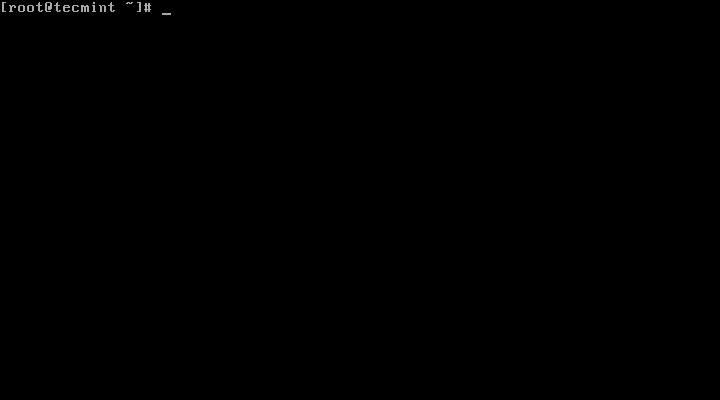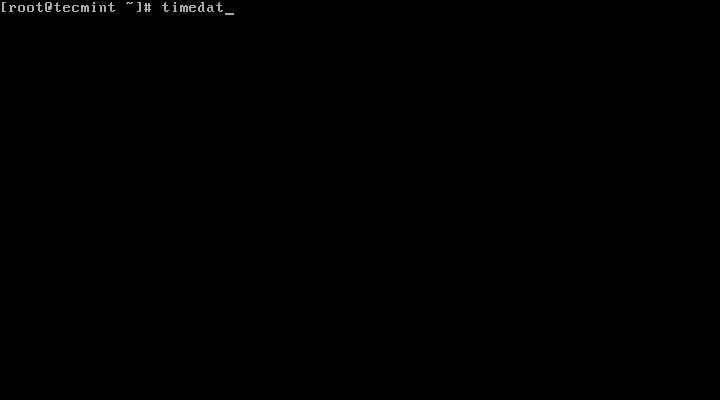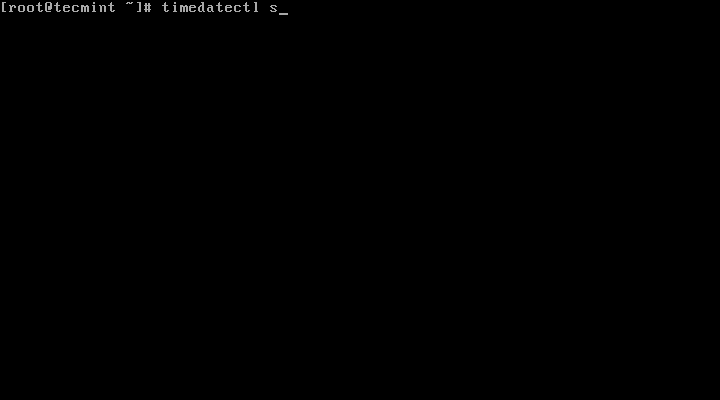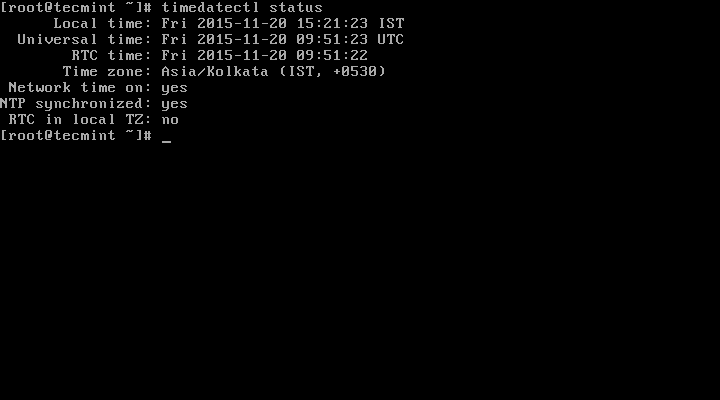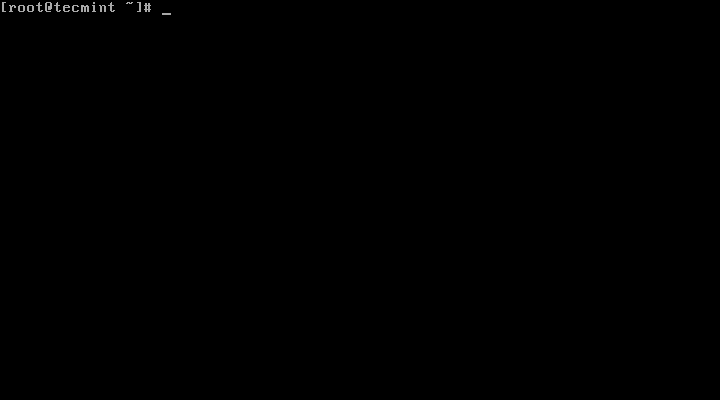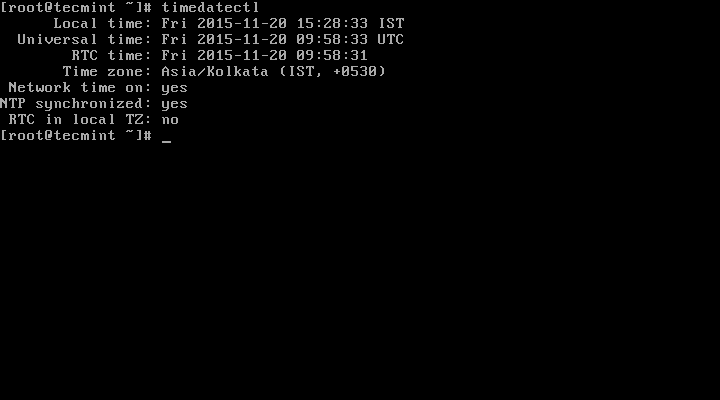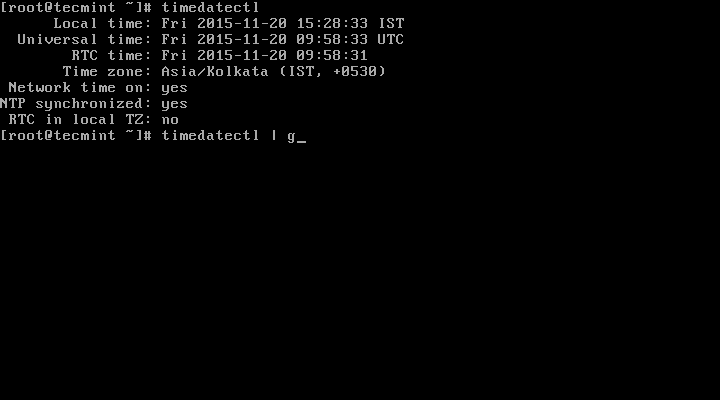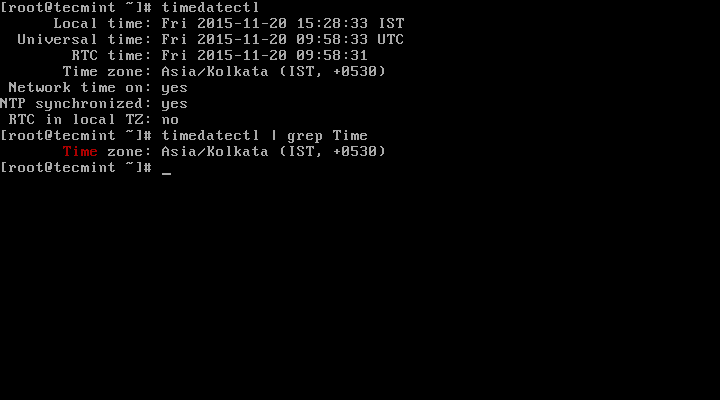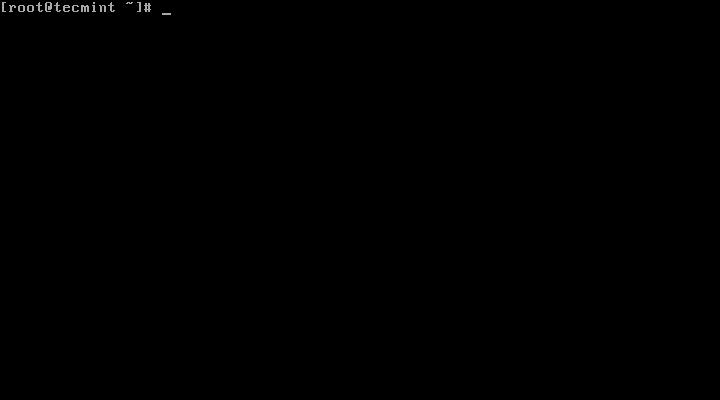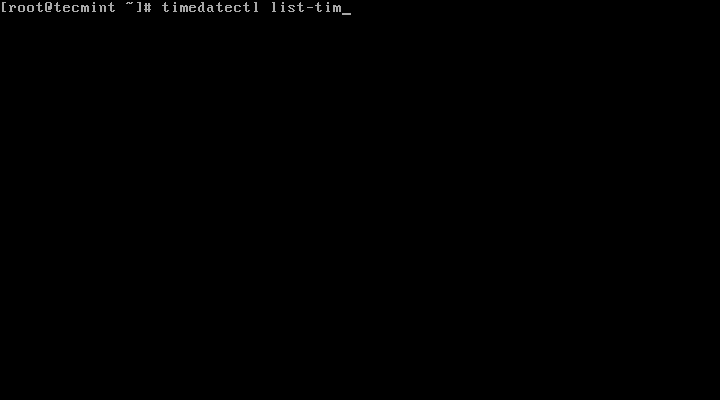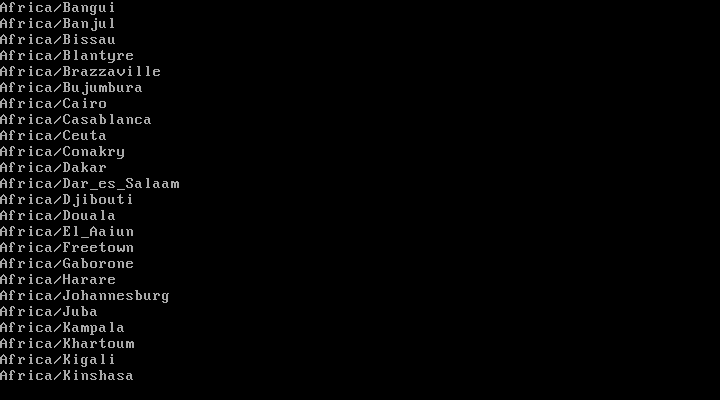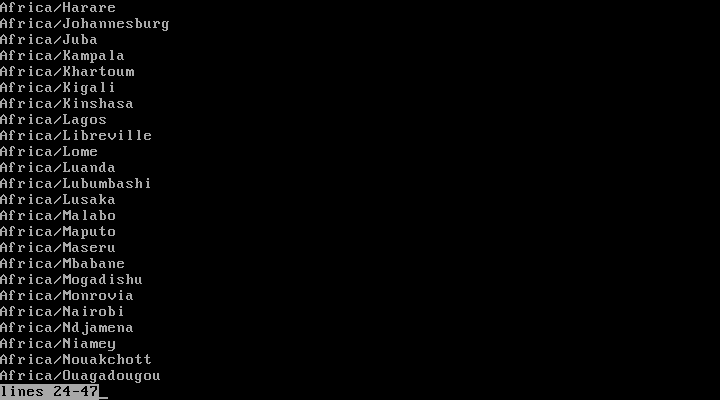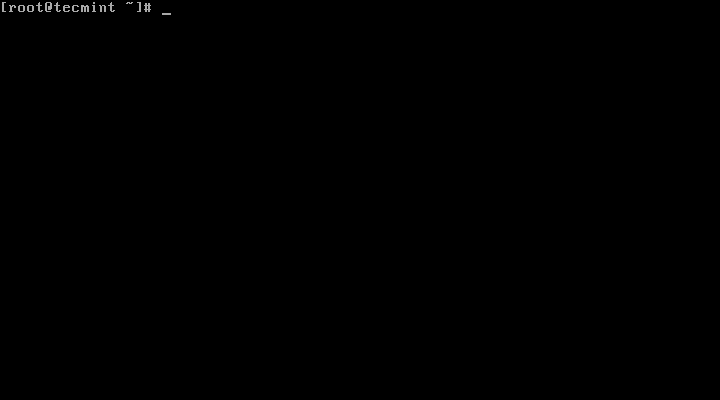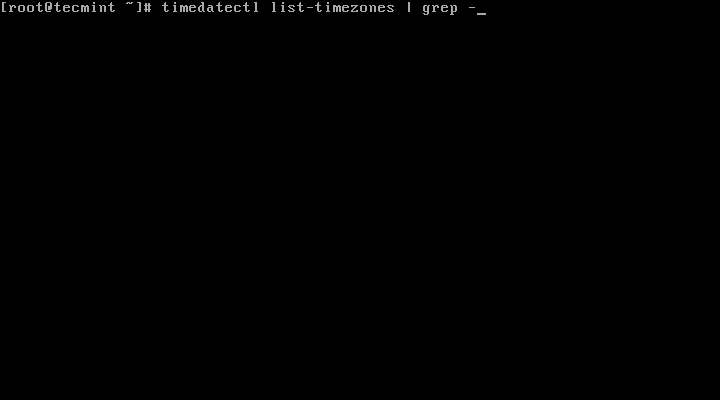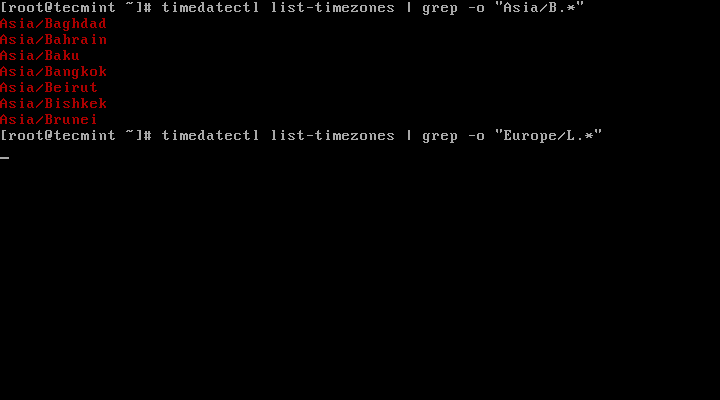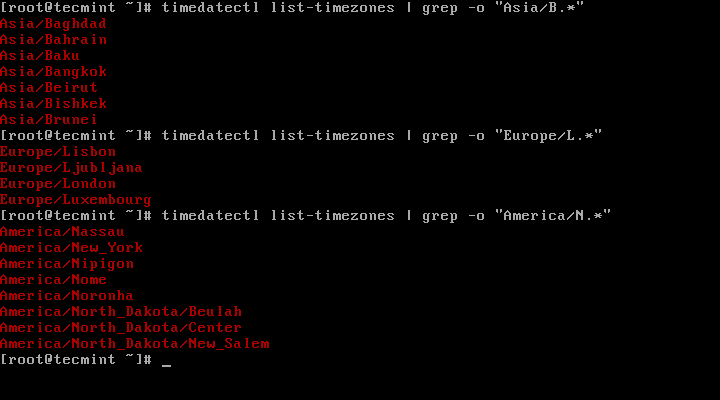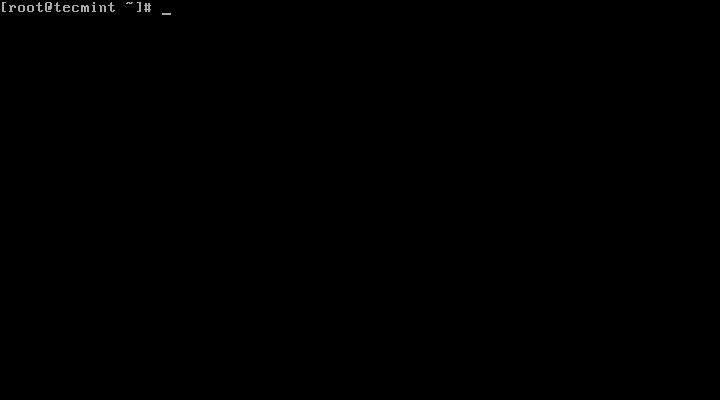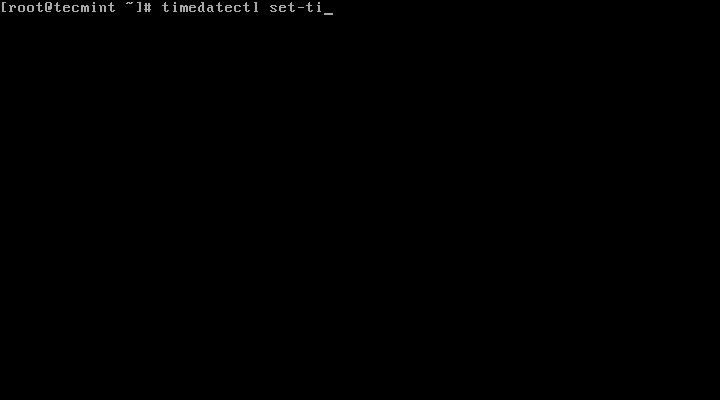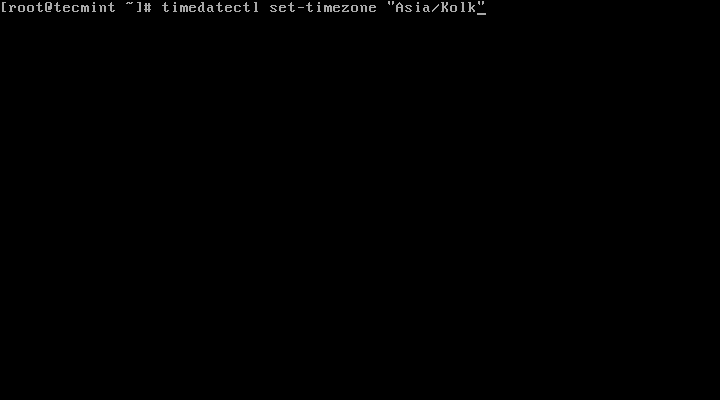