 |
| Kali Linux 2017.1 MATE Installation on Oracle VirtualBox |
This video tutorial shows
Kali Linux 2017.1 MATE installation
on
Oracle VirtualBox
step by step. This tutorial is also helpful to install Kali Linux 2017 MATE on physical computer or laptop hardware. We also install Guest Additions on Kali Linux 2017 for better performance and usability features such as Automatic Resizing Guest Display, Shared Folder, Seamless Mode and Shared Clipboard, Improved Performance and Drag and Drop.
Kali Linux 2017.1 MATE Desktop Installation Steps on VirtualBox:
- Create Virtual Machine on Oracle VirtualBox
- Start Kali Linux 2017.1 MATE Installation
- Setup Kali Linux MATE Networking
- Install Lightdm Display Manager
- Install Guest Additions
- Test Guest Additions Features: Automatic Resizing Guest Display and Shared Clipboard
Installing Kali Linux 2017.1 MATE on Oracle VirtualBox
Kali Linux 2017.1 New Features and Improvements
Kali Linux
is a Debian-based distribution which features several security and forensics tools. Kali Linux 2017.1 features drivers for RTL8812AU wireless chipsets, improved GPU support and there are now Azure and AWS images of Kali Linux for cloud instances.
Kali Linux 2017.1
brings with it a bunch of exciting updates and features. As with all new releases, you have the common denominator of updated packages, an updated kernel that provides more and better hardware support, as well as a slew of updated tools.
Kali Linux Website:
What is MATE Desktop?
The MATE Desktop Environment is the continuation of GNOME 2. It provides an intuitive and attractive desktop environment using traditional metaphors for Linux and other Unix-like operating systems. MATE is under active development to add support for new technologies while preserving a traditional desktop experience.
MATE Desktop Website:
VirtualBox Guest Additions Features
The Guest Additions offer the following features below:
- Improved Video Support: While the virtual graphics card which VirtualBox emulates for any guest operating system provides all the basic features, the custom video drivers that are installed with the Guest Additions provide you with extra high and non-standard video modes as well as accelerated video performance.
