Glances is a free open source, modern, cross-platform, real-time top and htop-like monitoring tool with advanced features. It can run in different modes: as a standalone, in client/server mode and in web server mode.
InfluxDB is an open source and scalable time series database for metrics, events, and real-time analytics.
Grafana is an open source, feature rich, powerful, elegant and highly-extensible, cross-platform tool for monitoring and metric analytics, with beautiful and customizable dashboards. It is a de facto software for data analytics.
In this article, we will explain how to install and configure Glances, InfluxDB and Grafana to monitor performance of a CentOS 7 server.
Step 1: Install Glances in CentOS 7
1. First start by installing latest stable version of glances (v2.11.1) using PIP. If you don’t have pip, install it as follows, including Python-headers required for installing psutil.
# yum install python-pip python-devel
2. Once you have PIP and the Python-headers, run the following command to install the latest stable version of glances and verify the version.
# pip install glances # glances -V Glances v2.11.1 with psutil v5.4.7
Alternatively, if you already have glances installed, you can upgrade it to the latest version using following command.
# pip install --upgrade glances
3. Now you need to start glances via systemd so that it runs as a service. Create a new unit by creating a file called glances.service in /etc/systemd/system/.
# vim /etc/systemd/system/glances.service
Copy and paste the following configuration in the file glances.service. The --config specifies the config file, --export-influxdb option tells glances to export stats to an InfluxDB server and the --disable-ip option disables the IP module.
[Unit] Description=Glances After=network.target influxd.service [Service] ExecStart=/usr/bin/glances --config /home/admin/.config/glances/glances.conf --quiet --export-influxdb --disable-ip Restart=on-failure RestartSec=30s TimeoutSec=30s [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save the file and close it.
4. Then reload systemd manager configuration, start the glances service, view its status, and enable it to auto-start at boot time.
# systemctl daemon-reload # systemctl start glances.service # systemctl status glances.service # systemctl enable glances.service
5. Next, you need to download the glances configuration file provided by the developer using wget command as shown.
# mkdir ~/.config/glances/ # wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nicolargo/glances/master/conf/glances.conf -P ~/.config/glances/
6. In order to export Glances stats to an InfluxDB database, you need the Python InfluxdDB lib, which you can install it using pip command.
# sudo pip install influxdb
Step 2: Install InfluxDB in CentOS 7
7. Next, you need to add the InfluxDB Yum repository to install latest vesrion of InfluxDB package as shown.
# cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/influxdb.repo [influxdb] name = InfluxDB Repository - RHEL $releasever baseurl = https://repos.influxdata.com/rhel/$releasever/$basearch/stable enabled = 1 gpgcheck = 1 gpgkey = https://repos.influxdata.com/influxdb.key EOF
8. After adding the repository to the YUM configuration, install the InfluxDB package by running.
# yum install influxdb
9. Next, start the InfluxDB service via systemd, confirm that it is running by viewing its status and enable it to auto-start at system boot.
# systemctl start influxdb # systemctl status influxdb # systemctl enable influxdb
10. By default, InfluxDB uses TCP port 8086 for client-server communication over InfluxDB’s HTTP API, you need to open this port in your firewall using the firewall-cmd.
# firewall-cmd --add-port=8086/tcp --permanent # firewall-cmd --reload
11. Next, you need to create a database in InfluxDB for storing data from glances. The influx command which is included in the InfluxDB packages is the simplest way to interact with the database. So execute influx to start the CLI and automatically connect to the local InfluxDB instance.
# influx
Run the following commands to create a database called glances and view available databases.
Connected to http://localhost:8086 version 1.6.2 InfluxDB shell version: 1.6.2 > CREATE DATABASE glances > SHOW DATABASES name: databases name ---- _internal glances >
To exit the InfluxQL shell, type exit and hit Enter.
Step 3: Install Grafana in CentOS 7
12. Now, install Grafana from its official YUM repository, start by adding the following configuration to /etc/yum.repos.d/grafana.repo repository file.
[grafana] name=grafana baseurl=https://packagecloud.io/grafana/stable/el/7/$basearch repo_gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://packagecloud.io/gpg.key https://grafanarel.s3.amazonaws.com/RPM-GPG-KEY-grafana sslverify=1 sslcacert=/etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt
13. After adding the repository to the YUM configuration, install the Grafana package by running.
# yum install grafana
14. Once you have installed Grafana, reload systemd manager configuration, start the grafana server, check if the service is up and running by viewing its status and enable it to auto-start at boot time.