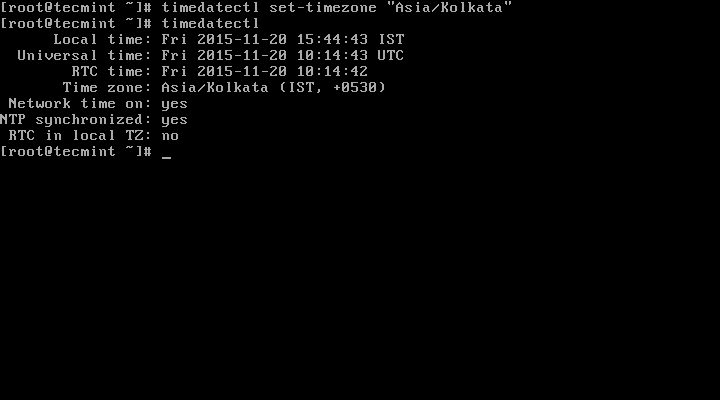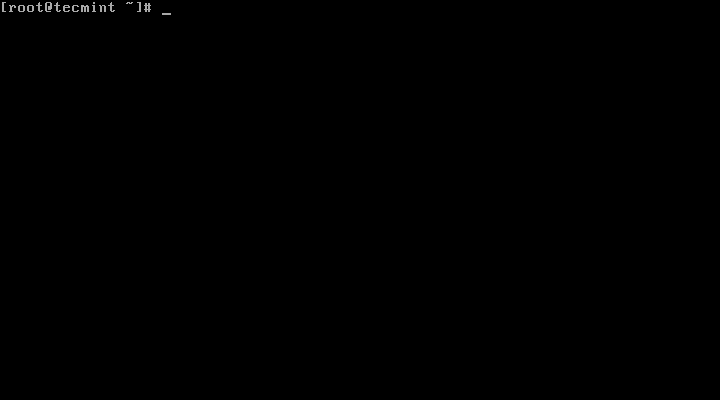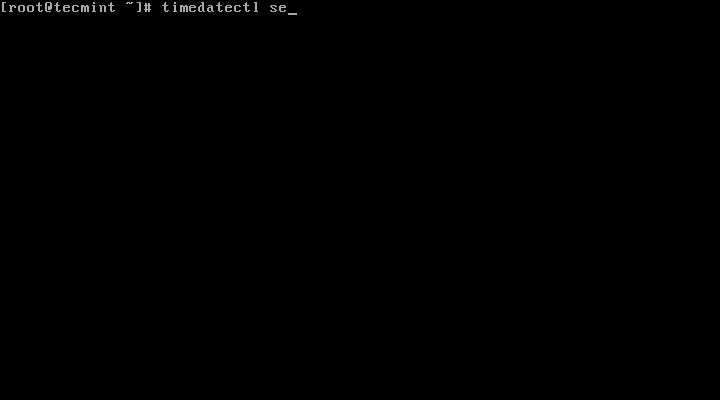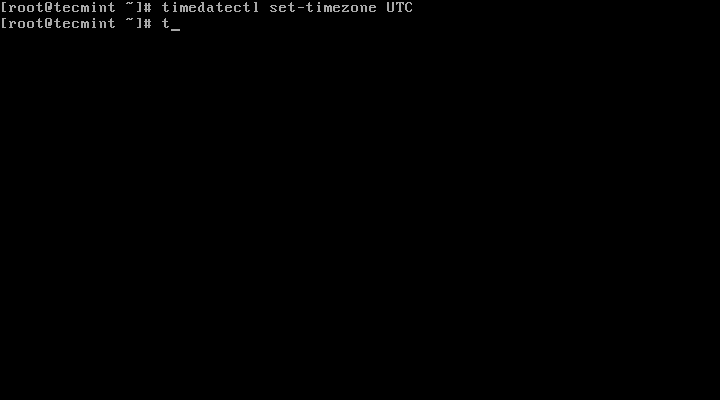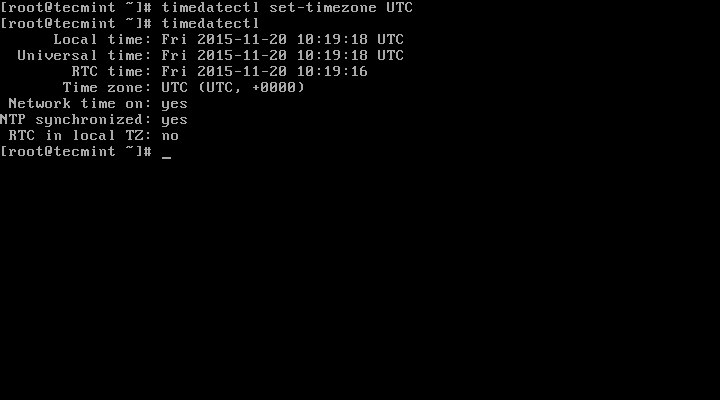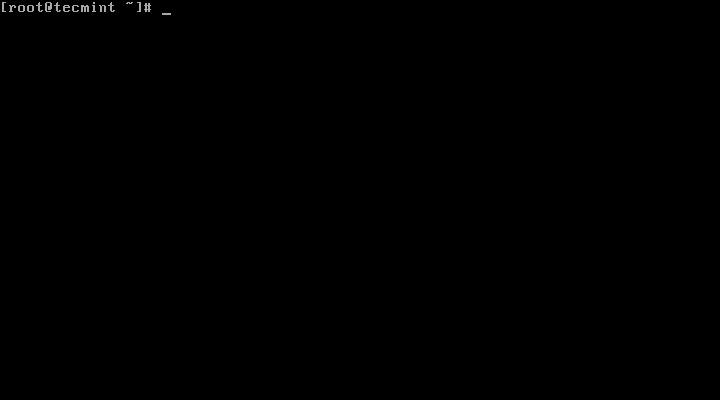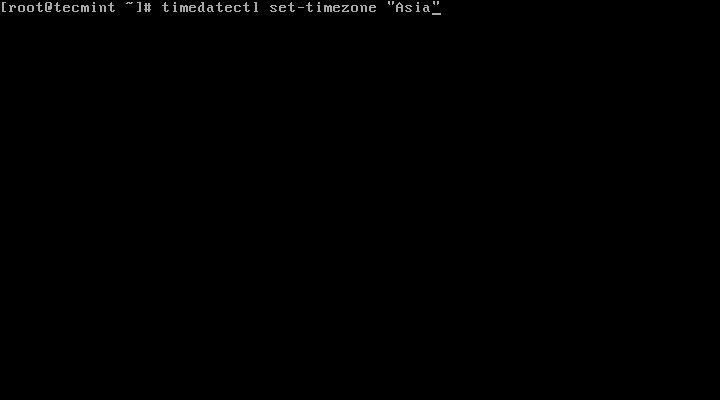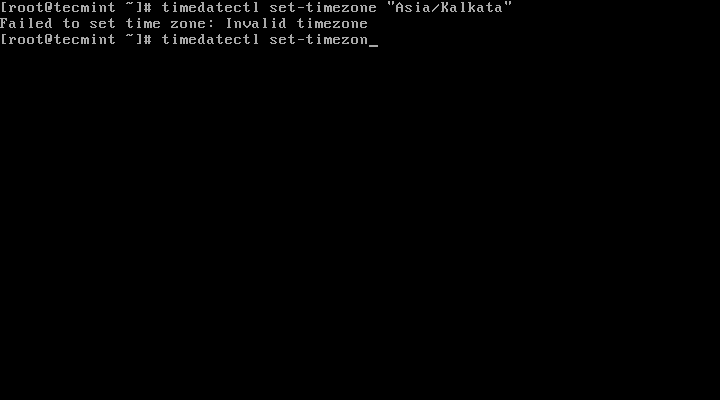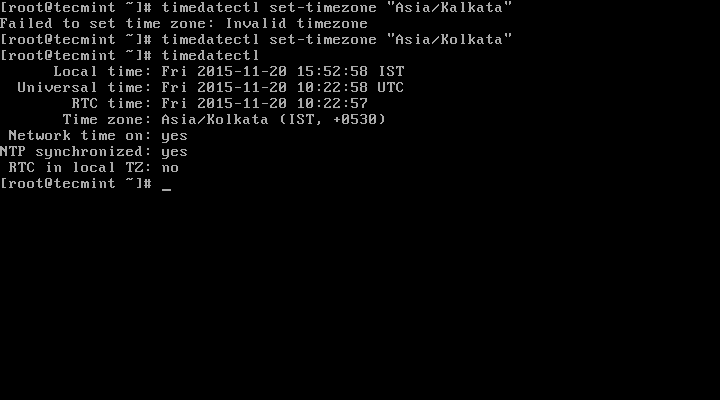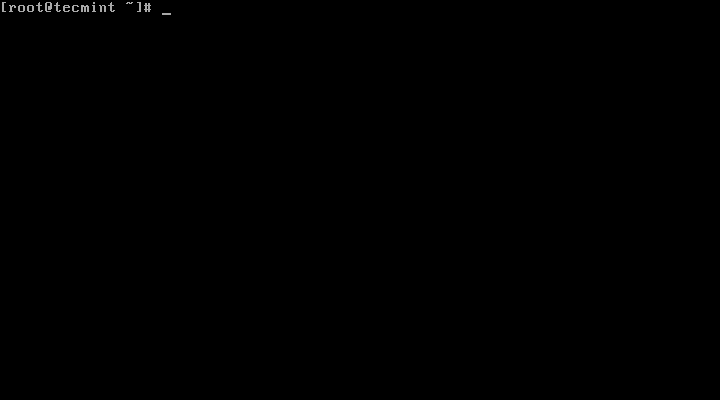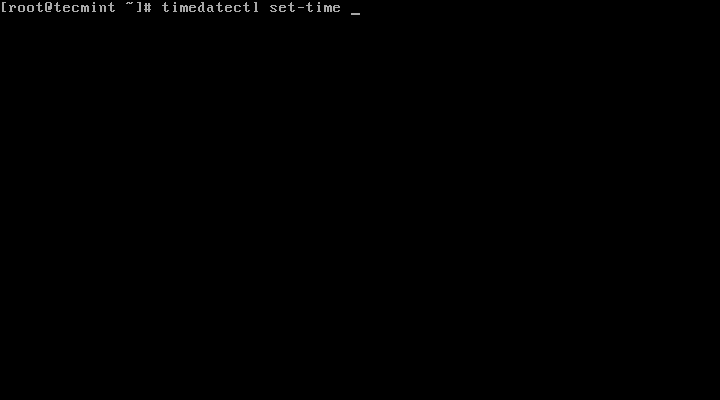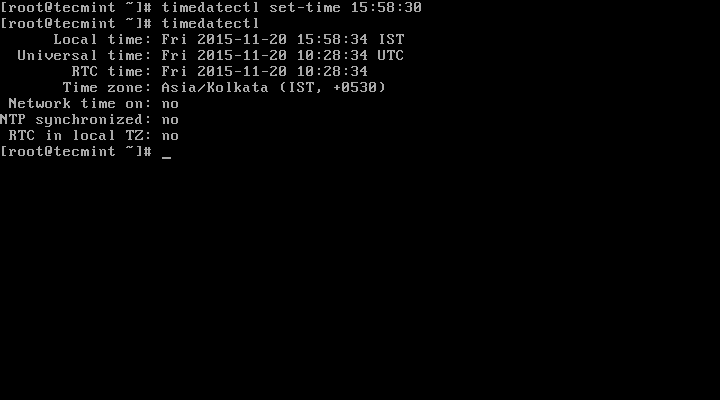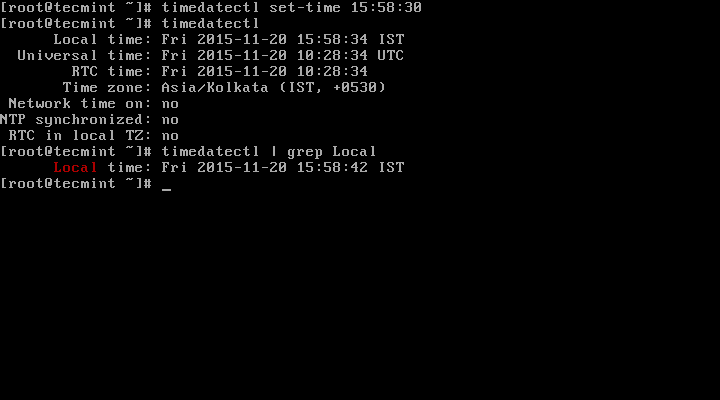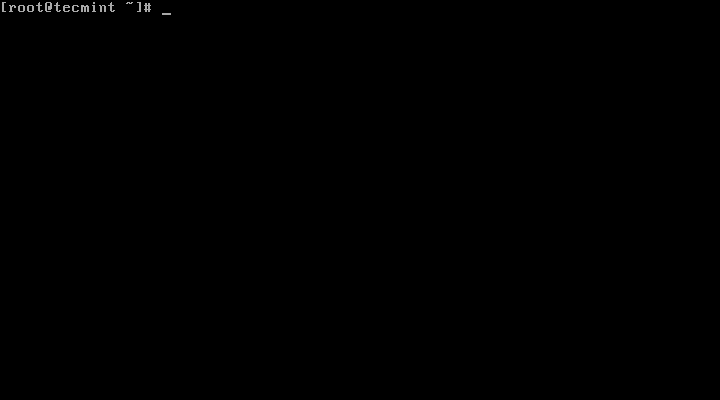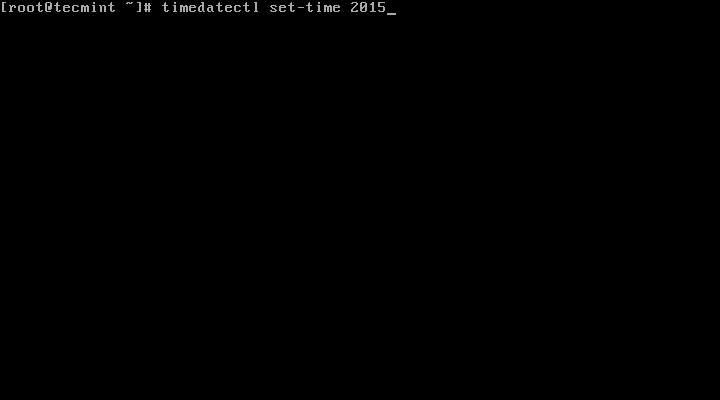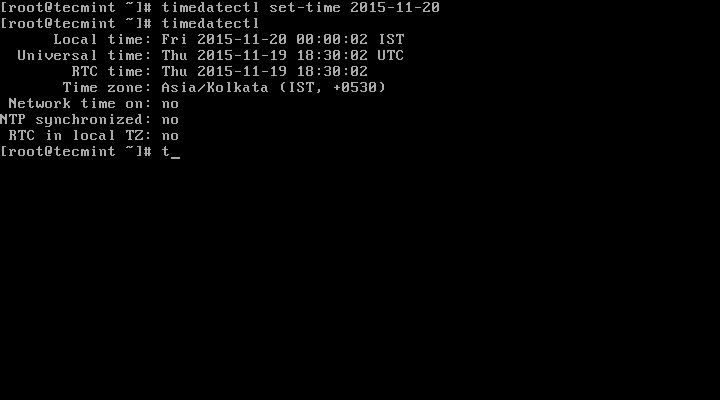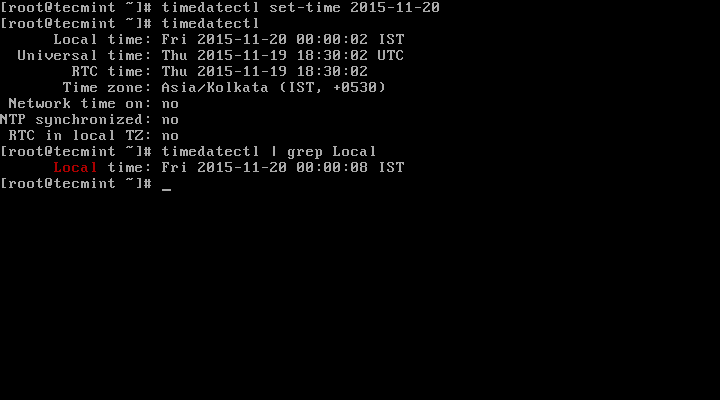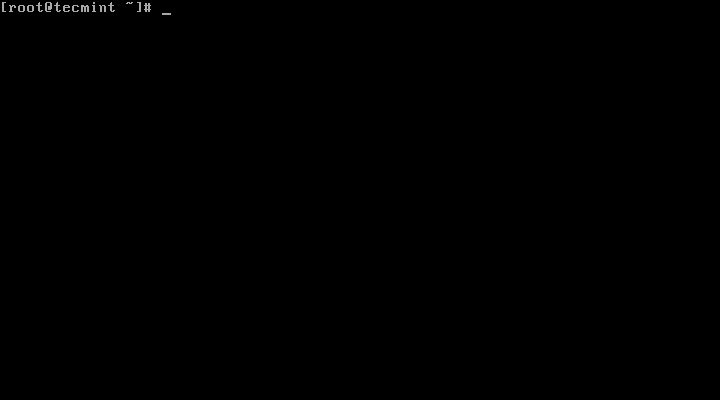