javax.microedition.media
Interface Player
- All Superinterfaces:
- Controllable
- public interface Player
- extends Controllable
Player controls the rendering of time based media data.
It provides the methods to manage the Player's life
cycle, controls the playback progress, obtains the presentation
components, controls and provides the means to synchronize
with other Players.
Simple Playback
A Player can be created from one of the
Manager's createPlayer methods.
After the Player is created,
calling start will start the playback as soon as possible.
The method will return when the
playback is started. The playback will continue in the background
and will stop automatically when the end of media is reached.
Simple playback example illustrates this.
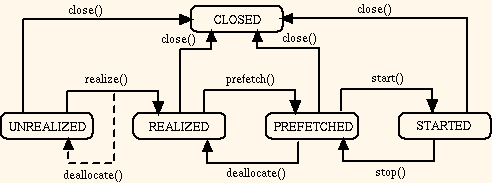
Player Life Cycle
A Player has five states:
UNREALIZED,
REALIZED,
PREFETCHED,
STARTED,
CLOSED.
The purpose of these life-cycle states is to provide
programmatic control over potentially time-consuming operations.
For example, when a Player is first constructed, it's in
the UNREALIZED state.
Transitioned from UNREALIZED to REALIZED, the
Player
performs the communication necessary to locate all of the resources
it needs to function (such as communicating with a server
or a file system).
The realize method allows an application to initiate this
potentially time-consuming process at an
appropriate time.
Typically, a Player moves from the UNREALIZED state
to the REALIZED state, then to the PREFETCHED state,
and finally on to the STARTED state.
A Player stops when it reaches the
end of media; when
its stop time is reached;
or when the stop method is invoked.
When that happens, the Player moves from the
STARTED state
back to the PREFETCHED state.
It is then ready to repeat the cycle.
To use a Player, you must set up parameters to
manage its movement through these life-cycle states and then
move it through the states using the Player's
state transition methods.
Player States
This section describes the semantics of each of the Player
states.
UNREALIZED State
A Player starts in
the UNREALIZED state.
An unrealized Player
does not have enough information to acquire all the resources it needs
to function.
The following methods must not be used
when the Player is in
the UNREALIZED state.
-
getContentType
-
setTimeBase
-
getTimeBase
-
setMediaTime
-
getControls
-
getControl
An IllegalStateException will be thrown.
The realize method transitions
the Player from the UNREALIZED state to the
REALIZED state.
REALIZED State
A Player is in the REALIZED state when it
has obtained
the information required to acquire the media resources.
Realizing a Player can be a resource and
time consuming process.
The Player may have to communicate with
a server, read a file, or interact with a set of objects.
Although a realized Player does not have
to acquire any resources, it
is likely to have acquired all of the resources it needs except
those that imply exclusive use of a
scarce system resource, such as an audio device.
Normally, a Player moves from the UNREALIZED state
to the REALIZED state.
After realize has been
invoked on a Player,
the only way it can return
to the UNREALIZED state is if
deallocate is
invoked before realize is completed.
Once a Player reaches the REALIZED state, it
never returns to the UNREALIZED state. It remains in one of four
states: REALIZED, PREFETCHED, STARTED or
CLOSED.
PREFETCHED State
Once realized, a Player may still need to
perform a number of time-consuming tasks before it is ready to be started.
For example, it may need to acquire scarce or exclusive resources,
fill buffers with media data, or perform other start-up processing.
Calling
prefetch
on the Player carries
out these tasks.
Once a Player is in the PREFETCHED state, it may
be started.
Prefetching reduces the startup latency of a Player
to the minimum possible value.
When a started Player stops,
it returns
to the PREFETCHED state.
STARTED State
Once prefetched, a Player can enter the
STARTED state by calling the
start method.
A STARTED Player
means the Player is running and processing data.
A Player returns to the PREFETCHED
state when it stops, because the
stop method was invoked,
it has reached the end of the media, or its stop time.
When the Player moves from the PREFETCHED
to the STARTED state, it posts a STARTED event.
When it moves from the STARTED state to the
PREFETCHED state,
it posts a STOPPED, END_OF_MEDIA or
STOPPED_AT_TIME event depending on the reason it
stopped.
The following methods must not be used
when the Player is in the STARTED state:
An IllegalStateException will be thrown.
CLOSED state
Calling close on the Player
puts it in the CLOSED state. In the CLOSED
state, the Player has
released most of its resources and must not
be used again.
The Player's five states and the state transition
methods are summarized in the following diagram:
Player Events
Player events asynchronously deliver
information about the Player's state changes
and other relevant information from the Player's
Controls.
