|
Oracle® Application Server 10g Administrator's Guide
10g (9.0.4) Part No. B10376-02 |
|
|
|
|
|
Oracle® Application Server 10g Administrator's Guide
10g (9.0.4) Part No. B10376-02 |
|
|
|
|
This chapter provides key considerations for managing the Oracle Application Server recommended topologies.
It contains the following topics:
Oracle Application Server is a flexible product that offers a variety of topology options. To assist users in designing a topology, Oracle developed a set of recommended topologies that support common development and deployment requirements. These recommended topologies are documented throughout the Oracle Application Server 10g documentation library as described in Table 10-1.
Table 10-1 Oracle Application Server 10g Documentation Guide to Recommended Topologies
| Topic | Description | See Also |
|---|---|---|
| Overview | High-level overview of each topology, including key considerations in the areas of installation, application deployment and performance, security, management, high availability deployment, and third party products | Oracle Application Server 10g Concepts
|
| Installation Steps | System requirements and step-by-step instructions for installing and configuring each topology | Oracle Application Server 10g Installation Guide
For Enterprise Topologies, see Oracle Application Server 10g Advanced Topologies for Enterprise Deployments |
| Management Considerations | Tips on managing each topology, including recommended tools and management tasks | Oracle Application Server 10g Administrator's Guide
|
| Security Considerations | Tips on providing secure Internet access for each topology | Oracle Application Server 10g Security Guide
|
| Performance Considerations | Performance goals, component distribution across hardware, application development strategies, and parameter tuning for each topology | Oracle Application Server 10g Performance Guide
|
| High Availability Considerations | High Availability tips for the Enterprise Data Center and Departmental topologies | Oracle Application Server 10g High Availability Guide
|
This chapter provides key considerations for managing the following topologies:
General Development Topologies—these topologies are based on development usage; they are:
General Deployment Topologies—these topologies are based on deployment usage; they are:
This section provides management considerations for the following recommended general development topologies:
This topology provides ease of development and deployment for Java developers. It is intended to run on low-end machines with Java IDE tools.
Key management considerations for the Java Developer Topology are:
Use the Application Server Control Console for:
Starting and stopping components as needed
Enabling/Disabling unused components so they do not consume system resources
Setting or changing configuration parameters for OC4J, Oracle HTTP Server, and OracleAS Web Cache
Deploying and configuring applications
Managing J2EE application security
Monitoring application and component performance and resource consumption in real-time
Viewing and setting port numbers
Viewing and searching log files
Managing OracleAS Clusters
Use the Application Server Control Console or JDeveloper to deploy applications
Command-line utilities are available for scripting and automation, or if you use standalone components
Use Oracle-recommended backup and recovery strategies
Figure 10-1 illustrates the Java Developer Topology. Note that "O_Hx" in the figure denotes an Oracle home directory.
This topology provides an environment for OracleAS Portal and OracleAS Wireless developers. It includes an Infrastructure, which is required to deploy and test their applications. It is intended to run on medium-sized machines.
Key management considerations for the Portal and Wireless Developer Topology are:
Use the Application Server Control Console for:
Starting and stopping components as needed
Enabling/Disabling unused components so they do not consume system resources
Setting or changing configuration parameters for OC4J, Oracle HTTP Server, and OracleAS Web Cache
Deploying and configuring applications
Managing application security
Monitoring application and component performance and resource consumption in real-time
Viewing and setting port numbers
Viewing and searching log files
Managing Infrastructure schemas
Use Oracle DBA Studio for managing the Metadata Repository
Command-line utilities are available for scripting and automation
Use Oracle-recommended backup and recovery strategies
Figure 10-2 illustrates the Portal and Wireless Developer Topology. Note that "O_Hx" in the figure denotes an Oracle home directory.