# systemctl daemon-reload # systemctl start grafana-server # systemctl status grafana-server # systemctl enable grafana-server
15. Next, open port 3000 which Grafana server listens on, in your firewall using the firewall-cmd.
# firewall-cmd --add-port=3000/tcp --permanent # firewall-cmd --reload
Step 4: Monitor CentOS 7 Server Metrics Via Grafana
16. At this point, you can use the following URL to access Grafana web interface, which will redirect to the login page, use the default credentials to login.
URL: http://SERVER_IP:3000 Username: admin Password: admin
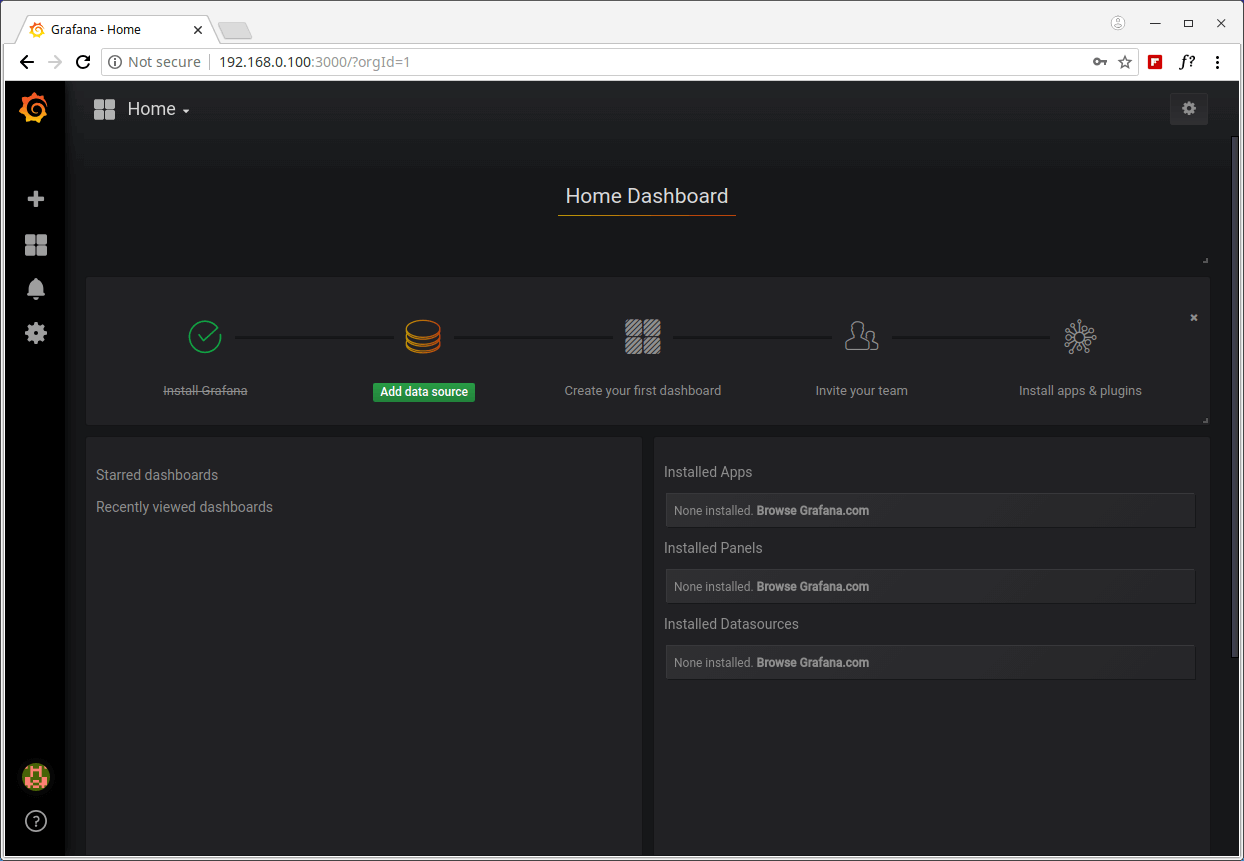
You will be asked to create a new password, once you have done that, you will be redirected to the home dashboard, as shown in the screenshot below.
