| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Universal Records Management 11g Release 1 (11.1.1) Part Number E10789-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Universal Records Management 11g Release 1 (11.1.1) Part Number E10789-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
Several optional tools are available to help administrators customize and track system performance and usage:
Performance monitoring can be used to check the length of time needed to process service requests, to monitor batch requests and to check for items that have failed to process.
Custom scripts can be written and applied to content for access control and to add notifications. This complies with DoD Chapter 4 certification requirements.
Audit trails capture and record all user activity configured to be included. An audit trail is critical for tracking user actions within a record management system.
This chapter discusses using monitoring, custom scripts, and audit trails. It covers the following topics:
Concepts
Tasks
Performance monitoring can be enabled to check the status of batch processing, service calls, and other system information.
Several default numbers have been set as a starting point for monitoring. Actual performance variations will depend on the hardware used at the site and other variables such as total amount of content and software in use.
Performance monitoring statistics are written to a database table and can be accessed later.
Follow this procedure to use performance monitoring:
Click Records then Audit from the Top menu. Click Configure then Performance Monitoring.
The Configure Performance Monitoring Page is displayed.
Select the items to monitor and the time intervals for reports and alerts.
Click Submit Update when done.
After enabling performance monitoring, current performance information can be checked using this procedure:
Click Records then Audit then Performance Monitoring from the Top menu.
The Performance Processing Results Page is displayed.
Choose the type of information to view by clicking the tab at the top of the body section of the page:
Performance Processing: this page contains a summary of requests processed, total items processed, total number of queries run, total time to run queries, total time to validate data, total service request parse time and total service request time per each external source. Averages for these are also included.
Report by Batch: this page contains a summary of batches/items pending, processed, and failed with a total for each source. If an item has failed, a batch file is created that can be re-run. Click on any value in a column to display a page showing details about that item and to access the option to re-run the batch.
Report by Item: this page contains the details per batch for a particular source, status or batch type as well as totals. The detail page for the item contains the batch type, start time, completed time, elapsed time, and number of items processed for each batch.
If any performance activites exceed the limits set on the Configure Performance Monitoring Page, a Performance Monitoring Alert Message is displayed automatically when you log in to the system.
Click any link on the Performance Monitoring Alert Message to see details about the specific alert. For example, the Monitoring Details Page is displayed when the first alert message is clicked. Click any link to display details about the specific items that caused the alert.
Custom scripts can be created using Idoc Script, a proprietary scripting language. This functionality is enabled by default when the DoD Configuration component is enabled. See the Oracle Fusion Middleware Setup Guide for Universal Records Management for details about different options.
Custom scripting can be disabled by deselecting the Enable Custom Script box in the DoD Config section of the Configure Retention Settings Page. To access that page click Records then Configure then Settings from the Top menu.
When enabled, new content fields are available which allow you to define which scripts will apply to a folder or category.
Caution:
You must have a thorough understanding of Idoc Script to use this feature. The Oracle URM software does not validate the script. You are responsible for creating usable scripts. See the Oracle Fusion Middleware Idoc Script Reference Guide for details about Idoc Script and its use.Two types of scripts can be created using the Custom Script functionality:
Security scripts, which allows users with the Records Administrator role to define and manage access control to content.
Custom Notification scripts, which notify users of events. One custom script is provided, which notifies a list of reviewers when items are due for destruction after being superseded. Notification is send in one consolidated email when batches are run. Additional scripts can be created.
Scripts can be applied at a category or folder level and will apply to the children in those objects. A script inherits the security on the folder or category to which it is applied.
Note:
Custom scripts comply with the DoD 5015.2 specification, chapter 4.19 and chapter 4.20.Note:
Any custom Idoc script which is entered is NOT verified for accuracy. You should have knowledge about Idoc script and its uses before creating scripts.Follow this procedure to set up a custom script. Use the same procedure for both types of scripts.
Click Records then Configure from the Top menu. Click Security then Custom Scripts.
The Configure Custom Script Page is displayed. Select the type of script to use (Notification or Security) by clicking the tab for the script type. To edit an existing script, select Edit from the existing script's Action menu. To add a script, click Add or select Edit on the Custom Script Information Page.
The Create or Edit Custom Script Page is displayed.
Add or edit the name for the script.
Add or edit the description for the script (optional).
Add or edit the Idoc code for the script. Note that the code is not verified for accuracy.
When finished adding a new script, click Create. When editing a script, click Submit Update. To reset the page without saving, click Reset.
Follow this procedure to delete a custom script. Use the same procedure for both types of scripts.
Click Records then Configure from the Top menu. Click Security then Custom Scripts.
The Configure Custom Script Page is displayed. Select the type of script for deletion by clicking the tab for either a Notification or a Security script.
To delete the script, click the box next to the script name and click Delete or select Delete Script from the script's Action menu. You can also click Delete on the Custom Script Information Page.
Follow this procedure to view a script's information:
Click Records then Configure from the Top menu. Click Security then Custom Scripts.
The Configure Custom Script Page is displayed. Select the script for viewing by clicking the tab for either a Notification or a Security script.
To view the script information, click the script name or select Script Information from the script's Action menu.
The Custom Script Information Page is displayed.
The audit trail is generated in the format specified by the Report Format setting on the Configure Report Settings Page.
Permissions:
The Admin.Audit right is required to work with audit trails. This right is assigned by default to the Records Administrator role. Administrative privileges are required to check in the audit trail.At certain points, the current audit trail can be cut off and archived and checked into the repository. This action can also be scheduled to occur on a regular basis. The audit trail must be cycled for growth reasons the same as other items. Be sure to check in the audit trail log on a regular basis to keep the file size smaller and the report generation time faster. Each current audit trail is generated from the time the system was installed or archived until the request to generate an audit trail.