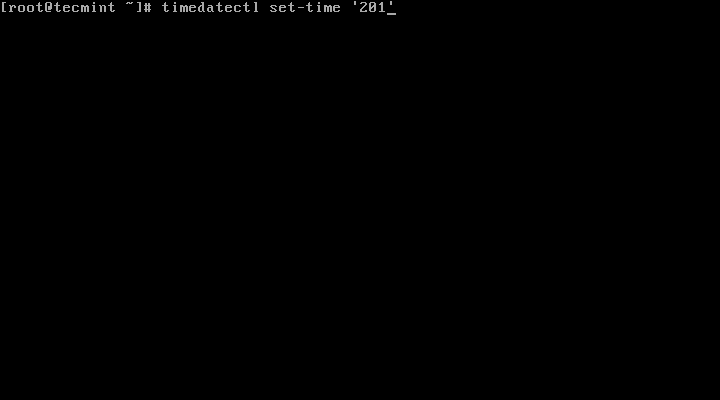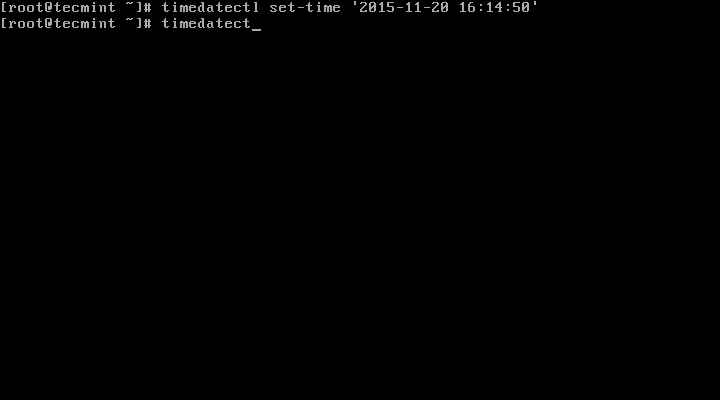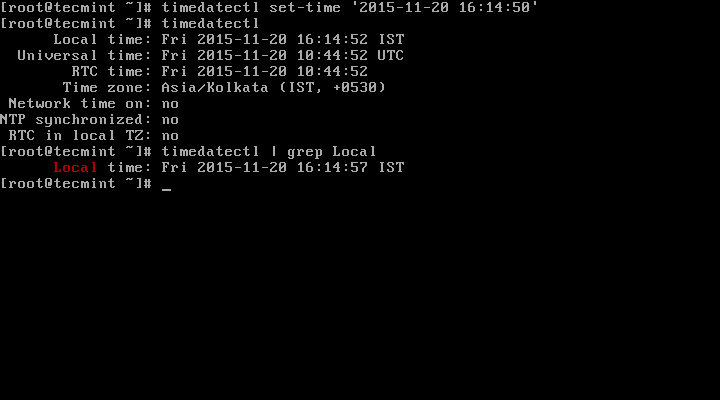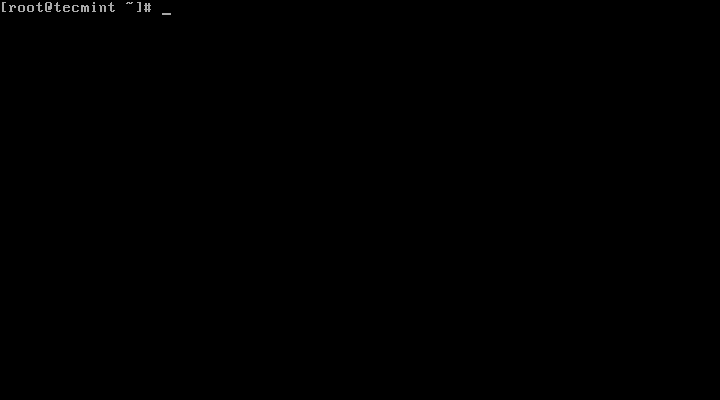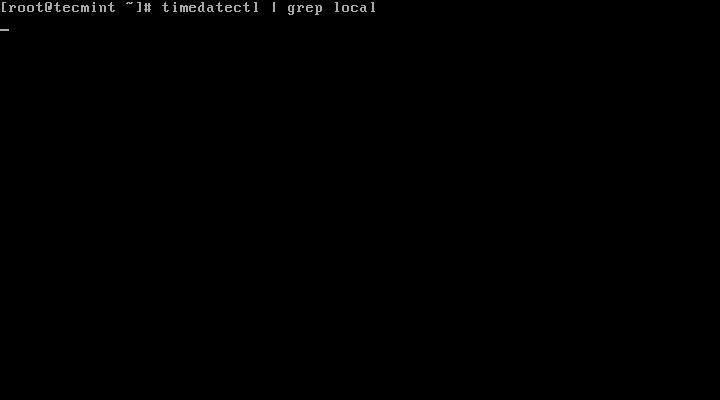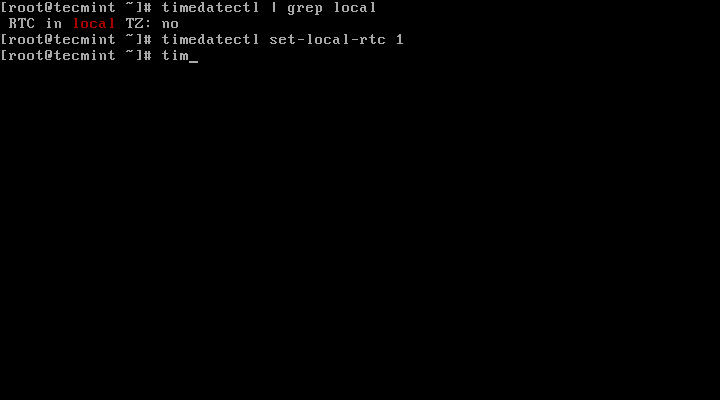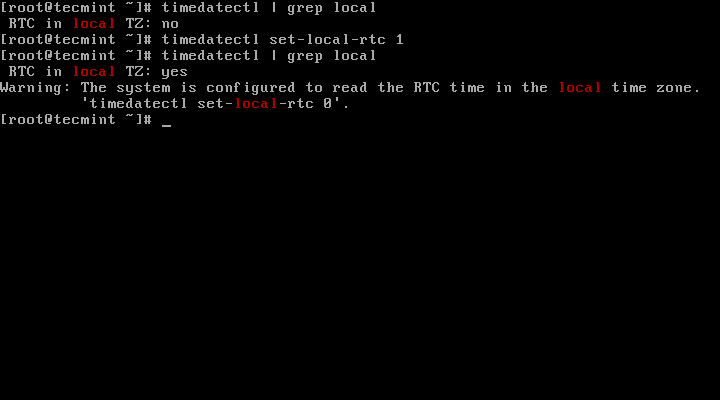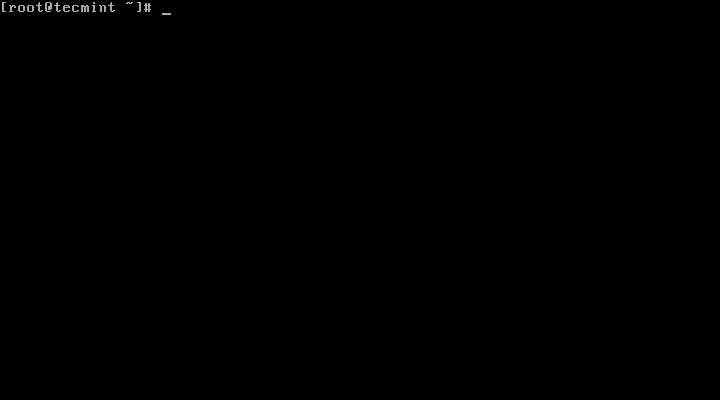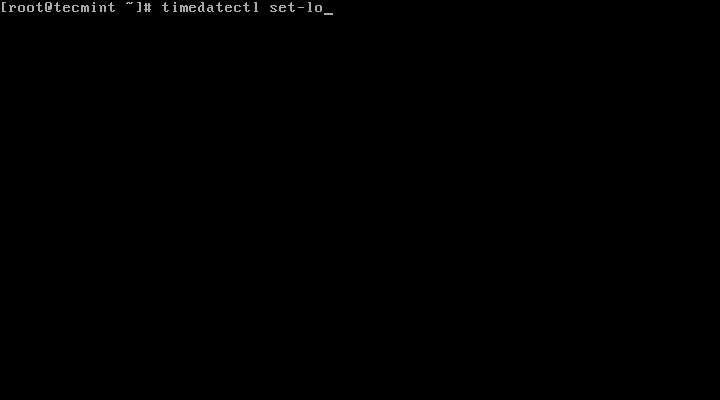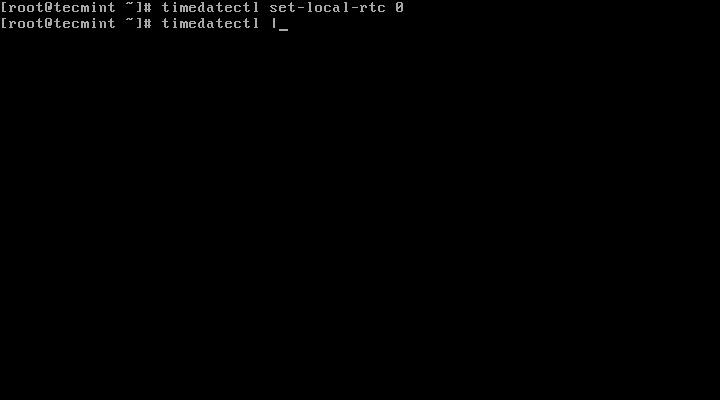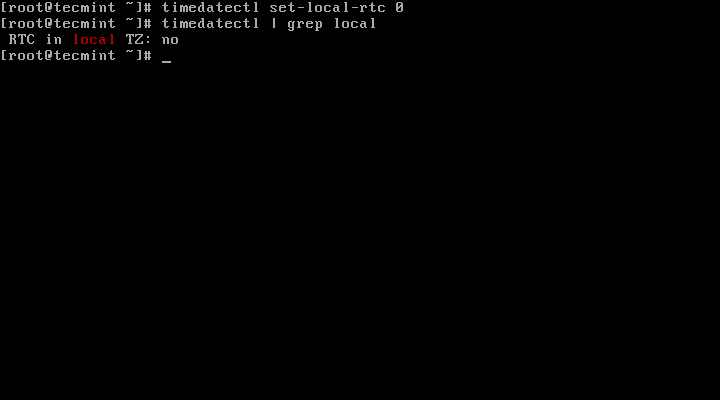The timedatectl command is a new utility for RHEL/CentOS 7 and Fedora 21+ based distributions, which comes as a part of systemd system and service manager, a replacement for old traditional date command used in sysvinit daemon based Linux distributions.
