|
Oracle® Application Server 10g Administrator's Guide
10g (9.0.4) Part No. B10376-02 |
|
|
|
|
|
Oracle® Application Server 10g Administrator's Guide
10g (9.0.4) Part No. B10376-02 |
|
|
|
|
This chapter provides procedures for changing the Infrastructure Services used by a middle-tier instance.
It contains the following topics:
Changing Oracle Internet Directory from Dual Mode to SSL Mode
Changing the Metadata Repository Used by a Middle-Tier Instance
Most middle-tier instances use Infrastructure Services, such as Identity Management Services and the Metadata Repository. These services are usually assigned during installation.
After installation, you may want to change the Infrastructure Services used by a middle-tier instance. For example, you may want to use an Identity Management Service on a different host. Or, you may want to use a different Metadata Repository.
You can change Infrastructure services using the Infrastructure Page on the Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control Console, shown in figure Figure 8-1. Notice that the page allows you to change the Identity Management or the Metadata Repository used by a middle-tier instance.
Figure 8-1 Application Server Control Console Infrastructure Page
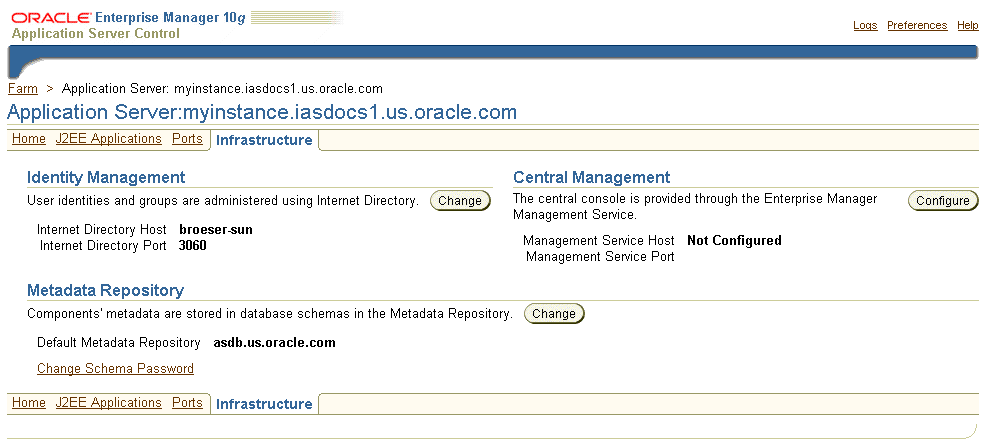
You must change Infrastructure Services when you change any of the following:
The HTTP Server (SSO) port number on an Identity Management installation
The Oracle Internet Directory non-SSL or SSL port number
The Oracle Internet Directory Mode (Dual-mode or SSL)
The host that Identity Management or the OracleAS Metadata Repository resides on
You cannot simply use the wizard to change from one Infrastructure service to another. You must first perform manual tasks in order to create and prepare the new Infrastructure service. This chapter provides the following supported procedures for changing Infrastructure services:
Changing the OID or HTTP (SSO) Ports on Identity Management
Use this procedure if you need to change the OID or HTTP listener ports on an Identity Management installation. In addition to changing the port numbers, you must update middle-tier instances with the new port information, which requires changing Infrastructure services.
Changing Oracle Internet Directory from Dual Mode to SSL Mode
Use this procedure if you would like to change the Oracle Internet Directory mode from non-SSL to SSL. In addition to changing the mode, you must update middle-tier instances with the new mode, which requires changing Infrastructure services.
Moving Identity Management to a New Host
Use this procedure if you would like to move your Identity Management installation, and its associated Metadata Repository, to a new host. After you perform the move, you must update middle-tier instances with the new host information for Identity Management, which requires changing Infrastructure services.
Changing from a Test to a Production Environment
This procedure describes how to set up an environment that allows you to develop and test applications in a test environment, then move them into a production environment.
Changing the Metadata Repository Used by a Middle-Tier Instance
Use this procedure if you would like to move the Metadata Repository used for product metadata by middle-tier instances to a new host.
If you would like to change the Oracle Internet Directory non-SSL or SSL port on an Identity Management installation, refer to Section 5.6.2, "Changing Oracle Internet Directory Ports".
If you would like to change the Oracle HTTP Server non-SSL or SSL listen port on an Identity Management installation, which effectively changes the SSO port, refer to Section 5.6.3, "Changing the HTTP Server (SSO) Port on Identity Management".
When you install Identity Management, you are asked to choose a mode for Oracle Internet Directory. The default mode is dual mode, which allows some components to access Oracle Internet Directory using non-SSL connections. During the installation, you can choose SSL mode, which specifies that all components must use SSL when connecting to the directory.
If you did not choose SSL mode during the installation, and would like to change to SSL mode after installation, you can follow the procedure in this section. It includes changing the mode of the Oracle Internet Directory, and updating middle-tier instances to use the new mode.
Task 1: Change the Oracle Internet Directory Mode
Perform this task on the Infrastructure that contains Oracle Internet Directory.
Create a file named mod.ldif that contains the following lines:
dn:cn=configset0,cn=osdldapd,cn=subconfigsubentry changetype:modify replace:orclsslenable orclsslenable:1
Run the following command:
ldapmodify -D cn=orcladmin -w orcladmin_passwd -p oid_port -v -f mod.ldif
oid_port is the non-SSL OID port. This is listed as OIDport in ORACLE_HOME/config/ias.properties.
Stop the entire instance that contains Oracle Internet Directory:
emctl stop iasconsole opmnctl stopall
Edit the following file:
(UNIX) ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/ldap.ora (Windows) ORACLE_HOME\network\admin\ldap.ora
Modify the following line to remove the non-SSL port number:
DIRECTORY_SERVERS=(myhost.myco.com::sslport)
Save and close the file.