OracleAS Forms Services, OracleAS Reports Services, and OracleAS Discoverer developers have similar application deployment requirements. They need an Infrastructure and Oracle Developer Suite to deploy and test their applications. This topology is intended to run on medium-sized machines
Key management considerations for the Forms, Reports, and Discoverer Developer Topology are:
Use the Application Server Control Console for:
Starting and stopping components as needed
Enabling/Disabling unused components so they do not consume system resources
Setting or changing configuration parameters for OC4J, Oracle HTTP Server, and OracleAS Web Cache
Deploying and configuring applications
Managing application security
Monitoring application and component performance and resource consumption in real-time
Viewing and setting port numbers
Viewing and searching log files
Managing Infrastructure schemas
Use Oracle DBA Studio for managing the Metadata Repository
Command-line utilities are available for scripting and automation
Use Oracle-recommended backup and recovery strategies
Figure 10-3 illustrates the Forms, Reports, and Discoverer Developer Topology. Note that "O_Hx" in the figure denotes an Oracle home directory.
Integration architects and process modelers require the OracleAS ProcessConnect middle-tier installation. They need appropriate adapters and an Infrastructure to deploy and test their integration applications. This topology is intended to run on medium-sized machines.
Key management considerations for Integration Architects and Process Modelers Topology are:
Use the Application Server Control Console for:
Starting and stopping components as needed
Enabling/Disabling unused components so they do not consume system resources
Setting or changing configuration parameters for OC4J, Oracle HTTP Server, and OracleAS Web Cache
Deploying and configuring applications
Managing application security
Monitoring application and component performance and resource consumption in real-time
Viewing and setting port numbers
Viewing and searching log files
Managing Infrastructure schemas
Use Oracle DBA Studio for managing the Metadata Repository
Command-line utilities are available for scripting and automation
Use Oracle-recommended backup and recovery strategies
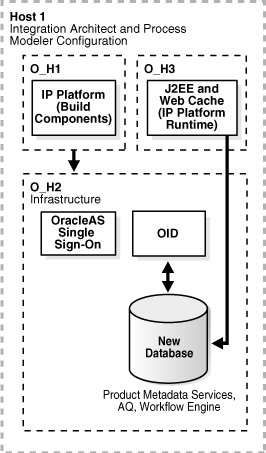
Figure 10-4 illustrates the Integration Architect and Process Modeler Topology. Note that "O_Hx" in the figure denotes an Oracle home directory.
Figure 10-4 Integration Architect and Process Modeler Topology
This section provides management considerations for the following recommended general deployment topologies:
Enterprise Data Center topologies can be used by multiple departments sharing the same data center. There are two Enterprise Data Center topologies:
Key management considerations for Enterprise Data Center topologies are:
Use the Application Server Control Console for:
Starting and stopping components as needed
Enabling/Disabling unused components so they do not consume system resources
Setting or changing configuration parameters for OC4J, Oracle HTTP Server, and OracleAS Web Cache
Deploying and configuring applications
Managing application security
Monitoring application and component performance and resource consumption in real-time
Viewing and setting port numbers
Viewing and searching log files
Managing Infrastructure schemas
Use Oracle DBA Studio for managing the Metadata Repository
Command-line utilities are available for scripting and automation
Use Oracle-recommended backup and recovery strategies
Enterprise Data Center Topology for Java Applications
This topology assumes that you want to create new databases for Product, Management, and Security services. If you choose to use an existing database, the product metadata will inherit the high availability solution already deployed for that database.
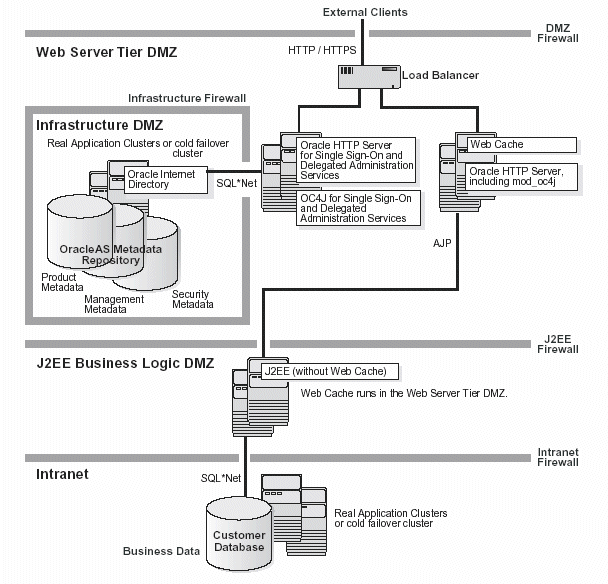
Figure 10-5 illustrates the Enterprise Data Center Topology for Java Applications.