The timedatectl command allows you to query and change the configuration of the system clock and its settings, you can use this command to set or change the current date, time and timezone or enable automatic system clock synchronization with a remote NTP server.
In this tutorial, am going to take you through the ways you can manage time on your Linux system by setting the date, time, timezone and synchronize time with NTP from the terminal using new timedatectl command.
It is always a good practice to maintain the correct time on your Linux server or system and it can have the following advantages:
- maintain a timely operation of system tasks since most tasks in Linux are controlled by time.
- correct time for logging events and other information on the system and many more.
How to Find and Set Local Timezone in Linux
1. To display the current time and date on your system, use the timedatectl command from the commandline as follows:
# timedatectl status
In the scrrentcast above, RTC time: is the hardware clock time.
2. The time on your Linux system is always managed through the timezone set on the system, to view your current timezone, do it as follows:
# timedatectl OR # timedatectl | grep Time
3. To view all available timezones, run the command below:
# timedatectl list-timezones
4. To find the local timezone according to your location, run the following command:
# timedatectl list-timezones | egrep -o “Asia/B.*” # timedatectl list-timezones | egrep -o “Europe/L.*” # timedatectl list-timezones | egrep -o “America/N.*”
5. To set your local timezone in Linux, we will use set-timezone switch as shown below.