Edit the following file:
(UNIX) ORACLE_HOME/config/ias.properties (Windows) ORACLE_HOME\config\ias.properties
Change the SSLOnly parameter as follows:
SSLOnly=true
Save and close the file.
Start the entire instance that contains Oracle Internet Directory:
opmnctl startall emctl start iasconsole
Reconfigure SSO to communicate to OID in SSL mode:
Obtain the ORASSO schema password:
ldapsearch -p oid_port -U 1 -h hostname -D "cn=orcladmin" -w orcladmin_password -b "orclresourcename=orasso, orclreferencename=global_db_name, cn=ias infrastructure databases, cn=ias, cn=products, cn=oraclecontext" -s base "objectclass=*" orclpasswordattribute
oid_port is the non-SSL OID port. This is listed as OIDport in ORACLE_HOME/config/ias.properties.
global_db_name is the name of the entry for the Metadata Repository in ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/tnsnames.ora. For example: asdb.myco.com.
This command prints the ORASSO password in a line like the following:
orclpasswordattribute=LAetjdQ5
Change to the following directory:
(UNIX) cd ORACLE_HOME/sso/admin/plsql/sso (Windows) cd ORACLE_HOME\sso\admin\plsql/sso
Run the following command:
sqlplus orasso/orasso_password @ssooconf.sql
Where orasso_password is the ORASSO schema password you obtained in the previous step.
The following prompts appear. Press return for attributes you did not change, and enter a new value for attributes that you changed.
Enter value for new_oid_host:
Press return.
Enter value for new_oid_port:
Enter the OID SSL port number and press return.
Enter value for new_sso_server_password:
Press Return.
Enter value for new_ldapusessl:
Enter Y in this field, then press return. A message appears indicating that the value new_ldapusessl has been updated.
Restart the instance that contains Oracle Internet Directory.
opmnctl stopall opmnctl startall
Task 2: Change Middle-Tier Instances to Use SSL Mode
In each middle-tier instance, run the Change Identity Management wizard and restart the instance:
Using the Application Server Control Console, navigate to the Instance Home Page for the middle-tier instance.
Click Infrastructure.
On the Infrastructure Page, in the Identity Management section, click Change.
On the Internet Directory page:
Host: Enter the fully-qualified name of the OID host.
Port: Enter the SSL OID port number.
Use only SSL connections with Internet Directory: Check this box.
Click Next.
On the Login page:
User Name: Enter cn=orcladmin, or the distinguished name of a user in the iASAdmins group.
Password: Enter the password for the user.
Click Next.
On the Validation page, you will receive informational messages regarding the validation of this operation. If you receive any error message, follow the instructions for investigating them. Otherwise, if the operation is valid, click Finish.
Edit ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/ldap.ora in the middle-tier Oracle home to remove the non-SSL port number. Change the following line from:
DIRECTORY_SERVERS = (replica_host:replica_oid_port:replica_ssl_oid_port)
to the following:
DIRECTORY_SERVERS = (replica_host::replica_ssl_oid_port)
When the operation is finished, you must restart the components in the middle-tier instance.
Click Home to navigate back to the Instance Home Page.
Click Start All.
|
Note: Now that you have disabled the non-SSL OID port, you must provide the "-U 1" option when using LDAP command-line utilities (such asldapsearch, ldapmodify, and ldapaddmt) to connect to the SSL port.
|
This section provides a procedure for moving Identity Management to a new host. This procedure involves creating a replica (or copy) of the original Identity Management on a different host, along with its own new Metadata Repository, and then changing the middle-tier instance to use the new Identity Management.
|
Note: You cannot simply change a middle-tier instance from one Identity Management to another. The new Identity Management must be a replica of the original, created using the instructions in this procedure. |
The following are sample uses for this procedure:
You have an existing Identity Management and associated Metadata Repository that is used by one or more middle-tier instances. Your organization intends to replace the current Identity Management host with a new system. You can use this procedure to create a replica of the Identity Management, along with its own Metadata Repository, and change your middle-tier instances to use the new Identity Management. You can then retire the original host.
You would like to create a failover environment for your Identity Management. You can use this procedure to create a replica of the current Identity Management, along with its own Metadata Repository. You can keep the replica running so it stays in sync with the original Identity Management. You can perform regular exports of data in the original Metadata Repository and save them. In the event that you lose the original Identity Management, you can import the data to the new Metadata Repository, and change your middle-tier instances to use the new Identity Management. Refer to Section 8.4.5, "Strategy for Performing Failover with this Procedure" for more information.
For both the original and new installations, the Identity Management and Metadata Repository can exist in the same Oracle home, or in separate Oracle homes (same or different host). If they are in separate Oracle homes, perform the operations on each in their own Oracle home.
For both the original and new installations, the Identity Management components (SSO, OID, DAS, and DIP) may exist in the same Oracle home, or may exist in separate Oracle homes (same or different host). If they exist in separate Oracle homes, perform the operations on each in their own Oracle home.
The Metadata Repository used by middle-tier instances for product metadata is not affected by this procedure.
If the middle-tier instances use product metadata in the same Metadata Repository that the original Identity Management uses, they will continue to use that Metadata Repository after they have changed to the new Identity Management. If you want, you can change them to use a different Metadata Repository after you have finished moving Identity Management. Refer to Section 8.6, "Changing the Metadata Repository Used by a Middle-Tier Instance".
If the middle-tier instances use a separate Metadata Repository for product metadata, they will continue to use that Metadata Repository after they have changed to the new Identity Management.
