Asterisk is an open source framework used for building communication applications. You can use it to turn a local computer or server to communication server. It is used to power IP PBX systems, VoIP gateways, conference servers and other solutions. It’s used by all kind of organizations worldwide and finally, but not last it is free and open source.
In this tutorial, we are going to show you how to install Asterisk on CentOS 7 (instructions also works on RHEL 7), but before we start, we will need to make some preparations so Asterisk can run smoothly after the installation.
Step 1: Disable SELinux on CentOS 7
To do this, first SSH to your system and using your favorite command line text editor, open /etc/selinux/configand disable SELINUX.
# vim /etc/selinux/config
SELinux line should look like this:
SELINUX=disabled
Now reboot your system. Once it comes back SSH again to that system.
Step 2: Install Required Packages
Asterisk has quite a few requirements that need to be installed. You can use the following yum command to install required packages as shown.
# yum install -y epel-release dmidecode gcc-c++ ncurses-devel libxml2-devel make wget openssl-devel newt-devel kernel-devel sqlite-devel libuuid-devel gtk2-devel jansson-devel binutils-devel
Before we continue further, create a new user through which we will use asterisk.
# adduser asterisk -c "Asterisk User" # su asterisk
Next, install PJSIP, is a free open source multimedia communication library that implements standard based protocols such as SIP,SDP,RTP,STUN,TURN and ICE. It is the Asterisk SIP channel driver that should improve the clarity of the calls.
To get the latest version, first let’s create a temporary directory where we will build the package from source.
$ mkdir ~/build && cd ~/build
Now go the PJSIP download page and grab the package or use the following wget command to download the package directly in terminal.
Note that by the writing of this article the latest version is 2.8, this may change in future, thus make sure to use the latest version:
$ wget https://www.pjsip.org/release/2.8/pjproject-2.8.tar.bz2
Once the download is complete, extract the file and change to that directory.
$ tar xvjf pjproject-2.8.tar.bz2 $ cd pjproject-2.8
The next step is to prepare the package to be compiled. You can use the following command:
$ ./configure CFLAGS="-DNDEBUG -DPJ_HAS_IPV6=1" --prefix=/usr --libdir=/usr/lib64 --enable-shared --disable-video --disable-sound --disable-opencore-amr
You should not see any errors or warnings. Ensure that all dependencies are met:
$ make dep
And now we can complete the install and link libraries with:
$ make && sudo make install && sudo ldconfig
Finally ensure that all libraries are installed and present:
$ ldconfig -p | grep pj
You should get the following output:
libpjsua2.so.2 (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjsua2.so.2
libpjsua2.so (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjsua2.so
libpjsua.so.2 (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjsua.so.2
libpjsua.so (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjsua.so
libpjsip.so.2 (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjsip.so.2
libpjsip.so (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjsip.so
libpjsip-ua.so.2 (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjsip-ua.so.2
libpjsip-ua.so (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjsip-ua.so
libpjsip-simple.so.2 (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjsip-simple.so.2
libpjsip-simple.so (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjsip-simple.so
libpjnath.so.2 (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjnath.so.2
libpjnath.so (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjnath.so
libpjmedia.so.2 (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjmedia.so.2
libpjmedia.so (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjmedia.so
libpjmedia-videodev.so.2 (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjmedia-videodev.so.2
libpjmedia-videodev.so (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjmedia-videodev.so
libpjmedia-codec.so.2 (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjmedia-codec.so.2
libpjmedia-codec.so (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjmedia-codec.so
libpjmedia-audiodev.so.2 (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjmedia-audiodev.so.2
libpjmedia-audiodev.so (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjmedia-audiodev.so
libpjlib-util.so.2 (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjlib-util.so.2
libpjlib-util.so (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpjlib-util.so
libpj.so.2 (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpj.so.2
libpj.so (libc6,x86-64) => /lib64/libpj.so
Step 3: Install Asterisk in CentOS 7
We are now ready to initiate the installation of Asterisk. Navigate back to our ~/build directory:
$ cd ~/build
Go to Asterisk download page and grab the the latest version or you can use the following wget command to download the file in terminal.
$ wget http://downloads.asterisk.org/pub/telephony/asterisk/asterisk-16-current.tar.gz
By the writing of this tutorial, the latest Asterisk version is 16. Make sure that you are downloading the latest version of Asterisk, when you are following the steps.