An audit trail can be generated at any time. The columns within the audit trail correspond directly with the fields by which you can search within the Search Audit Trail Page.
If the generated file is in PDF format, Adobe Acrobat version 6.0 or later is required to view it.
Several tasks are involved in managing Audit Trails:
The configuration on the Configure Audit Page determines the administrator and user actions recorded for an audit trail.
Permissions:
The Admin.Audit right is required to perform this action. This right is assigned by default to the Records Administrator role.To configure an audit trail, complete the following steps:
Click Records then Audit from the Top menu. Click Configure then Audit Trail.
The Configure Audit Page is displayed.
Select the boxes for the actions to audit for each entity.
Click Submit Update. A message indicates configuring the audit was successful. The next time the audit trail is generated, the trail reflects the chosen selections.
Click OK. The Configure Audit Page is displayed again with the updated settings.
Caution:
If actions are deselected for objects, the actions are not captured by the audit trail. It is recommended you leave all settings selected and use the Search Audit Trail Page to narrow down searches of the audit trail. If transactions are heavy and the audit log grows too large too fast, you might want to consider turning off capturing browsing actions to manage the audit trail size.Use this procedure to specify which metadata fields should be included in the audit trail.
Permissions:
The Admin.SelectMeta right is required to perform this action. This right is assigned to the Records Administrator role by default.Click Records then Audit from the Top menu. Click Configure then Audit Fields.
The Audit Fields Page is displayed.
Select the boxes for the metadata field to include in the audit trail.
Click Submit Update when done.
Any changes take effect immediately without restarting the system.
Use this procedure to further refine a search within the current audit trail. For example, you can search for all delete actions, or all delete actions by a particular user, or all actions by a particular user, and so on. To search within archived audit trails, see "Searching an Archived Audit Trail".
Permissions:
The Admin.Audit right is required to perform this action. This right is assigned by default to the Records Administrator role.Click Records then Audit from the Top menu. Click Search Audit Trail.
The Search Audit Trail Page is displayed.
Make the selections to narrow the search. As much or as little detail can be included. To adjust the scope (narrow or widen) of the search, use the Boolean operators before each field.
Click Search. The search results are displayed in the format specified by the Report Format setting on the Configure Report Settings Page.
Setting the default metadata is useful for setting similar check-in attributes. You must set the default metadata before checking in an audit trail for the first time. This is a required step during the setup of the software.
Permissions:
The Admin.Audit right is required to perform this action. This right is assigned by default to the Records Administrator role.To set the default metadata for checking in and archiving a portion of the audit trail, complete the following steps:
Click Records then Audit from the Top menu. Click Checked-in Audit Entries.
The Checked-in Audit Entries Page is displayed.
Click the Default Metadata for Checked-In Audit Entries link.
The Default Metadata for Checked-In Audit Entries Page is displayed.
Make selections reflecting the metadata most commonly used when checking in an archived audit trail. When finished, click Submit Update. A message is displayed saying the default metadata has been updated successfully.
Click OK.
A user must have performed at least one action while logged into the system to generate an audit trail entry. If an empty audit trail is submitted for checkin, a message is displayed indicating there are no entries in the audit trail. Before checking in an audit trail for the first time, set the default metadata for the check-in (see "Setting Default Metadata for Checking In Audit Trails").
Permissions:
The Admin.Audit right is required to perform this action. This right is assigned by default to the Records Administrator role.Click Records then Audit from the Top menu. Click Checked-in Audit Entries.
The Checked-in Audit Entries Page is displayed.
In the Check In Audit Entries area, specify the date and time to cut off the audit trail in the Date box, and click Archive.
The check-in confirmation page is displayed. The content ID of the checked-in audit trail is AUDITLOGARCHIVE. Every time it is checked in, a new revision is generated.
Click Content Info to view the information about the archived audit log. The Content Information Page is displayed. To view the audit log just checked in, click the Web Location or the Native File in the Links area of the content information page.
Use this procedure to search for all checked in and archived audit trails.
Prerequisites
"Checking In and Archiving the Audit Trail"
Permissions:
The Admin.Audit right is required to perform this action. This right is assigned by default to the Records Administrator role.Click Records then Audit from the Top menu. Click Checked-in Audit Entries.
The Checked-in Audit Entries Page is displayed.
Click Search Audit Entries. The results of the search are displayed in the search results page. From the search results page, click options in the Query Actions list to:
search within the results
save the search
Use this procedure to view an archived audit trail for which you have searched.
Prerequisites
To view an archived audit log from the search results page, do one of the following:
click the ID (quickest method)
click the information icon then click the PDF links on the content information page.
An audit trail report is automatically generated in the format specified by the Report Format setting on the Configure Report Settings Page. If the generated file is in PDF format, Adobe Acrobat version 6.0 or later is required to view it.
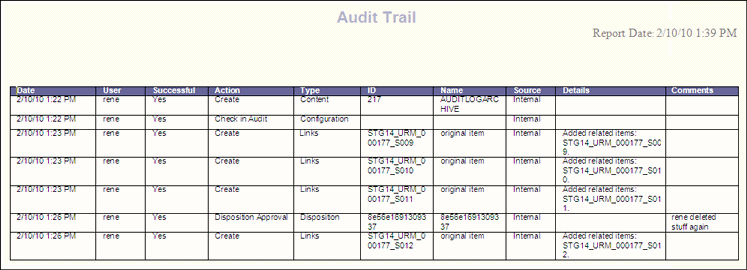
The following is a sample audit trail report.