This procedure does not take OracleAS Certificate Authority into consideration.
|
See Also: Oracle Application Server Certificate Authority Administrator's Guide for information on updating OracleAS Certificate Authority when changing Identity Management services |
An overview of the procedure is as follows:
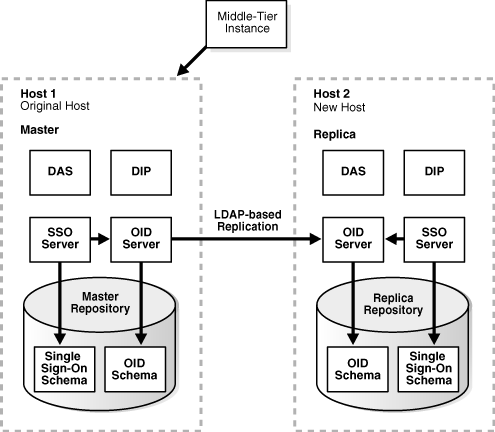
You have an original Identity Management (also called the Master) used by one or more middle-tier instances. The Identity Management has a Metadata Repository. You install and setup a new Identity Management (also called the Replica). This Identity Management has its own Metadata Repository. The Oracle Internet Directory in the new Identity Management is an LDAP-based Replica of the original OID. Replication takes place constantly from the original OID to the new OID.
Figure 8-2 shows a sample of this setup.
Figure 8-2 Original Host (Master) and New Host (Replica)
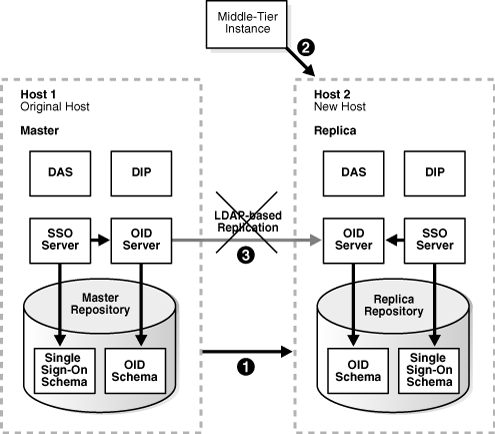
You perform the following steps to change to the new Identity Management. The steps are shown in Figure 8-3.
Step 1: Migrate SSO and DIP data from the original Metadata Repository (Master) to the new Metadata Repository (Replica)
Step 2: Change the middle-tier instances to use the new Metadata Repository.
Step 3: Stop the LDAP-based replication.
Figure 8-3 Changing from Original to New Identity Management
This procedure contains the following tasks:
Task 1: Install and Set Up the New Identity Management and Metadata Repository
Task 3: Change Middle-Tier Instances to the New Identity Management
Task 1: Install and Set Up the New Identity Management and Metadata Repository
In this task, you install and set up the new Identity Management and its associated Metadata Repository. The new Identity Management is an LDAP-based replica of the original Identity Management.
Read Section F.1, "About LDAP-based Replicas" to learn about LDAP-based Replicas and how they are used for this procedure.
Follow the procedure in Section F.2, "Installing and Setting Up an LDAP-based Replica" to install and set up the new Identity Management and Metadata Repository.
Task 2: Migrate SSO and DIP Data
In this task, you migrate the SSO and DIP data from the original Metadata Repository to the new Metadata Repository.
Follow the procedure in Section F.3, "Migrating SSO and DIP Data". The source for the migration is the original Metadata Repository (Master) and the target for the migration is the new Metadata Repository (Replica).
Task 3: Change Middle-Tier Instances to the New Identity Management
In each middle-tier instance, run the Change Identity Management wizard and restart the instance:
Using the Application Server Control Console, navigate to the Instance Home Page for the middle-tier instance.
Click Infrastructure.
On the Infrastructure Page, in the Identity Management section, click Change.
Follow the steps in the wizard for supplying the new Identity Management information.
Edit ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/ldap.ora in the middle-tier Oracle home to reflect the new OID information. Change the following line:
DIRECTORY_SERVERS = (replica_host:replica_oid_port:replica_ssl_oid_port)
When the wizard is finished, navigate to the Instance Home Page and start your instance by clicking Start All.
If you have a problem changing the middle-tier instances to the new host, check to make sure replication is running and try again.
Task 4: Stop Replication
Stop the replication between the original Identity Management and the new Identity Management (replica) by running the following command in the new Identity Management Oracle home:
oidctl connect=global_db_name server=oidrepld instance=1 flags="-p oid_port" stop
global_db_name is the global db name of the new Identity Management. (This is referred to as replica_db_name in Section F.2.)
oid_port is the non-SSL OID port in the new Identity Management. (This is referred to as replica_oid_port in Section F.2.)
As mentioned in Section 8.4.1, "Sample Uses for this Procedure", you can modify this procedure to perform failover for Identity Management. This enables you to move your middle-tier instances to the new Identity Management in case the original is lost.
To perform failover:
Install and set up the new Identity Management as described in Task 1: Install and Set Up the New Identity Management and Metadata Repository.
Export SSO and DIP data on a regular basis from the original Metadata Repository. You do not need to import the data into the new Metadata Repository. You only need to export the data and copy the files to the new Metadata Repository Host. Refer to Section F.3, "Migrating SSO and DIP Data".
If you lose the original Identity Management:
Stop replication. Refer to Task 4: Stop Replication.
Import your most recent copy of the SSO and DIP data into the new Identity Management repository. Refer to Section F.3, "Migrating SSO and DIP Data".
Change the middle-tier instances to use the new Identity Management. Refer to Task 3: Change Middle-Tier Instances to the New Identity Management.
This section provides a procedure for changing from a test to production environment. This allows you to have a test environment for your applications, and then move your test applications and, optionally, test data into your production environment.