To receive events, an object must implement the
PlayerListener interface and use the
addPlayerListener method to register its
interest in a Player's events.
All Player events are posted to each
registered listener.
The events are guaranteed to be delivered in the order
that the actions representing the events occur.
For example, if a Player
stops shortly after it starts because it is playing back
a very short media file, the STARTED event
must always
preceed the END_OF_MEDIA event.
An ERROR event may be sent any time
an irrecoverable error has occured. When that happens, the
Player is in the CLOSED state.
The Player event mechanism is extensible and
some Players define events other than
the ones described here. For a list of pre-defined player
events, check the PlayerListener interface.
Managing the Resources Used by a Player
The prefetch
method is used to acquire scarce or exclusive resources
such as the audio device.
Conversely, the deallocate
method is used to release the scarce or exclusive
resources. By using these two methods, an application can
programmatically manage the Player's resources.
For example, in an implementation with an exclusive audio device, to
alternate the audio playback of multiple Players,
an application can selectively deallocate and prefetch individual
Players.
Player's TimeBase
The TimeBase of a Player provides the
basic measure of time for the Player to synchronize
its media playback. Each Player must provide one
default TimeBase. The getTimeBase
method can be used to retrieve that.
Setting a different TimeBase on a
Player instructs the Player to synchronize
its playback rate according to the given TimeBase.
Two Players can be synchronized by getting the
TimeBase from one Player and setting
that on the second Player.
However, not all Players support using a different
TimeBase other than its own. In such cases,
a MediaException will be thrown when
setTimeBase is called.
Player's Controls
Player implements Controllable which
provides extra controls via some type-specific Control
interfaces. getControl and getControls
cannot be called when the Player is in the
UNREALIZED or CLOSED state.
An IllegalStateException will be thrown.
Simple Playback Example
try {
Player p = Manager.createPlayer("http://abc.mpg");
p.realize();
VideoControl vc;
if ((vc = (VideoControl)p.getControl("VideoControl")) != null)
add((Component)vc.initDisplayMode(vc.USE_GUI_PRIMITIVE, null));
p.start();
} catch (MediaException pe) {
} catch (IOException ioe) {
}
|
Field Summary |
static int |
CLOSED
The state of the Player indicating that the
Player is closed. |
static int |
PREFETCHED
The state of the Player indicating that it has
acquired all the resources to begin playing. |
static int |
REALIZED
The state of the Player indicating that it has
acquired the required information but not the resources to function. |
static int |
STARTED
The state of the Player indicating that the
Player has already started. |
static long |
TIME_UNKNOWN
The returned value indicating that the requested time is unknown. |
static int |
UNREALIZED
The state of the Player indicating that it has
not acquired the required information and resources to function. |
|
Method Summary |
void |
addPlayerListener(PlayerListener playerListener)
Add a player listener for this player. |
void |
close()
Close the Player and release its resources. |
void |
deallocate()
Release the scarce or exclusive
resources like the audio device acquired by the Player. |
java.lang.String |
getContentType()
Get the content type of the media that's
being played back by this Player. |
long |
getDuration()
Get the duration of the media. |
long |
getMediaTime()
Gets this Player's current media time. |
int |
getState()
Gets the current state of this Player. |
TimeBase |
getTimeBase()
Gets the TimeBase that this Player is using. |
void |
prefetch()
Acquires the scarce and exclusive resources
and processes as much data as necessary
to reduce the start latency. |
void |
realize()
Constructs portions of the Player without
acquiring the scarce and exclusive resources. |
void |
removePlayerListener(PlayerListener playerListener)
Remove a player listener for this player. |
void |
setLoopCount(int count)
Set the number of times the Player will loop
and play the content. |
long |
setMediaTime(long now)
Sets the Player's media time. |
void |
setTimeBase(TimeBase master)
Sets the TimeBase for this Player. |
void |
start()
Starts the Player as soon as possible. |
void |
stop()
Stops the Player. |
UNREALIZED
public static final int UNREALIZED
- The state of the
Player indicating that it has
not acquired the required information and resources to function.
Value 100 is assigned to UNREALIZED.
REALIZED
public static final int REALIZED
- The state of the
Player indicating that it has
acquired the required information but not the resources to function.
Value 200 is assigned to REALIZED.
PREFETCHED
public static final int PREFETCHED
- The state of the
Player indicating that it has
acquired all the resources to begin playing.
Value 300 is assigned to PREFETCHED.
