Exodus is a simple yet useful program for easily and securely copying Linux ELF binaries from one system to another. For example, if you have htop (Linux Process Monitoring Tool) installed on your desktop machine, but not installed on your remote Linux server, exodus gives a way to copy/install the htop binary from the desktop machine to the remote server.
It bundles all of the binary’s dependencies, compiling a statically linked wrapper for the executable that invokes the relocated linker directly, and installing the bundle in the ~/.exodus/ directory, on the remote system.
You can see it in action here.

Install Exodus in Linux Systems
You can install exodus using Python PIP package manager, as follows. The command below will perform a user specific installation (only for the account you have logged on with).
$ sudo apt install python-pip [Install PIP On Debian/Ubuntu] $ sudo yum install epel-release python-pip [Install PIP On CentOS/RHEL] $ sudo dnf install python-pip [Install PIP On Fedora] $ pip install --user exodus-bundler [Install Exodus in Linux]
Next, add the directory ~/.local/bin/ to your PATH variable in your ~/.bashrc file, in order to run the exodus executable like any other system command.
export PATH="~/.local/bin/:${PATH}"
Save and close the file. Then open another terminal window to start using exodus.
Note: It is also highly recommended that you install gcc and one of either musl libc or diet libc (C libraries used to compile small statically linked launchers for the bundled applications), on the machine where you’ll be packaging binaries.
Use Exodus to Copy Local Binary To a Remote Linux System
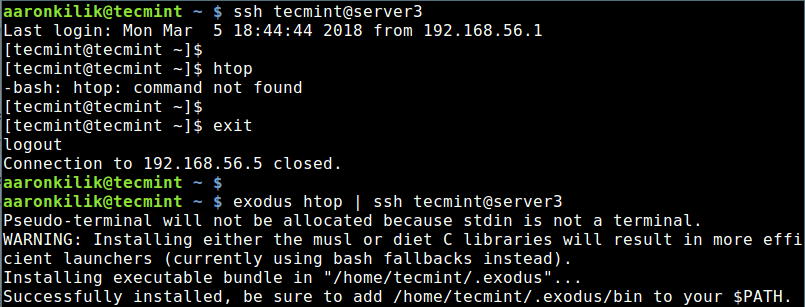
Once you have installed exodus, you can copy a local binary (htop tool) to a remote machine by simply running the following command.
$ exodus htop | ssh tecmint@server3
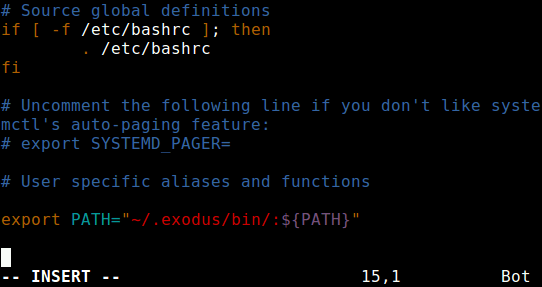
Then login to the remote machine, and add the directory /home/tecmint/.exodus/bin to your PATH in your ~/.bashrc file, in order to run the htop like any other system command.
export PATH="~/.exodus/bin:${PATH}"
Save and close the file, then source it as follows, for the changes to take effect.
$ source ~/.bashrc
Now you should be able to run htop on your remote Linux machine.
$ htop
If you have two or more binaries with the same name (for example, more than one version of htop installed on your system, one /usr/bin/htop and another /usr/local/bin/htop), you can copy and install them in parallel with the -r flag, it enables for assigning of aliases for each binary on the remote machine.
The following command will install the two htop versions in parallel with /usr/bin/grep called htop-1 and /usr/local/bin/htop called htop-2 as shown.
$ exodus -r htop-1 -r htop-2 /usr/bin/htop /usr/local/bin/htop | ssh tecmint@server3
Attention: Exodus has a number of limitations and it may fail to work with non-ELF binaries, incompatible CPU architectures, incompatible Glibc and kernel versions, driver dependent libraries, pro-grammatically loaded libraries and non-library dependencies.
For more information, see the exodus help page.
$ exodus -h
Exodus Github repository: https://github.com/intoli/exodus
Conclusion
Exodus is simple yet powerful tool for copying binaries from one Linux machine to another remote Linux system. Try it out and give us your feedback via the comment form below.