The following are sample uses for this procedure:
You have a production environment, and would like to create a test environment for developing and testing your applications. You would then like to roll out these applications to your production environment.
You have a Oracle9iAS Release 2 (9.0.2/9.0.3) production environment, and would like to create an Oracle Application Server 10g (9.0.4) test environment to test your applications before upgrading.
|
See Also: Oracle Application Server 10g Upgrading to 10g (9.0.4) for compatibility rules for different versions of Oracle9iAS and Oracle Application Server |
An overview of the procedure is as follows:
You have an existing production environment that includes middle-tier instances, an Identity Management installation with a Metadata Repository, and one or more Metadata Repositories used for product metadata.
You create a test environment by installing and setting up a replica (or copy) of the production Identity Management. This Identity Management has its own Metadata Repository. The Oracle Internet Directory in the test Identity Management is an LDAP-based Replica of the production OID. Replication takes place constantly from the production OID to the test OID.This replica has its own Metadata Repository. You then install test middle-tier instances to use the test Identity Management. These middle-tier instances use a separate Metadata Repository for their product metadata. You can develop and test your applications in the test environment.
Figure 8-4 shows a sample production and test environment.
When you are ready to roll out your test applications to your production environment, you perform the following steps. The steps are shown in Figure 8-5.
Step 1: Migrate data from the test environment to the production environment
Step 2: Change the test middle-tier instances to use the production environment.
You have several options for the test Metadata Repository used for product metadata:
You can continue to use the test Metadata Repository in your production environment, thereby deeming it to be a production Metadata Repository.
You can copy the Metadata Repository to a production host and change your middle-tier instances to use it.
If you do not want to retain the test data in the Metadata Repository, you can install a new Metadata Repository in the production environment, and change the middle-tier instances to use that.
You may have used a production Metadata Repository to begin with, in which case you can just continue to use that.
|
Note: You cannot copy parts of a product Metadata Repository to another Metadata Repository; you must copy the entire database. Therefore, it is not possible to migrate only some of your test product metadata to the production environment. You must copy the entire Metadata Repository. Refer to Section 8.6, "Changing the Metadata Repository Used by a Middle-Tier Instance". |
This procedure contains the following tasks:
Task 1: Install and Set Up the Test Identity Management and Metadata Repository
Task 3: Start the Test Oracle Internet Directory in Pilot Mode
Task 6: Migrate Data from the Test to Production Environment
Task 7: Change Middle-Tier Instances to the Production Identity Management
Task 8: Move the Test Product Metadata Repository to Production
Task 1: Install and Set Up the Test Identity Management and Metadata Repository
In this task, you install and set up the test Identity Management and its associated Metadata Repository. The test Identity Management is an LDAP-based replica of the original Identity Management.
Read Section F.1, "About LDAP-based Replicas" to learn about LDAP-based Replicas and how they are used for this procedure.
Follow the procedure in Section F.2, "Installing and Setting Up an LDAP-based Replica" to install and set up the test Identity Management and Metadata Repository.
Task 2: Identify the Replica as a Pilot Replica
Perform this task in the Oracle home of the test (replica) Oracle Internet Directory:
Create a file called mod.ldif that contains the following lines:
dn:orclreplicaid=replica_replicaid,cn=replication configuration changetype:modify replace:orclreplicatype orclreplicatype:2
Where replica_replicaid is the test (replica) replica ID you obtained in Section F.2, "Installing and Setting Up an LDAP-based Replica".
Run the following command:
ldapmodify -D cn=orcladmin -w replica_orcladmin_passwd -p replica_oid_port -v -f mod.ldif
Where replica_orcladmin_passwd is the test (replica) orcladmin password and replica_oid_port is the test (replica) non-SSL OID port you obtained in Section F.2, "Installing and Setting Up an LDAP-based Replica".
Restart OID on the test (replica) node:
opmnctl stopproc ias-component=OID opmnctl startproc ias-component=OID
Task 3: Start the Test Oracle Internet Directory in Pilot Mode
Perform this task in the Oracle home of the test (replica) Oracle Internet Directory:
Create a file called mod.ldif that contains the following lines:
dn:orclreplicaid=replica_replicaid,cn=replication configuration changetype:modify replace:orclpilotmode orclpilotmode:1
Where replica_replicaid is the test (replica) replica ID you obtained in Section F.2, "Installing and Setting Up an LDAP-based Replica".
Run the following command:
ldapmodify -D cn=orcladmin -w replica_orcladmin_passwd -p replica_oid_port -v -f mod.ldif
Where replica_orcladmin_passwd is the test (replica) orcladmin password and replica_oid_port is the test (replica) non-SSL OID port you obtained in Section F.2, "Installing and Setting Up an LDAP-based Replica".
Task 4: Install Test Middle-Tier Instances
Install your test middle-tier instances and configure them to use the test Identity Management. You should use a separate Metadata Repository for the product metadata.
Task 5: Develop and Test Your Applications
Develop and test application in your test environment.
Task 6: Migrate Data from the Test to Production Environment
When you are ready to move your applications from your test to production environment, you must migrate data.
Follow the procedure in Section F.4, "Migrating Oracle Internet Directory Data".
Task 7: Change Middle-Tier Instances to the Production Identity Management
In each middle-tier instance, run the Change Identity Management wizard and restart the instance:
Using the Application Server Control Console, navigate to the Instance Home Page for the middle-tier instance.
Click Infrastructure.
On the Infrastructure Page, in the Identity Management section, click Change.
Follow the steps in the wizard for supplying the production Identity Management information.
Edit ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/ldap.ora in the middle-tier Oracle home to reflect the new OID information. Change the following line:
DIRECTORY_SERVERS = (replica_host:replica_oid_port:replica_ssl_oid_port)
When the wizard is finished, navigate to the Instance Home Page and start your instance by clicking Start All.