STARTED
public static final int STARTED
- The state of the
Player indicating that the
Player has already started.
Value 400 is assigned to STARTED.
CLOSED
public static final int CLOSED
- The state of the
Player indicating that the
Player is closed.
Value 0 is assigned to CLOSED.
TIME_UNKNOWN
public static final long TIME_UNKNOWN
- The returned value indicating that the requested time is unknown.
Value -1 is assigned to TIME_UNKNOWN.
realize
public void realize()
throws MediaException
- Constructs portions of the
Player without
acquiring the scarce and exclusive resources.
This may include examining media data and may
take some time to complete.
When realize completes successfully,
the Player is in the
REALIZED state.
If realize is called when the Player is in
the REALIZED, PREFETCHTED or STARTED state,
the request will be ignored.
- Throws:
IllegalStateException - Thrown if the Player
is in the CLOSED state.MediaException - Thrown if the Player cannot
be realized.SecurityException - Thrown if the caller does not
have security permission to realize the Player.
prefetch
public void prefetch()
throws MediaException
- Acquires the scarce and exclusive resources
and processes as much data as necessary
to reduce the start latency.
When prefetch completes successfully,
the Player is in
the PREFETCHED state.
If prefetch is called when the Player
is in the UNREALIZED state,
it will implicitly call realize.
If prefetch is called when the Player
is already in the PREFETCHED state, the Player
may still process data necessary to reduce the start
latency. This is to guarantee that start latency can
be maintained at a minimum.
If prefetch is called when the Player
is in the STARTED state,
the request will be ignored.
If the Player cannot obtain all
of the resources it needs, it throws a MediaException.
When that happens, the Player will not be able to
start. However, prefetch may be called again when
the needed resource is later released perhaps by another
Player or application.
- Throws:
IllegalStateException - Thrown if the Player
is in the CLOSED state.MediaException - Thrown if the Player cannot
be prefetched.SecurityException - Thrown if the caller does not
have security permission to prefetch the Player.
start
public void start()
throws MediaException
- Starts the
Player as soon as possible.
If the Player was previously stopped
by calling stop or reaching a preset
stop time, it will resume playback
from where it was previously stopped. If the
Player has reached the end of media,
calling start will automatically
start the playback from the start of the media.
When start returns successfully,
the Player must have been started and
a STARTED event will
be delivered to the registered PlayerListeners.
However, the Player is not guaranteed to be in
the STARTED state. The Player may have
already stopped (in the PREFETCHED state) because
the media has 0 or a very short duration.
If start is called when the Player
is in the UNREALIZED or REALIZED state,
it will implicitly call prefetch.
If start is called when the Player
is in the STARTED state,
the request will be ignored.
- Throws:
IllegalStateException - Thrown if the Player
is in the CLOSED state.MediaException - Thrown if the Player cannot
be started.SecurityException - Thrown if the caller does not
have security permission to start the Player.
stop
public void stop()
throws MediaException
- Stops the
Player. It will pause the playback at
the current media time.
When stop returns, the Player is in the
PREFETCHED state.
A STOPPED event will be delivered to the registered
PlayerListeners.
If stop is called on
a stopped Player, the request is ignored.
- Throws:
IllegalStateException - Thrown if the Player
is in the CLOSED state.MediaException - Thrown if the Player
cannot be stopped.
deallocate
public void deallocate()
- Release the scarce or exclusive
resources like the audio device acquired by the
Player.
When deallocate returns, the Player
is in the UNREALIZED or REALIZED state.
If the Player is blocked at
the realize call while realizing, calling
deallocate unblocks the realize call and
returns the Player to the UNREALIZED state.
Otherwise, calling deallocate returns the
Player to the REALIZED state.
If deallocate is called when the Player
is in the UNREALIZED or REALIZED
state, the request is ignored.
If the Player is STARTED
when deallocate is called, deallocate
will implicitly call stop on the Player.
- Throws:
IllegalStateException - Thrown if the Player
is in the CLOSED state.
close
public void close()
- Close the
Player and release its resources.
When the method returns, the Player is in the
CLOSED state and can no longer be used.
A CLOSED event will be delivered to the registered
PlayerListeners.
If close is called on a closed Player
the request is ignored.
setTimeBase
public void setTimeBase(TimeBase master)
throws MediaException
- Sets the
TimeBase for this Player.
A Player has a default TimeBase that
is determined by the implementation.
To reset a Player to its default
TimeBase, call setTimeBase(null).