Now extract the archive and navigate to the newly created directory:
$ tar -zxvf asterisk-16-current.tar.gz $ cd asterisk-16.0.0
This is the time to mention, that if you wish to enable mp3 support to play music while client is on hold, you will need to install few more dependencies. These steps are optional:
# yum install svn # ./contrib/scripts/get_mp3_source.sh
After the second step, you should get output similar to these:
A addons/mp3 A addons/mp3/MPGLIB_README A addons/mp3/common.c A addons/mp3/huffman.h A addons/mp3/tabinit.c A addons/mp3/Makefile A addons/mp3/README A addons/mp3/decode_i386.c A addons/mp3/dct64_i386.c A addons/mp3/MPGLIB_TODO A addons/mp3/mpg123.h A addons/mp3/layer3.c A addons/mp3/mpglib.h A addons/mp3/decode_ntom.c A addons/mp3/interface.c
Start by running the configure script to prepare the package for compiling:
$ sudo contrib/scripts/install_prereq install $ ./configure --libdir=/usr/lib64 --with-jansson-bundled $ make menuselect
If you get any missing dependencies install them. In my case, I got the following error:
configure: error: patch is required to configure bundled pjproject
To go around this simply run:
# yum install patch
And re-run the configure script. Now lets start the build process:
$ make menuselect
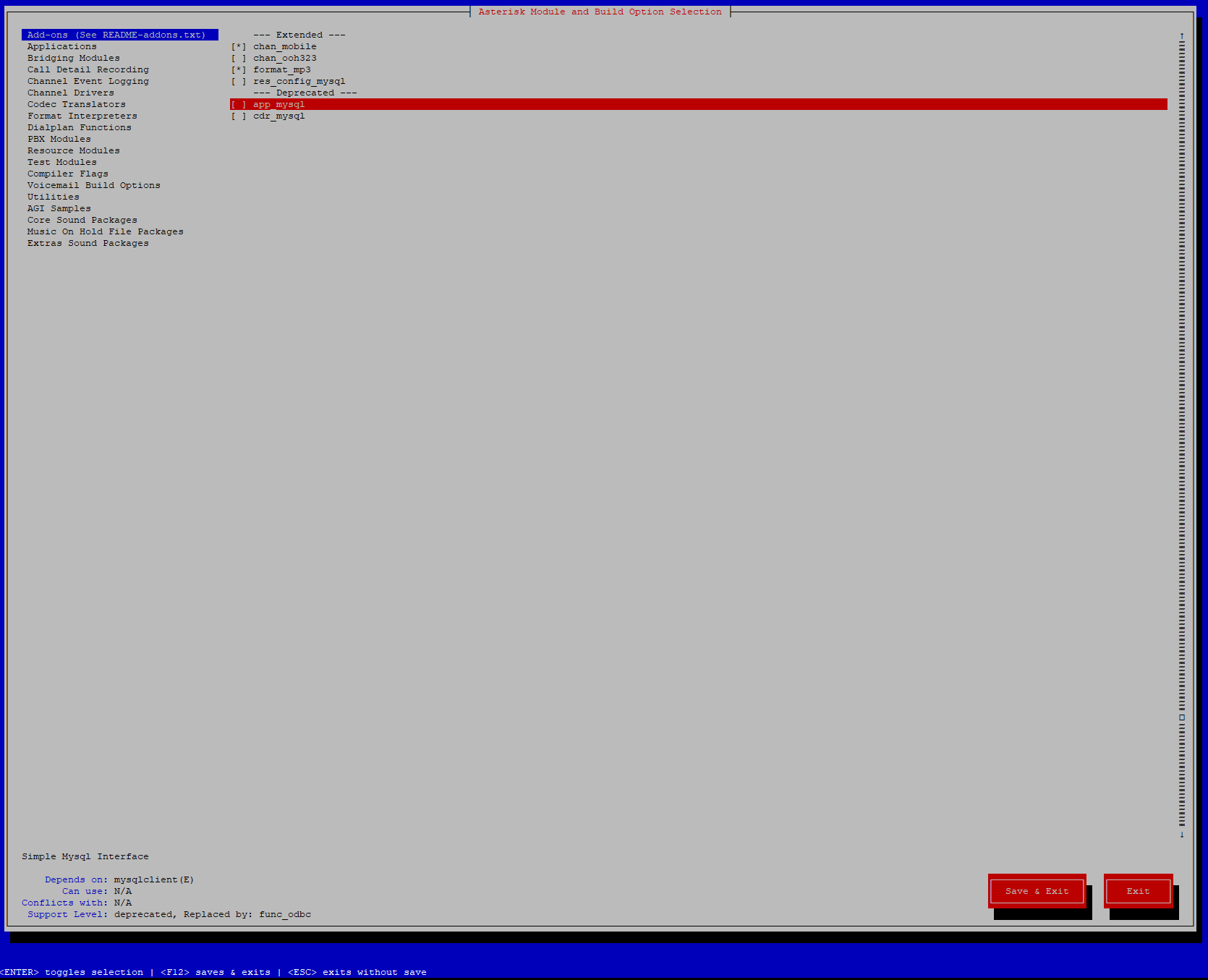
After few seconds, you should get a list of features to enable:
If you attempt to use music on hold feature, you will need to enable the “format_mp3” feature from “Add-ons” section. Save your list and run the following command:
make && sudo make install
To install the sample configuration files, use the command below:
sudo make samples
To start Asterisk on boot, use:
sudo make config
As root user update the ownership of the following directories and files:
# chown asterisk. /var/run/asterisk
# chown asterisk. -R /etc/asterisk
# chown asterisk. -R /var/{lib,log,spool}/asterisk
Finally let’s test our installation with:
$ sudo service asterisk start $ sudo asterisk -rvv
You should see output similar to this one:
Asterisk 16.0.0, Copyright (C) 1999 - 2018, Digium, Inc. and others. Created by Mark Spencer <markster@digium.com> Asterisk comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY; type 'core show warranty' for details. This is free software, with components licensed under the GNU General Public License version 2 and other licenses; you are welcome to redistribute it under certain conditions. Type 'core show license' for details. ========================================================================= Connected to Asterisk 16.0.0 currently running on asterisk (pid = 3985) asterisk*CLI>
If you want to see a list of available commands type:
asterisk*CLI> core show help
To exit the Asterisk prompt, simply type:
asterisk*CLI> exit
Asterisk will still be running in the background.
Conclusion
Now you have a running Asterisk server and you can start connecting phones and extensions and adjust your configuration per your needs. For more details how to achieve this, it is recommended to use the Asterisk Wiki page. If you have any questions or comments, please let us know in the comment section below.