Task 8: Move the Test Product Metadata Repository to Production
You have several options for moving your test product Metadata Repository to your production environment:
You can continue to use the test Metadata Repository in your production environment, thereby deeming it to be a production Metadata Repository.
In this case, no further action is required.
You can copy the Metadata Repository to a production host and change your middle-tier instances to use it.
Follow the procedure in Section 8.6, "Changing the Metadata Repository Used by a Middle-Tier Instance".
If you do not want to retain the test data in the Metadata Repository, you can install a new Metadata Repository in the production environment, and change the middle-tier instances to use that.
Install an Infrastructure using Oracle Universal Installer. Select the Metadata Repository only option. Register the Metadata Repository with the production Identity Management.
Change each of the former test middle-tier instances to use the new Metadata Repository. On each middle-tier instance:
Using the Application Server Control Console, navigate to the Instance Home Page for the middle-tier instance.
Click Infrastructure.
On the Infrastructure Page, in the Metadata Repository section, click Change.
Follow the steps in the wizard for supplying the new Metadata Repository information.
When the wizard is finished, navigate to the Instance Home Page and start your instance by clicking Start All.
Task 9: (Optional) Continue to Use Your Test Environment
You can continue to use your test environment by installing new middle-tier instances against the test Identity Management.
This section provides a procedure for changing the Metadata Repository used by a middle-tier instance. This procedure involves making a copy of the original Metadata Repository on a different host, and then changing the middle-tier instance to use the new Metadata Repository.
|
Note: You cannot simply change a middle-tier instance from one Metadata Repository to another. The new Metadata Repository must be a copy of the original, created using the instructions in this procedure. |
The following are sample uses for this procedure:
You have an existing Metadata Repository that is used by one or more middle-tier instances. Your organization intends to replace the current Metadata Repository host with a new system. You can use this procedure to copy the Metadata Repository to the new host and change your middle-tier instances to use the new Metadata Repository. You can then retire the original host.
You would like to move a Metadata Repository from a host in your test environment, to a host in your Production Environment. You can use this procedure to copy the Metadata Repository from the test to production host, and change your test middle-tier instances to use the new Metadata Repository.
The middle-tier instances must use Identity Management
That Identity Management must not use the original Metadata Repository for its Identity Management schemas; it must use a separate Metadata Repository
The original Metadata Repository:
Must be used for product metadata and DCM management only (it cannot be used by Identity Management)
Must be registered with Oracle Internet Directory
The new Metadata Repository:
Must not be registered with OID initially. During the procedure, you will register it with the same OID as the original Metadata Repository.
Must be created with the same Oracle home, datafile location, SID, and global database name as the original Metadata Repository. You will eventually change the global database name to a unique name.
This procedure does not take OracleAS Certificate Authority into consideration.
|
See Also: Oracle Application Server Certificate Authority Administrator's Guide for information on updating OracleAS Certificate Authority when changing Metadata Repository services |
If the Metadata Repository is used for OracleAS Clusters, the cluster members will not be accessible until all members of the cluster have been changed over to the new Metadata Repository.
An overview of the procedure is as follows:
You have an original Metadata Repository. It is used by one or more middle-tier instances for product metadata. The middle-tier instances use Identity Management, and the Metadata Repository is registered with Oracle Internet Directory in that Identity Management.
Figure 8-6 shows a sample original Metadata Repository (asdb1.myco.com).
The following table shows sample attributes for the original Metadata Repository:
| Attribute | Original Metadata Repository | New Metadata Repository |
|---|---|---|
| Oracle home | /private/oraHome
|
N/A |
| Datafile location | /private/oraHome/oradata
|
N/A |
| SID | asdb1
|
N/A |
| Global db name | asdb1.myco.com
|
N/A |
| Registered with OID? | Yes | N/A |
You create a copy of the original Metadata Repository by installing a new Metadata Repository, backing up the original Metadata Repository, and restoring to the new Metadata Repository.
Figure 8-7 shows sample original and new Metadata Repositories.
Figure 8-7 Original Metadata Repository and New Metadata Repository
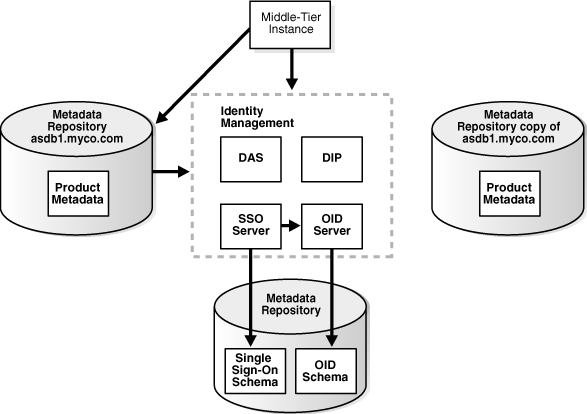
The following table shows sample attributes for the original and new Metadata Repositories:
| Attribute | Original Metadata Repository | New Metadata Repository |
|---|---|---|
| Oracle home | /private/oraHome
|
/private/oraHome
|
| Datafile location | /private/oraHome/oradata
|
/private/oraHome/oradata
|
| SID | asdb1
|
asdb1
|
| Global db name | asdb1.myco.com
|
asdb1.myco.com
|
| Registered with OID? | Yes | No |
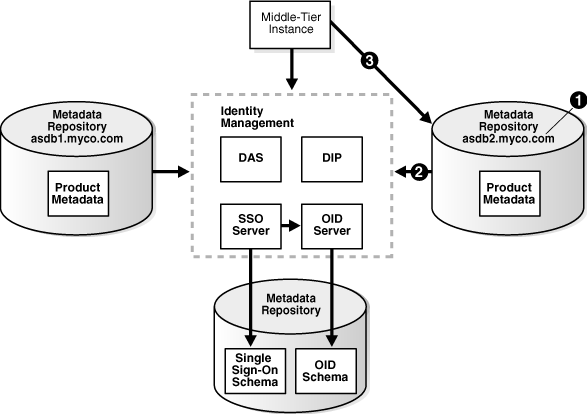
You perform the following steps to change to the new Metadata Repository. The steps are shown in Figure 8-8.