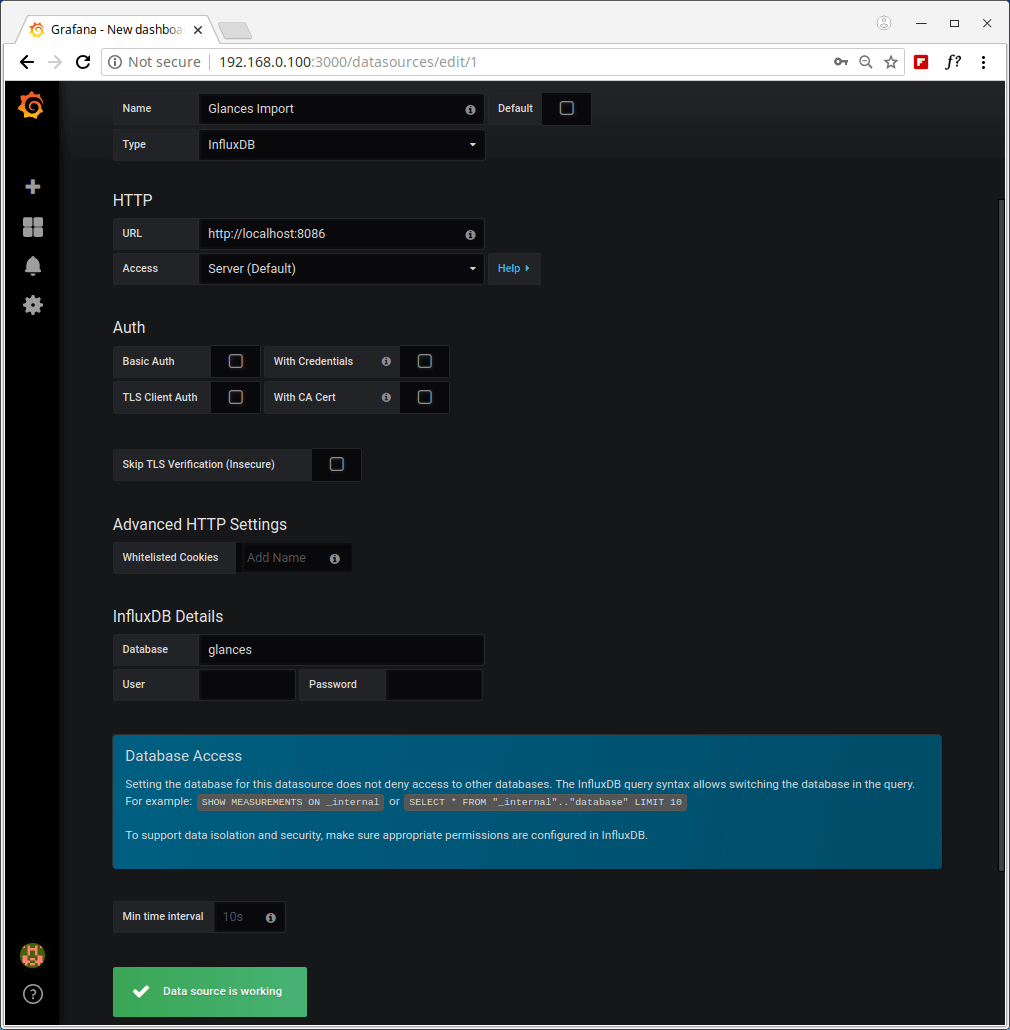
17. Next, click on Create your first data source, which should be an InfluxDB database. Under Settings, enter a suitable name e.g Glances Import, then use the following values for the other two important variables (HTTP URL and InfluxDB Database) as shown in the screenshot.
HTTP URL: http://localhost:8086 InfluxDB Details - Database: glances
Then click on Save & Test to connect to the data source. You should receive a feedback indicating “Data source is working”.