- Mouse Pointer Integration: This provides with seamless mouse support. A special mouse driver would have to be installed in the guest OS, which would exchange information with the actual mouse driver on the host. The special mouse driver then allows users to control the guest mouse pointer.
- Time Synchronization: With the Guest Additions installed, VirtualBox can ensure that the guest’s system time is better synchronized with that of the host.
- Shared Folders: These provide an easy way to exchange files between the host and the guest.
- Seamless Windows: With this feature, the individual windows that are displayed on the desktop of the virtual machine can be mapped on the host’s desktop, as if the underlying application was actually running on the host.
- Shared Clipboard: With the Guest Additions installed, the clipboard of the guest operating system can optionally be shared with your host operating system.
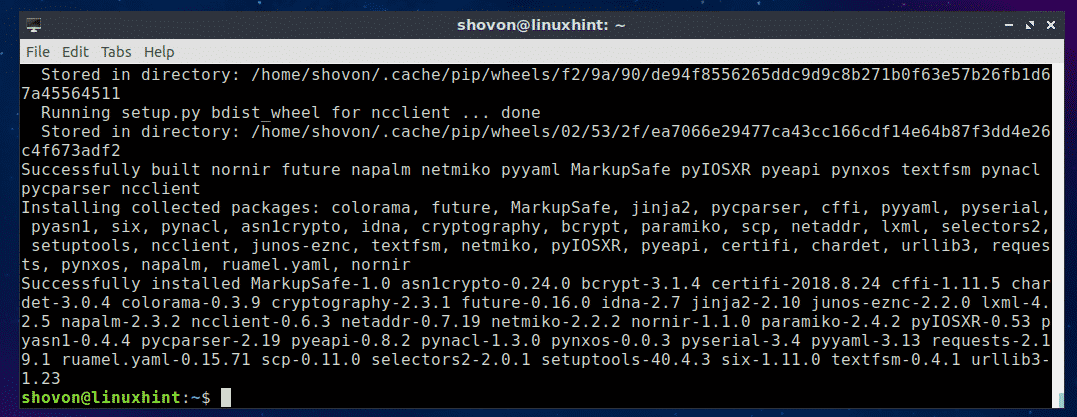
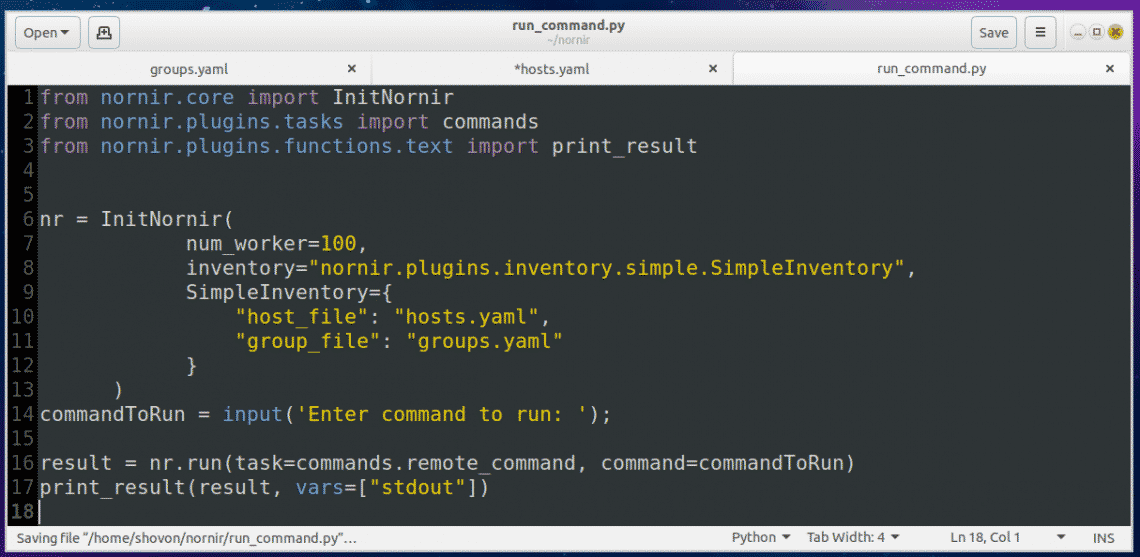
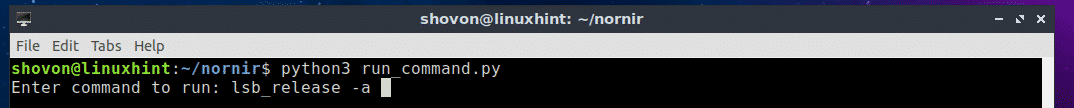
Hope you found this Kali Linux 2017.1 MATE installation on Oracle VirtualBox tutorial helpful and informative. Please consider sharing it. Your feedback and questions are welcome!













 Cirrus7 unveiled an “AI-Box TX2” mini-PC with a Jetson TX2 module and -20 to 70°C support. The company also offers four, similarly Linux-friendly Kaby Lake-based mini-PCs and a new Gemini Lake model.
Cirrus7 unveiled an “AI-Box TX2” mini-PC with a Jetson TX2 module and -20 to 70°C support. The company also offers four, similarly Linux-friendly Kaby Lake-based mini-PCs and a new Gemini Lake model.




















 Kazam Version 1.4.5
Kazam Version 1.4.5 Kazam Version 1.5.3
Kazam Version 1.5.3 Screen recording with Kazam
Screen recording with Kazam Countdown before screen recording
Countdown before screen recording Pause or finish screen recording
Pause or finish screen recording Save recording
Save recording Accessing Kazam preferences
Accessing Kazam preferences Autosave in a chosen location
Autosave in a chosen location Don’t use RAW files
Don’t use RAW files Record mouse clicks
Record mouse clicks