Step 1: Change the global db name of the new Metadata Repository to a unique name (in this sample, asdb2.myco.com).
Step 2: Register the new Metadata Repository with the same Oracle Internet Directory as the old Metadata Repository.
Step 3: Change the middle-tier instances to use the new Metadata Repository.
Figure 8-8 Changing from the Original to the New Metadata Repository
| Attribute | Original Metadata Repository | New Metadata Repository |
|---|---|---|
| Oracle home | /private/oraHome
|
/private/oraHome
|
| Datafile location | /private/oraHome/oradata
|
/private/oraHome/oradata
|
| SID | asdb1
|
asdb1
|
| Global db name | asdb1.myco.com
|
asdb2.myco.com
|
| Registered with OID? | Yes | Yes |
If you are using the scenario where you no longer require the original Metadata Repository, you can discard the original Metadata Repository.
This procedure contains the following tasks:
Task 4: Configure Ultra Search Metadata in the New Metadata Repository
Task 5: Change the Global DB Name for the New Metadata Repository
Task 7: Change Middle-Tier Instances to the New Metadata Repository
Before You Begin
If your middle-tier instances use OracleAS Portal and Oracle Ultra Search, you will need to supply the WKSYS schema password later in this procedure in Task 4: Configure Ultra Search Metadata in the New Metadata Repository. You should obtain this password now from the old Metadata Repository.
Task 1: Install the New Metadata Repository
Install the new Metadata Repository as follows:
Make sure to install the Metadata Repository into an Oracle home that has the same path as the old Metadata Repository Oracle home
Use Oracle Universal Installer to install the Metadata Repository
Choose to install an Infrastructure
Choose to install a Metadata Repository only
Do not register the Metadata Repository with OID
Specify the same SID and global db name as the old Metadata Repository
Specify the same datafile location as the old Metadata Repository
Task 2: Back Up the Original Metadata Repository
In this task, you create a backup of the original Metadata Repository. This task provides the steps for doing this using RMAN, however, if you are an experience DBA, you can back up the Metadata Repository according to your standard practices.
Perform all of the steps in this task on the original Metadata Repository host.
Create directories to store backup files and log files. For example:
mkdir -p BACKUP_DIR/log_files mkdir -p BACKUP_DIR/db_files
Make sure the original Metadata Repository is up and running.
Make sure you have set the ORACLE_HOME and ORACLE_SID environment variables you run the SQL*Plus command.
Obtain the DBID of the original Metadata Repository using SQL*Plus:
SQL> SELECT DBID FROM v$database;
Make note of this value; you will use it later in the procedure.
Create a file named BACKUP_DIR/cold_backup.rcv that contains the following lines. In the file, substitute the full path for BACKUP_DIR.
shutdown immediate;
startup mount;
configure controlfile autobackup on;
configure controlfile autobackup format for device type disk to 'BACKUP_DIR/db_files/%F';
run {
allocate channel dev1 device type disk format
'BACKUP_DIR/db_files/%U';
backup database plus archivelog;
release channel dev1;
}
Run RMAN to back up the Metadata Repository (the following is a single command; type it all on one line):
ORACLE_HOME/bin/rman target cmdfile=BACKUP_DIR/cold_backup.rcv > BACKUP_DIR/log_files/backup.log
Copy the backup directories to the new host. You do not need to use the same path for BACKUP_DIR on the new host.
BACKUP_DIR/log_files BACKUP_DIR/db_files
Task 3: Restore the Backup to the New Metadata Repository
In this task you restore the backup to the new Metadata Repository.
Perform all of the steps in this task on the new Metadata Repository host.
Make sure the new Metadata Repository is down:
sqlplus "sys/SYS_PASSWORD as sysdba" SQL> shutdown immediate;
Regenerate the password file:
On UNIX:
prompt> mv ORACLE_HOME/dbs/orapwORACLE_SID ORACLE_HOME/dbs/orapwORACLE_SID.old prompt> ORACLE_HOME/bin/orapwd file=ORACLE_HOME/dbs/orapwORACLE_SID password=new_password
On Windows:
prompt> mv ORACLE_HOME\database\PWDORACLE_SID.ora ORACLE_HOME\database\PWDORACLE_SID.ora.old prompt> ORACLE_HOME\bin\orapwd file=ORACLE_HOME\database\PWDORACLE_SID.ora password=new_password
new_password is the new SYS password. You can use the old SYS password, or set it to a new password.
Start the new Metadata Repository but do not mount it:
SQL> startup nomount;
Create a file named BACKUP_DIR/restore.rcv that contains the following lines. In the file, substitute the full path for BACKUP_DIR and the DBID obtained in the previous task.
set dbid=DBID;
connect target /;
set controlfile autobackup format for device type disk to 'BACKUP_DIR/db_files/%F';
restore controlfile from autobackup;
startup mount force;
run {
allocate channel dev1 device type disk format
'BACKUP_DIR/db_files/%U';
restore database;
release channel dev1;
alter database open resetlogs;
}
Run RMAN to restore the Metadata Repository:
prompt> ORACLE_HOME/bin/rman cmdfile=BACKUP_DIR/restore.rcv > BACKUP_DIR/log_files/restore.log
After you restore using RMAN, determine if the TEMP tablespace has a datafile by connecting to the database as a use with SYSDBA privileges and running the following command in SQL*Plus:
SQL> select file_name from dba_temp_files where tablespace_name like 'TEMP';
If the preceding command does not return any files, add a datafile:
SQL> alter tablespace "TEMP" add tempfile 'ORACLE_HOME/oradata/ \ db_name/temp01.dbf' size 5120K autoextend on next 8k maxsize unlimited;
Where db_name is the first portion of the new global db name.