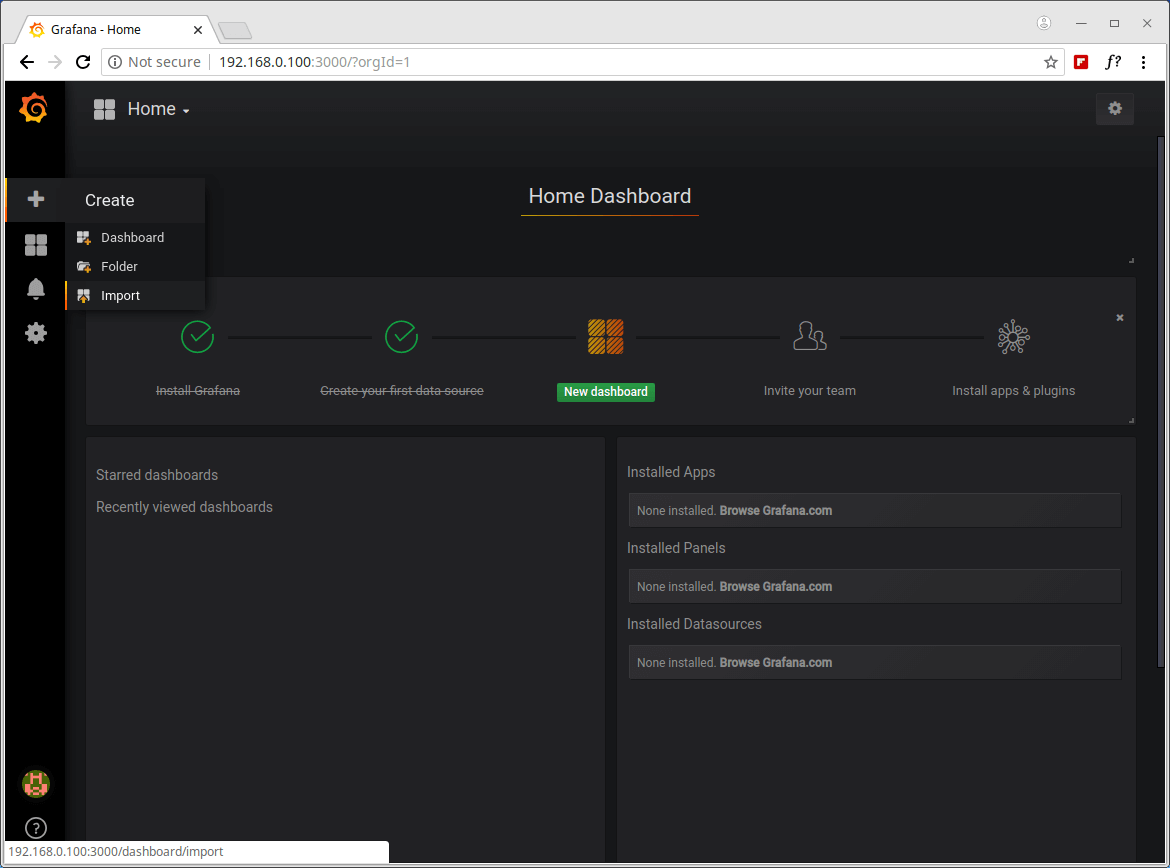
18. Now you need to import the Glances dashboard. Click on the plus (+) and go to Import as shown in the screenshot.
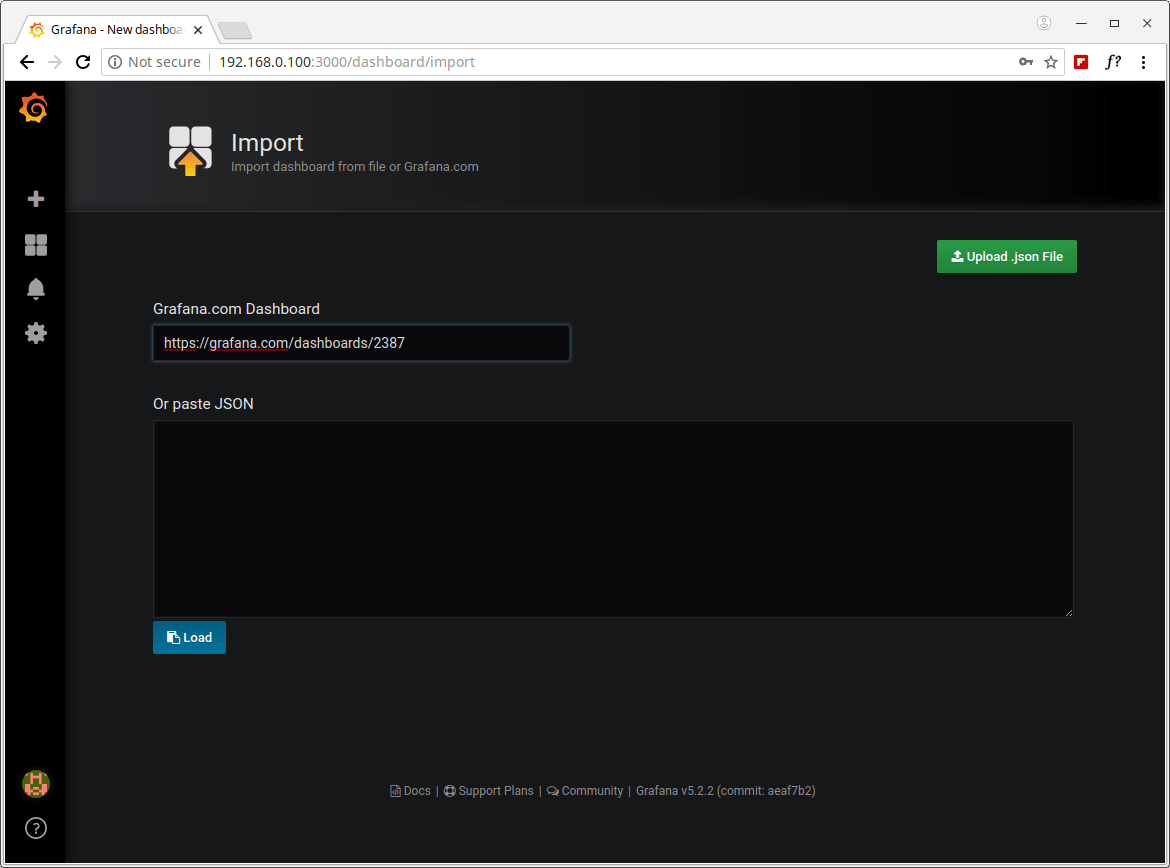
17. You will need either the Glances Dashboard URL or ID or upload its .JSON file which you can find from Grafana.com. In this case, we will use the Glances Dashboard created by the developer of Glances, its URL is https://grafana.com/dashboards/2387 or ID is 2387.