# timedatectl set-timezone “Asia/Kolkata”
It is always recommended to use and set the coordinated universal time, UTC.
# timedatectl set-timezone UTC
You need to type the correct name timezone other wise you may get errors when changing the timezone, in the following example, the timezone “Asia/Kalkata” is not correct therefore causing the error.
How to Set Time and Date in Linux
6. You can set the date and time on your system, using the timedatectl command as follows:
Set Time in Linux
To set time only, we can use set-time switch along the format of time in HH:MM:SS (Hour, Minute and Seconds).
# timedatectl set-time 15:58:30
Set Date in Linux
7. To set date only, we can use set-time switch along the format of date in YY:MM:DD (Year, Month, Day).
# timedatectl set-time 20151120
8. To set both date and time:
# timedatectl set-time '2015-11-20 16:14:50'
How to Find and Set Hardware Clock in Linux
9. To set your hardware clock to coordinated universal time, UTC, use the set-local-rtc boolean-value option as follows:
First Find out if your hardware clock is set to local timezone:
# timedatectl | grep local
Set your hardware clock to local timezone:
# timedatectl set-local-rtc 1
Set your hardware clock to coordinated universal time (UTC):
# timedatectl set-local-rtc 0
Synchronizing Linux System Clock with a Remote NTP Server
NTP stands for Network Time Protocol is a internet protocol, which is used to synchronize system clock between computers. The timedatectl utility enables you to automatically sync your Linux system clock with a remote group of servers using NTP.
Please note that, you must have NTP installed on the system to enable automatic time synchronization with NTP servers.
To start automatic time synchronization with remote NTP server, type the following command at the terminal.
# timedatectl set-ntp true
To disable NTP time synchronization, type the following command at the terminal.
# timedatectl set-ntp false
Summary
These are very easy examples described in this tutorial and I hope you will find them helpful for setting various Linux system clocks and timezones. To learn more about this tool, head over to timedatectl man page.