For any person, who does not have a sound knowledge of Linux Operating System and Linux File System, dealing with the files and their location, their use may be horrible, and a newbie may really mess up.
This article is aimed to provide the information about Linux File System, some of the important files, their usability and location.
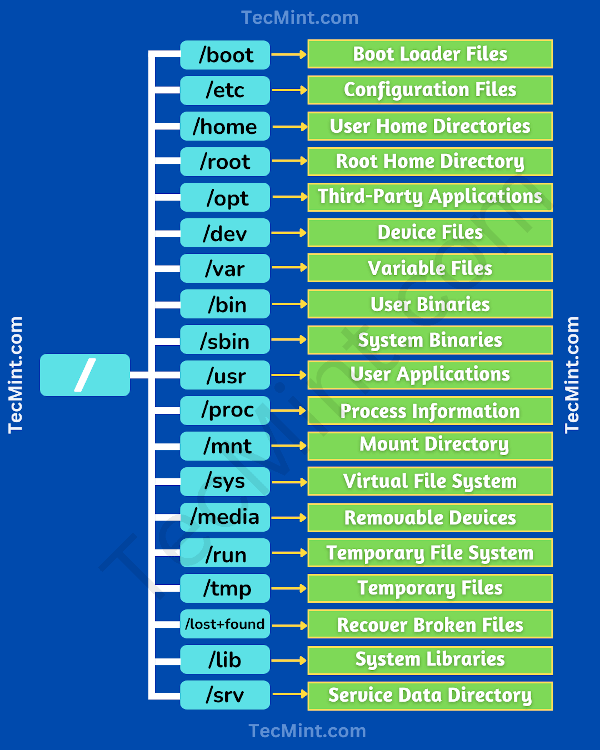
Linux Directory Structure Diagram
A standard Linux distribution follows the directory structure as provided below with Diagram and explanation.
Each of the above directory (which is a file, at the first place) contains important information, required for booting to device drivers, configuration files, etc. Describing briefly the purpose of each directory, we are starting hierarchically.
- /bin : All the executable binary programs (file) required during booting, repairing, files required to run into single-user-mode, and other important, basic commands viz., cat, du, df, tar, rpm, wc, history, etc.
- /boot : Holds important files during boot-up process, including Linux Kernel.
- /dev : Contains device files for all the hardware devices on the machine e.g., cdrom, cpu, etc
- /etc : Contains Application’s configuration files, startup, shutdown, start, stop script for every individual program.
- /home : Home directory of the users. Every time a new user is created, a directory in the name of user is created within home directory which contains other directories like Desktop, Downloads, Documents, etc.
- /lib : The Lib directory contains kernel modules and shared library images required to boot the system and run commands in root file system.
- /lost+found : This Directory is installed during installation of Linux, useful for recovering files which may be broken due to unexpected shut-down.
- /media : Temporary mount directory is created for removable devices viz., media/cdrom.
- /mnt : Temporary mount directory for mounting file system.
- /opt : Optional is abbreviated as opt. Contains third party application software. Viz., Java, etc.
- /proc : A virtual and pseudo file-system which contains information about running process with a particular Process-id aka pid.
- /root : This is the home directory of root user and should never be confused with ‘/‘
- /run : This directory is the only clean solution for early-runtime-dir problem.
- /sbin : Contains binary executable programs, required by System Administrator, for Maintenance. Viz., iptables, fdisk, ifconfig, swapon, reboot, etc.
- /srv : Service is abbreviated as ‘srv‘. This directory contains server specific and service related files.
- /sys : Modern Linux distributions include a /sys directory as a virtual filesystem, which stores and allows modification of the devices connected to the system.
- /tmp :System’s Temporary Directory, Accessible by users and root. Stores temporary files for user and system, till next boot.
- /usr : Contains executable binaries, documentation, source code, libraries for second level program.
- /var : Stands for variable. The contents of this file is expected to grow. This directory contains log, lock, spool, mail and temp files.
Linux is a complex system which requires a more complex and efficient way to start, stop, maintain and reboota system unlike Windows. There is a well defined configuration files, binaries, man pages, info files, etc. for every process in Linux.
- /boot/vmlinuz : The Linux Kernel file.
- /dev/hda : Device file for the first IDE HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
- /dev/hdc : Device file for the IDE Cdrom, commonly
- /dev/null : A pseudo device, that don’t exist. Sometime garbage output is redirected to /dev/null, so that it gets lost, forever.
- /etc/bashrc : Contains system defaults and aliases used by bash shell.
- /etc/crontab : A shell script to run specified commands on a predefined time Interval.
- /etc/exports : Information of the file system available on network.
- /etc/fstab : Information of Disk Drive and their mount point.
- /etc/group : Information of Security Group.
- /etc/grub.conf : grub bootloader configuration file.
- /etc/init.d : Service startup Script.
- /etc/lilo.conf : lilo bootloader configuration file.
- /etc/hosts : Information of Ip addresses and corresponding host names.
- /etc/hosts.allow : List of hosts allowed to access services on the local machine.
- /etc/host.deny : List of hosts denied to access services on the local machine.
- /etc/inittab : INIT process and their interaction at various run level.
- /etc/issue : Allows to edit the pre-login message.
- /etc/modules.conf : Configuration files for system modules.
- /etc/motd : motd stands for Message Of The Day, The Message users gets upon login.
- /etc/mtab : Currently mounted blocks information.
- /etc/passwd : Contains password of system users in a shadow file, a security implementation.
- /etc/printcap : Printer Information
- /etc/profile : Bash shell defaults
- /etc/profile.d : Application script, executed after login.
- /etc/rc.d : Information about run level specific script.
- /etc/rc.d/init.d : Run Level Initialisation Script.
- /etc/resolv.conf : Domain Name Servers (DNS) being used by System.
- /etc/securetty : Terminal List, where root login is possible.
- /etc/skel : Script that populates new user home directory.
- /etc/termcap : An ASCII file that defines the behaviour of Terminal, console and printers.
- /etc/X11 : Configuration files of X-window System.
- /usr/bin : Normal user executable commands.
- /usr/bin/X11 : Binaries of X windows System.
- /usr/include : Contains include files used by ‘c‘ program.
- /usr/share : Shared directories of man files, info files, etc.
- /usr/lib : Library files which are required during program compilation.
- /usr/sbin : Commands for Super User, for System Administration.
- /proc/cpuinfo : CPU Information
- /proc/filesystems : File-system Information being used currently.
- /proc/interrupts : Information about the current interrupts being utilised currently.
- /proc/ioports : Contains all the Input/Output addresses used by devices on the server.
- /proc/meminfo : Memory Usages Information.
- /proc/modules : Currently using kernel module.
- /proc/mount : Mounted File-system Information.
- /proc/stat : Detailed Statistics of the current System.
- /proc/swaps : Swap File Information.
- /version : Linux Version Information.
- /var/log/lastlog : log of last boot process.
- /var/log/messages : log of messages produced by syslog daemon at boot.
- /var/log/wtmp : list login time and duration of each user on the system currently.
That’s all for now.