Note that the above command creates a file called temp01.dbf and adds it to the TEMP tablespace. If the temp01.dbf file already exists in the directory, add a "reuse" clause to the command:
SQL> alter tablespace "TEMP" add tempfile 'ORACLE_HOME/oradata/ \ db_name/temp01.dbf' size 5120K reuse autoextend on next 8k maxsize unlimited;
Task 4: Configure Ultra Search Metadata in the New Metadata Repository
Perform this task on the new Metadata Repository.
Make sure the ORACLE_HOME and ORACLE_SID environment variables are set.
Run the following commands:
cd ORACLE_HOME/ultrasearch/admin sqlplus "sys/SYS_PASSWORD as sysdba" SQL> @wk0config.sql WKSYSPW JDBC_CONNSTR LAUNCH_ANYWHERE ""
Where:
WKSYSPW is the password of the WKSYS schema that you obtained at the beginning of this procedure.
JDBC_CONNSTR is the JDBC connection string host:port:SID, for example: myhost:1521:testdb.
LAUNCH_ANYWHERE is TRUE if the Metadata Repository is in Real Application Cluster mode, otherwise FALSE. For this procedure, you should set it to FALSE.
Task 5: Change the Global DB Name for the New Metadata Repository
In this task, you change the global db name of the new Metadata Repository to a new, unique name so you can register it with OID.
|
See Also: You can find more information on changing the global db name in article 137483.1 athttp://metalink.oracle.com
|
Perform all of the steps in this task on the new Metadata Repository host.
Run the following commands to set up the database:
sqlplus "sys/SYS_PASSWORD as sysdba" SQL> alter system switch logfile; SQL> alter database backup controlfile to trace resetlogs;
Check the spfile using SQL*Plus:
SQL> select value from v$parameter where name='spfile';
If the previous command returns no rows, you can skip this step.
If the previous command returns output like the following:
VALUE ---------------------------------- ?/dbs/spfile@.ora
run the following command to create a pfile from the spfile:
SQL> create pfile='initORACLE_SID.ora' from spfile;
Where ORACLE_SID is the SID of the original and new Metadata Repository.
Shut down the new Metadata Repository:
SQL> shutdown immediate;
The database must be shut down with SHUTDOWN NORMAL or SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE. You should not use SHUTDOWN ABORT.
Rename the spfile so the pfile will be used when the database instance is restarted:
cd ORACLE_HOME/dbs mv spfileORACLE_SID.ora spfileORACLE_SID.ora.save
Edit the following file:
On UNIX:
ORACLE_HOME/dbs/initORACLE_SID.ora
On Windows:
ORACLE_HOME\database\initORACLE_SID.ora
Update the db_name to the new db name (the first portion of the new global db name). For example, if the new global db name is asdb1.myco.com, the value of db_name should be asdb1. Note that this is not necessarily (nor likely) the same value as the SID on the new Metadata Repository.
Rename the following directory with the new db_name:
ORACLE_HOME/oradata/db_name
Rename the control files so they do not exist later when the new ones are created:
cd ORACLE_HOME/oradata/db_name mv control01.ctl control01.ctl.old mv control02.ctl control02.ctl.old mv control03.ctl control03.ctl.old
Rename the following directory with the new db_name:
ORACLE_HOME/admin/db_name
Edit the following file:
On UNIX:
ORACLE_HOME/admin/db_name/pfile/initORACLE_SID.ora
On Windows:
ORACLE_HOME\admin\db_name\pfile\init.ora
Change all instances of the old db name to the new db name; do not update the SID. To do this, change the old db name in all directory paths and the db_name parameter. Do not update the instance_name parameter, because that is set to the SID.
Change to the trace file directory:
cd ORACLE_HOME/admin/db_name/udump
Note that the above is the default location for the trace file directory. This location can be overridden by the user_dump_dest parameter in initORACLE_SID.ora or spfileORACLE_SID.ora.
Locate the trace file; it has a name of the form oraNNNNN.trc, where NNNNN is a number. Choose the trace file with the most recent modification date.
Copy the contents of the trace file, starting from the line with "STARTUP NOMOUNT" down to the end of the file, into a new file named BACKUP_DIR/ccf.sql.
Edit BACKUP_DIR/ccf.sql as follows (an example of ccf.sql after performing the edits in this step is shown in Example 8-1.)
Update the following line with the new global db name and change "REUSE" to "SET":
Before modification:
CREATE CONTROLFILE REUSE DATABASE "OLD_GLOBAL_DB_NAME" RESETLOGS ...
After modification:
CREATE CONTROLFILE SET DATABASE "NEW_GLOBAL_DB_NAME" RESETLOGS ...
Remove the following line:
# STANDBY LOGFILE
Comment out the following lines, if they exist, with "REM", as shown:
REM RECOVER DATABASE USING BACKUP CONTROLFILE
REM VARIABLE RECNO NUMBER;
REM EXECUTE :RECNO := SYS.DBMS_BACKUP_RESTORE.SETCONFIG('CONTROLFILE
AUTOBACKUP','ON');
REM VARIABLE RECNO NUMBER;
REM EXECUTE :RECNO := SYS.DBMS_BACKUP_RESTORE.SETCONFIG('CONTROLFILEAUTOBACKUP FORMAT FOR DEVICE TYPE','DISK TO BACKUP_DIR/db_files/%F');
REM ALTER TABLESPACE TEMP ADD TEMPFILE 'ORACLE_HOME/TEMP01.DBF' SIZE 5242880 AUTOEXTEND ON MAXSIZE 4294950912 REUSE;
Change all comment symbols (#) to "REM".