- Parameters:
master - The new TimeBase or
null to reset the Player
to its default TimeBase.- Throws:
IllegalStateException - Thrown if the Player
is in the UNREALIZED, STARTED or CLOSED state.MediaException - Thrown if
the specified TimeBase cannot be set on the
Player.- See Also:
getTimeBase()
getTimeBase
public TimeBase getTimeBase()
- Gets the
TimeBase that this Player is using.
- Returns:
- The
TimeBase that this Player is using. - Throws:
IllegalStateException - Thrown if the Player
is in the UNREALIZED or CLOSED state.- See Also:
setTimeBase(javax.microedition.media.TimeBase)
setMediaTime
public long setMediaTime(long now)
throws MediaException
- Sets the
Player's media time.
For some media types, setting the media time may not be very
accurate. The returned value will indicate the
actual media time set.
Setting the media time to negative values will effectively
set the media time to zero. Setting the media time to
beyond the duration of the media will set the time to
the end of media.
There are some media types that cannot support the setting
of media time. Calling setMediaTime will throw
a MediaException in those cases.
- Parameters:
now - The new media time in microseconds.- Returns:
- The actual media time set in microseconds.
- Throws:
IllegalStateException - Thrown if the Player
is in the UNREALIZED or CLOSED state.MediaException - Thrown if the media time
cannot be set.- See Also:
getMediaTime()
getMediaTime
public long getMediaTime()
- Gets this
Player's current media time.
If the media time cannot be determined,
getMediaTime returns TIME_UNKNOWN.
- Returns:
- The current media time in microseconds or
TIME_UNKNOWN. - Throws:
IllegalStateException - Thrown if the Player
is in the CLOSED state.- See Also:
setMediaTime(long)
getState
public int getState()
- Gets the current state of this
Player.
The possible states are: UNREALIZED,
REALIZED, PREFETCHED, STARTED, CLOSED.
- Returns:
- The
Player's current state.
getDuration
public long getDuration()
- Get the duration of the media.
The value returned is the media's duration
when played at the default rate.
If the duration cannot be determined (for example, the
Player is presenting live
media) getDuration returns TIME_UNKNOWN.
- Returns:
- The duration in microseconds or
TIME_UNKNOWN. - Throws:
IllegalStateException - Thrown if the Player
is in the CLOSED state.
getContentType
public java.lang.String getContentType()
- Get the content type of the media that's
being played back by this
Player.
See content type
for the syntax of the content type returned.
- Returns:
- The content type being played back by this
Player. - Throws:
IllegalStateException - Thrown if the Player
is in the UNREALIZED or CLOSED state.
setLoopCount
public void setLoopCount(int count)
- Set the number of times the
Player will loop
and play the content.
By default, the loop count is one. That is, once started,
the Player will start playing from the current
media time to the end of media once.
If the loop count is set to N where N is bigger than one,
starting the Player will start playing the
content from the current media time to the end of media.
It will then loop back to the beginning of the content
(media time zero) and play till the end of the media.
The number of times it will loop to the beginning and
play to the end of media will be N-1.
Setting the loop count to 0 is invalid. An
IllegalArgumentException will be thrown.
Setting the loop count to -1 will loop and play the content
indefinitely.
If the Player is stopped before the preset loop
count is reached either because stop is called or
a preset stop time (set with the StopTimeControl)
is reached, calling start again will
resume the looping playback from where it was stopped until it
fully reaches the preset loop count.
An END_OF_MEDIA event will be posted
every time the Player reaches the end of media.
If the Player loops back to the beginning and
starts playing again because it has not completed the loop
count, a STARTED event will be posted.
- Parameters:
count - indicates the number of times the content will be
played. 1 is the default. 0 is invalid. -1 indicates looping
indefintely.- Throws:
IllegalArgumentException - Thrown if the given
count is invalid.IllegalStateException - Thrown if the
Player is in the STARTED
or CLOSED state.
addPlayerListener
public void addPlayerListener(PlayerListener playerListener)
- Add a player listener for this player.
- Parameters:
playerListener - the listener to add.
If null is used, the request will be ignored.- Throws:
IllegalStateException - Thrown if the Player
is in the CLOSED state.- See Also:
removePlayerListener(javax.microedition.media.PlayerListener)
removePlayerListener
public void removePlayerListener(PlayerListener playerListener)
- Remove a player listener for this player.
- Parameters:
playerListener - the listener to remove.
If null is used or the given
playerListener is not a listener for this
Player, the request will be ignored.- Throws:
IllegalStateException - Thrown if the Player
is in the CLOSED state.- See Also:
addPlayerListener(javax.microedition.media.PlayerListener)
