1. Be honest about Linux.
Linux is great. It’s not perfect, though. It can be perplexing and sometimes frustrating for new users. It’s best to prepare the person you’re helping with a short pep talk.
What should you talk about? Briefly explain what Linux is and how it differs from other operating systems. Explain what you can and can’t do with it. Let them know some of the pain points they might encounter when using Linux daily.
If you take a bit of time to ease them into Linux and open source, the switch won’t be as jarring.
2. It’s not about you.
It’s easy to fall into what I call the power user fallacy: the idea that everyone uses technology the same way you do. That’s rarely, if ever, the case.
This isn’t about you. It’s not about your needs or how you use a computer. It’s about the person you’re helping’s needs and intentions. Their needs, especially if they’re not particularly technical, will be different from yours.
It doesn’t matter if Ubuntu or Elementary or Manjaro aren’t your distros of choice. It doesn’t matter if you turn your nose up at window managers like GNOME, KDE, or Pantheon in favor of i3 or Ratpoison. The person you’re helping might think otherwise.
Put your needs and prejudices aside and help them find the right Linux distribution for them. Find out what they use their computer for and tailor your recommendations for a distribution or three based on that.
3. Not everyone’s a techie.
And not everyone wants to be. Everyone I’ve helped move to Linux in the last 10 months has no interest in compiling kernels or code nor in editing and tweaking configuration files. Most of them will never crack open a terminal window. I don’t expect them to be interested in doing any of that in the future, either.
Guess what? There’s nothing wrong with that. Maybe they won’t get the most out ofLinux (whatever that means) by not embracing their inner geeks. Not everyone will want to take on challenges of, say, installing and configuring Slackware or Arch. They need something that will work out of the box.
4. Take stock of their hardware.
In an ideal world, we’d all have tricked-out, high-powered laptops or desktops with everything maxed out. Sadly, that world doesn’t exist.
That probably includes the person you’re helping move to Linux. They may have slightly (maybe more than slightly) older hardware that they’re comfortable with and that works for them. Hardware that they might not be able to afford to upgrade or replace.
Also, remember that not everyone needs a system for heavy-duty development or gaming or audio and video production. They just need a computer for browsing the web, editing photos, running personal productivity software, and the like.
One person I recently helped adopt Linux had an Acer Aspire 1 laptop with 4GB of RAM and a 64GB SSD. That helped inform my recommendations, which revolved around a few lightweight Linux distributions.
5. Help them test-drive some distros.
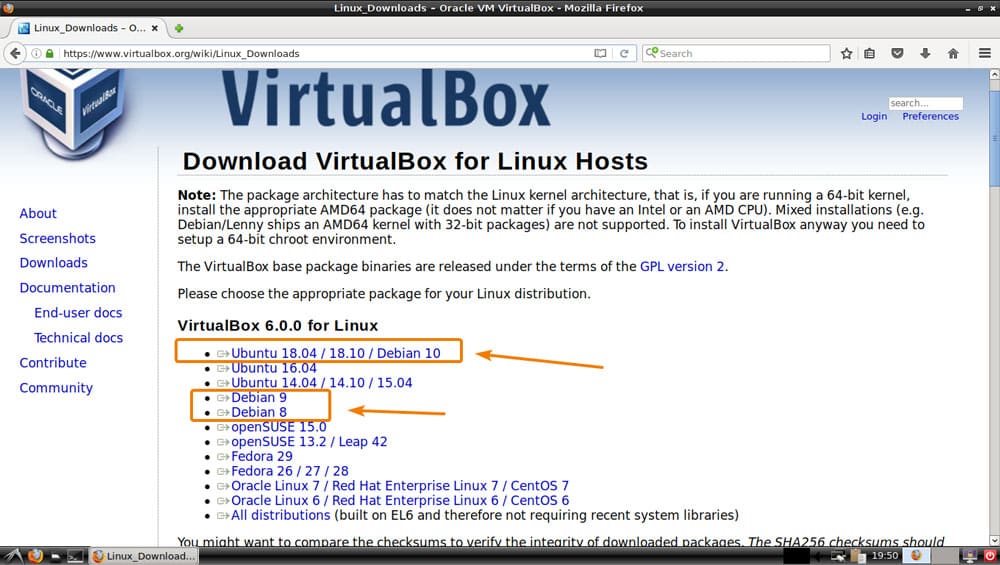
The DistroWatch database contains close to 900 Linux distributions. You should be able to find three to five Linux distributions to recommend. Make a short list of the distributions you think would be a good fit for them. Also, point them to reviews so they can get other perspectives on those distributions.
When it comes time to take those Linux distributions for a spin, don’t just hand someone a bunch of flash drives and walk away. You might be surprised to learn that most people have never run a live Linux distribution or installed an operating system. Any operating system. Beyond plugging the flash drives in, they probably won’t know what to do.
Instead, show them how to create bootable flash drives and set up their computer’s BIOS to start from those drives. Then, let them spend some time running the distros off the flash drives. That will give them a rudimentary feel for the distros and their window managers’ quirks.
6. Walk them through an installation.
Running a live session with a flash drive tells someone only so much. They need to work with a Linux distribution for a couple or three weeks to really form an opinion of it and to understand its quirks and strengths.
There’s a myth that Linux is difficult to install. That might have been true back in the mid-1990s, but today most Linux distributions are easy to install. You follow a few graphical prompts and let the software do the rest.
For someone who’s never installed any operating system, installing Linux can be a bit daunting. They might not know what to choose when, say, they’re asked which filesystem to use or whether or not to encrypt their hard disk.
Guide them through at least one installation. While you should let them do most of the work, be there to answer questions.
7. Be prepared to do a couple of installs.
As I mentioned a paragraph or two ago, using a Linux distribution for two weeks gives someone ample time to regularly interact with it and see if it can be their daily driver. It often works out. Sometimes, though, it doesn’t.
Remember the person with the Acer Aspire 1 laptop? She thought Xubuntu was the right distribution for her. After a few weeks of working with it, that wasn’t the case. There wasn’t a technical reason—Xubuntu ran smoothly on her laptop. It was just a matter of feel. Instead, she switched back to the first distro she test drove: MX Linux. She’s been happily using MX ever since.
8. Teach them to fish.
You can’t always be there to be the guiding hand. Or to be the mechanic or plumber who can fix any problems the person encounters. You have a life, too.
Once they’ve settled on a Linux distribution, explain that you’ll offer a helping hand for two or three weeks. After that, they’re on their own. Don’t completely abandon them. Be around to help with big problems, but let them know they’ll have to learn to do things for themselves.
Introduce them to websites that can help them solve their problems. Point them to useful articles and books. Doing that will help make them more confident and competent users of Linux—and of computers and technology in general.
Final thoughts
Helping someone move to Linux from another, more familiar operating system can be a challenge—a challenge for them and for you. If you take it slowly and follow the advice in this article, you can make the process smoother.
Do you have other tips for helping a non-techie switch to Linux? Feel
Read more at OpenSource.com