Example 8-1 Example ccf.sql File after Edits
STARTUP NOMOUNT
CREATE CONTROLFILE set DATABASE "<NEW DATABASE>" RESETLOGS ARCHIVELOG
MAXLOGFILES 50
MAXLOGMEMBERS 5
MAXDATAFILES 100
MAXINSTANCES 1
MAXLOGHISTORY 226
LOGFILE
GROUP 1 '/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/redo01.log' SIZE 50M,
GROUP 2 '/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/redo02.log' SIZE 50M,
GROUP 3 '/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/redo03.log' SIZE 50M
DATAFILE
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/system01.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/undotbs01.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/drsys01.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/dcm.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/portal.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/ptldoc.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/ptlidx.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/ptllog.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/oca.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/discopltc1.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/discopltm1.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/oss_sys01.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/wcrsys01.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/uddisys01.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/ip_dt.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/ip_rt.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/ip_idx.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/ip_lob.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/attrs1_oid.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/battrs1_oid.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/gcats1_oid.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/gdefault1_oid.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/svrmg1_oid.dbf',
'/private1/inst/oradata/asdb/ias_meta01.dbf'
CHARACTER SET WE8MSWIN1252
;
REM Configure RMAN configuration record 1
REM VARIABLE RECNO NUMBER;
REM EXECUTE :RECNO := SYS.DBMS_BACKUP_RESTORE.SETCONFIG('CONTROLFILE
AUTOBACKUP','ON');
REM Configure RMAN configuration record 2
REM VARIABLE RECNO NUMBER;
REM EXECUTE :RECNO := SYS.DBMS_BACKUP_RESTORE.SETCONFIG('CONTROLFILE AUTOBACKUP
FORMAT FOR DEVICE TYPE','DISK TO /private1/inst/backup_dir/db_files/%F');
REM Recovery is required if any of the datafiles are restored backups,
REM or if the last shutdown was not normal or immediate.
REM RECOVER DATABASE USING BACKUP CONTROLFILE
REM Database can now be opened zeroing the online logs.
ALTER DATABASE OPEN RESETLOGS;
REM No tempfile entries found to add.
Determine if the TEMP tablespace has a datafile by connecting to the database as a use with SYSDBA privileges and running the following command in SQL*Plus:
SQL> select file_name from dba_temp_files where tablespace_name like 'TEMP';
If the preceding command does not return any files, add a datafile:
SQL> alter tablespace "TEMP" add tempfile 'ORACLE_HOME/oradata/ \ db_name/temp01.dbf' size 5120K autoextend on next 8k maxsize unlimited;
Where db_name is the first portion of the new global db name.
Note that the above command creates a file called temp01.dbf and adds it to the TEMP tablespace. If the temp01.dbf file already exists in the directory, add a "reuse" clause to the command:
SQL> alter tablespace "TEMP" add tempfile 'ORACLE_HOME/oradata/ \ db_name/temp01.dbf' size 5120K reuse autoextend on next 8k maxsize unlimited;
Run the ccf.sql script:
SQL> @BACKUP_DIR/ccf.sql
Change the global db name in the database:
SQL> alter database rename global_name to NEW_GLOBAL_DB_NAME;
Update the service name and the global db name to the new global db name in the following files:
ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/tnsnames.ora (UNIX) ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/listener.ora (Windows) ORACLE_HOME\network\admin\listener.ora
Note that you should not change the SID.
Edit the following file:
(UNIX) ORACLE_HOME/config/ias.properties (Windows) ORACLE_HOME\config\ias.properties
Change the InfrastructureDBCommonName parameter to the new global db name.
Task 6: Register the New Metadata Repository with OID
In this task, you register the new Metadata Repository with the same OID used by the original Metadata Repository. To do this, you run Oracle Application Server Repository Creation Assistant (OracleAS RepCA), a wizard that guides you through the registration.
|
Note: OracleAS RepCA is available on the "OracleAS RepCA and Utilities" CD-ROM. |
To register the new Metadata Repository with Oracle Internet Directory, start up OracleAS RepCA on the host where the new Metadata Repository is installed:
runRepca -OH ORACLE_HOME -REGISTER
Where ORACLE_HOME is the new Metadata Repository Oracle home.
The wizard will guide you through the process.
|
See Also: Oracle Application Server 10g Installation Guide for more information on registering the OracleAS Metadata Repository with Oracle Internet Directory |
Task 7: Change Middle-Tier Instances to the New Metadata Repository
On each middle-tier instance you want to change to the new Metadata Repository, run the Change Metadata Repository wizard and restart the instance:
Using the Application Server Control Console, navigate to the Instance Home Page for the middle-tier instance.
Make sure all components except Management are down. If not, click the Stop All button to stop them. Note that this will not stop Management.
Click Infrastructure.
On the Infrastructure Page, in the Metadata Repository section, click Change.
Follow the steps in the wizard for supplying the new Metadata Repository information.
When the wizard is finished, navigate to the Instance Home Page and start your instance by clicking Start All.
Task 8: Update the Farm Name
Run the following command in the Oracle home of one of the middle-tier instances that you changed to use the new Metadata Repository in the previous task:
ORACLE_HOME/dcm/bin/dcmctl resetFarmName new_farm_name
Where new_farm_name is the global db name of the new Metadata Repository.
|
Note: You only need to run the command in one middle-tier instance. The command will update all other instances. |