Essentially bash scripting is just linking commands together. You can perform many tasks consistently using predefined scripts allowing them to become repeatable and standardized. If you are looking for more information you can check out the bash man page.
Each script should start with a “shebang” telling which environment to interpret the script, bash scripts start with
#!/bin/bash
In CentOS/RHEL 7 , /bin/sh is symlinked to /bin/bash
To make a script execute, you can either call it via the interpreter
/bin/bash myscript.sh
Or change the permissions to make it executable
chmod ug+x myscript.sh
and then execute it directly
./myscript.sh
Bash Test Comparison Operators
Test comparison operators are use to compare two pieces of information.
String Tests:
Are used to compare to strings together
$x = $y – if $x is equal to $y, this will be true
$x != $y – if $x is not equal to $y, this will be true
Integer Tests:
Integer tests are used to compare to integers together
$x -eq $y – if $x is equal to $y this will be true.
$x -ne $y – if $x is not equal to $y, this will be true.
$x -ge $y – if $x is greater than or equal to $y, this will be true.
$x -gt $y – if $x is greater than $y, this will be true.
$x -le $y -if $x is less than or equal to $y, this will be true.
$x -lt $y – if $x is less then $y, this will be true.
Bash Test Operators
Test operators are used to test if a condition is true.
-d FILE – True if file is a directory.
-e FILE – True if file exists.
-f FILE – True if exists and is a file.
-r FILE – True if file exists and is readable.
-w FILE – True if file exists and is granted write permissions.
-x FILE – True if file exists and is granted execute permissions.
Bash If Statements
To utilize the above test operators, you will need to use ‘if’ statements
To use a comparison:
if [ $x -eq $y ]; then
echo “x equals y”;
else
echo “x does not equal y”;
fi
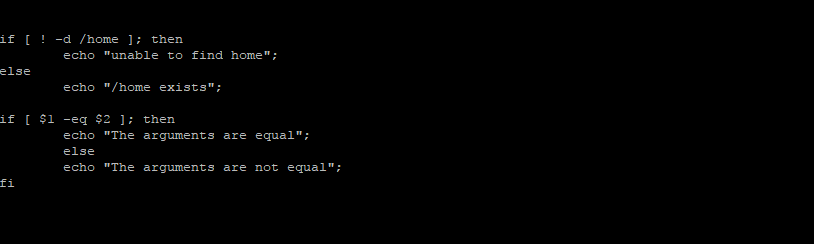
To use a test operator:
if [ -d /home ]; then
echo “/home exists”;
else
echo “/home does not exist”;
fi
Bash Loops
For Loops
Loops can be utilized to do the same task multiple times
for i in ; do
echo “I have a $”;
done
The output will be
I have a apple
I have a orange
I have a watermelon
While Loops
These are done, while something is true perform the following task
i=0
while [ $i -le 5 ]
do
echo “i is currently at $”;
((i++))
done
The output will be:
i is currently at 0
i is currently at 1
i is currently at 2
i is currently at 3
i is currently at 4
i is currently at 5
Bash Script Arguments
You can use arguments to pass stored data into a script and store it as a variable. The first argument is stored as $1, the second argument is stored as $2 and so on.
if [ $1 -eq $2 ]; then
echo “The arguments are equal”;
else
echo “The arguments are not equal”
fi
The output would be
./compare_arguments 3 5
The arguments are not equal
./compare_arguments 4 4
The arguments are equal
You can also require a certain number of arguments be entered by using $#
if [ $# -ne 2 ]; then
echo “the number of required arguments is 2”;
exit;
fi
Which indicates if the number of required arguments is not 2, then exit.
Jul 16, 2017LinuxAdmin.io