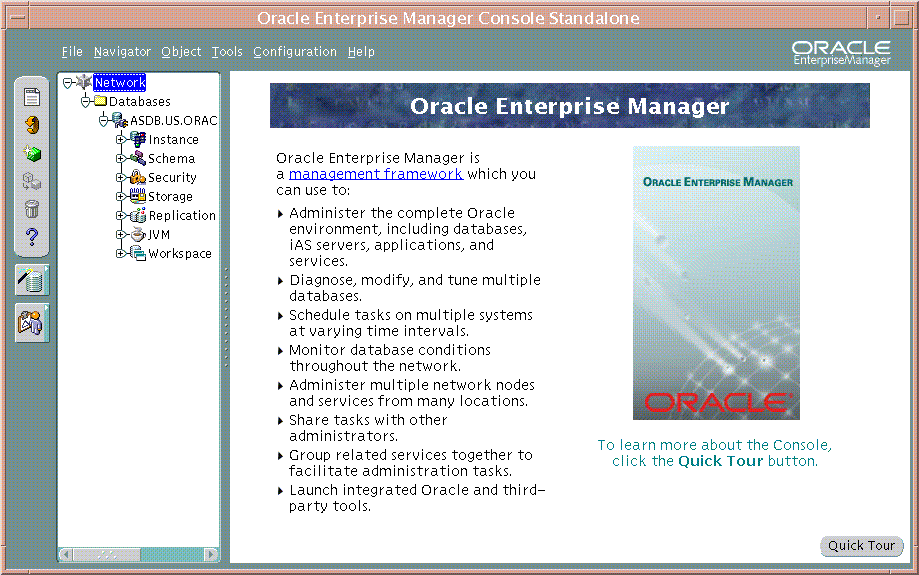
Figure 2-8 shows the Console window after you connect to the OracleAS Metadata Repository.
|
See Also: Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide in the Oracle9i documentation library and the Console online help |
Figure 2-8 Managing the OracleAS Metadata Repository with the Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Java Console
Application Server Control provides all the tools you need to manage your application server instances, farms, clusters, and system components. However, if you have an environment that includes other Oracle products and applications in addition to Oracle Application Server, consider using Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Grid Control.
Grid Control, when used with Application Server Control, provides a wider view of your Oracle environment beyond the application server. From a central location, you can use the Grid Control Console to manage databases, application servers, and Oracle applications across your entire network.
The Grid Control Console offers advanced management features, such as a notification system to notify administrators of changes in your environment and a Job system to automate standard and repetitive tasks, such as executing a SQL script or executing an operating system command.
The following sections provide more information about Grid Control:
When you centrally manage your enterprise, including your Oracle Application Server instances, you install and implement a three-tier architecture:
The Grid Control Console provides a Web-based graphical interface you can use to manage all aspects of your enterprise.
The Oracle Management Service and a database repository provide a scalable middle tier for storing crucial management data and processing system management tasks.
The Oracle Management Agent, which you install on each host computer, monitors the host services and executes tasks from the Management Service.
|
See Also: Oracle Enterprise Manager Concepts for more information about the Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g components and architecture |
You install Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Grid Control from a separate CD-ROM.
To centrally manage your enterprise, you typically perform the following steps:
Install the Management Service and the Management Repository on a host computer.
Install the Oracle Management Agent on each of the computers that you want to manage from the Grid Control Console.
|
Note: You install the Oracle Management Agent into its own Oracle Home directory on each managed hosts. |
On each host, the Management Agent gathers information about the various targets on the host. A target is a software component (such as Oracle Application Server), a host computer, and or other service that you manage with Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g.
|
See Also: Oracle Enterprise Manager Grid Control Installation and Basic Configuration for complete instructions about installing Database ControlOracle Enterprise Manager Advanced Configuration for information about starting and stopping the Grid Control components. |
After you have configured and started Oracle Management Service, you can log in to the Grid Control Console by entering the following URL in your Web browser:
http://grid_control_hostname.domain:port/em
If you are uncertain about the port number, you can refer to one of the following files:
ORACLE_HOME/install/setupinfo.txt, which includes information displayed by the Oracle Universal Installer at the end of the Grid Control install
ORACLE_HOME/install/portlist.ini on the Management Service host
When the Grid Control login page appears, enter the username and password for the Super administrator SYSMAN account, which you defined during the Grid Control installation.
After you log in, Enterprise Manager displays the Grid Control Console Home page (Figure 2-9).
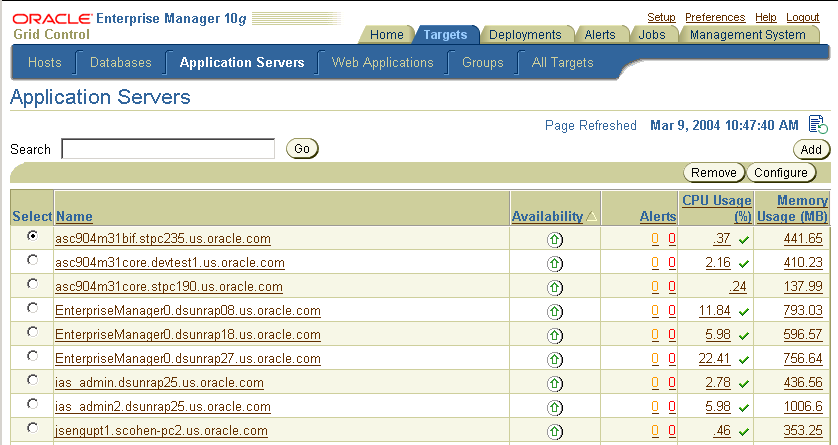
From the Grid Control Console Home page, click the Targets tab and then click Application Servers in the horizontal navigation bar. Enterprise Manager displays the Application Servers page (Figure 2-10), which lists all the application servers currently being monitored by Management Agents in your enterprise.
This list provides you with a snapshot of the availability, number of alerts, and the CPU and memory usage of each application server target.
Figure 2-10 List of Application Servers in the Grid Control Console
After you have installed the Management Agent on the Oracle Application Server hosts and have identified your application server targets in the Grid Control Console, you can perform a variety of monitoring tasks. For example, you can:
Set and adjust metric thresholds for the application servers that you monitor. You can then configure Enterprise Manager so you are notified automatically when a particular application server metric reaches its threshold.
Organize your application server targets into groups so you can monitor them as a single unit; groups also allow you to compare the performance of the application servers you monitor.
Review historical data and analyze trends in the performance of your application server components and J2EE applications.
Use Application Service Level Management to measure the performance and availability of your J2EE Web applications.
For information about starting, configuring, and using Grid Control, see the following documentation:
Oracle Enterprise Manager Grid Control Installation and Basic Configuration
Oracle Enterprise Manager Concepts
Oracle Enterprise Manager Advanced Configuration
The Grid Control Console also provides extensive online help. To display the Grid Control Console online help, click Help at the top of any of the Grid Control Console pages.