Figure 10-5 Enterprise Data Center Topology for Java Applications
Enterprise Data Center Topology for Portal, Wireless, Business Intelligence, and Forms Applications
This topology assumes that you want to create new databases for Product, Management, and Security services. If you choose to use an existing database, the product metadata will inherit the high availability solution already deployed for that database.
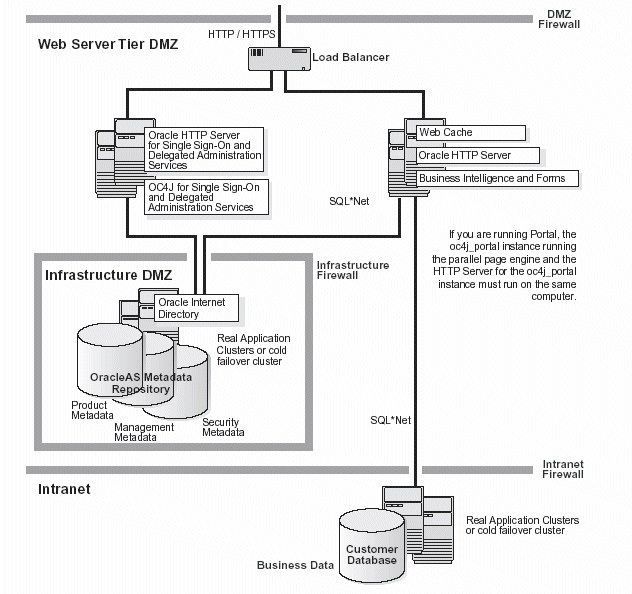
Figure 10-6 illustrates the Enterprise Data Center Topology for Portal, Wireless, Business Intelligence, and Forms Applications.
Figure 10-6 Enterprise Data Center Topology for Portal, Wireless, Business Intelligence, and Forms
The Departmental Topology can be used by departments hosting their applications. This topology consists of a subset of considerations and requirements from the Enterprise Data Center topologies.
Key management considerations for using the Departmental Topology are:
Use the Application Server Control Console for:
Starting and stopping components as needed
Enabling/Disabling unused components so they do not consume system resources
Setting or changing configuration parameters for OC4J, Oracle HTTP Server, and OracleAS Web Cache
Deploying and configuring applications
Managing application security
Monitoring application and component performance and resource consumption in real-time
Viewing and setting port numbers
Viewing and searching log files
Managing Infrastructure schemas
Use Oracle DBA Studio for managing the Metadata Repository
Command-line utilities are available for scripting and automation
Use Oracle-recommended backup and recovery strategies
Figure 10-7 illustrates the Departmental Topology.
The Development Life Cycle Support Topology provides a seamless environment for moving applications from the test environment to the staging environment, and from there to the production environment.
The Development Life Cycle Support Topology is a combination of other topologies which support moving applications from test to stage to production environments.
Test environment: Application developers test their applications in their own environments. Examples of testing environments:
Stage environment: QA personnel test all applications before deploying them to the production environment. In this environment, you can use the Departmental Topology. This topology in a stage environment runs applications from all departments, not just from a single department.
Production environment: Applications are ready for use by both internal and external users. See Enterprise Data Center Topologies.
Key management considerations for the Development Life Cycle Support Topology are:
Use the Application Server Control Console for:
Starting and stopping components as needed
Enabling/Disabling unused components so they do not consume system resources
Setting or changing configuration parameters for OC4J, Oracle HTTP Server, and OracleAS Web Cache
Deploying and configuring applications
Managing application security
Monitoring application and component performance and resource consumption in real-time
Viewing and setting port numbers
Viewing and searching log files
Managing Infrastructure schemas
Use Oracle DBA Studio for managing the Metadata Repository
Command-line utilities are available for scripting and automation
Use Oracle-recommended backup and recovery strategies
Use the Oracle-recommended procedures for changing Infrastructure services from test to production.