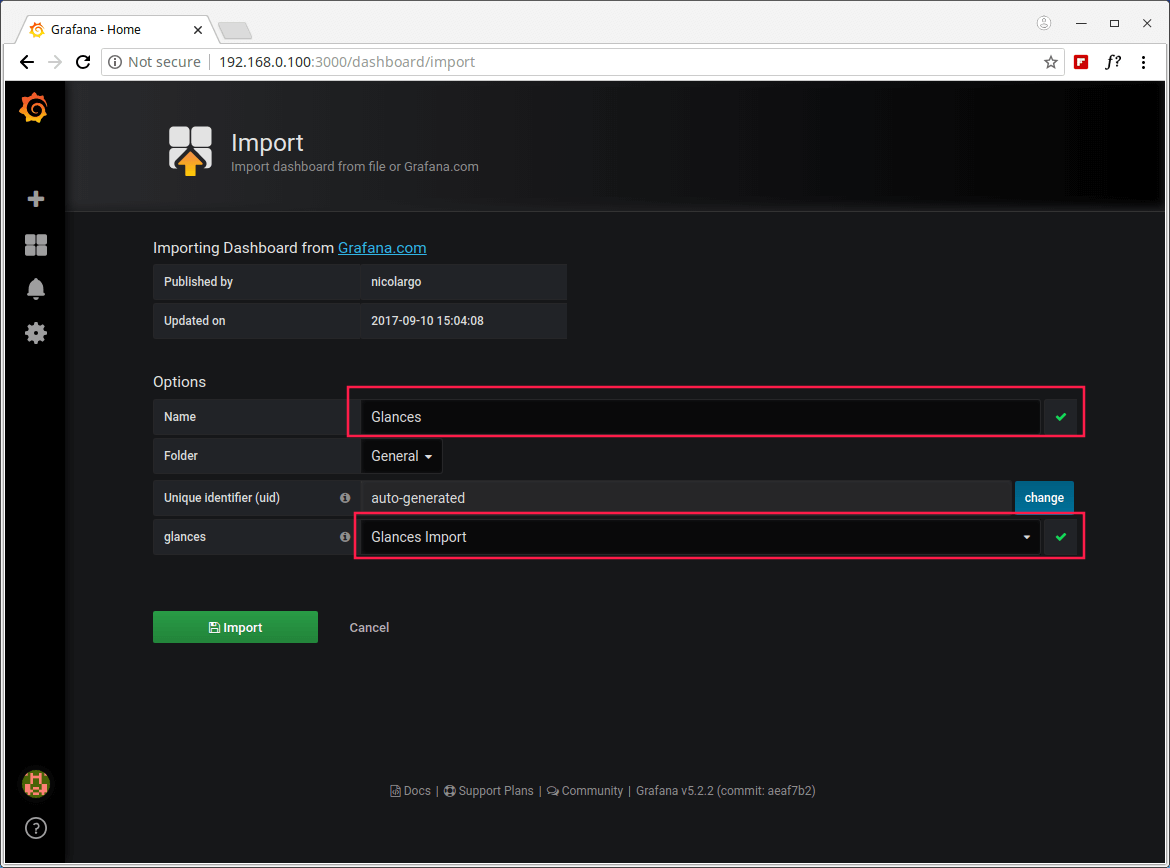
18. Once the Grafana dashboard has been loaded, under options, find glances and choose an InluxDB data source (Glances Import) which you created earlier on, then click on Import as shown in the following screenshot.
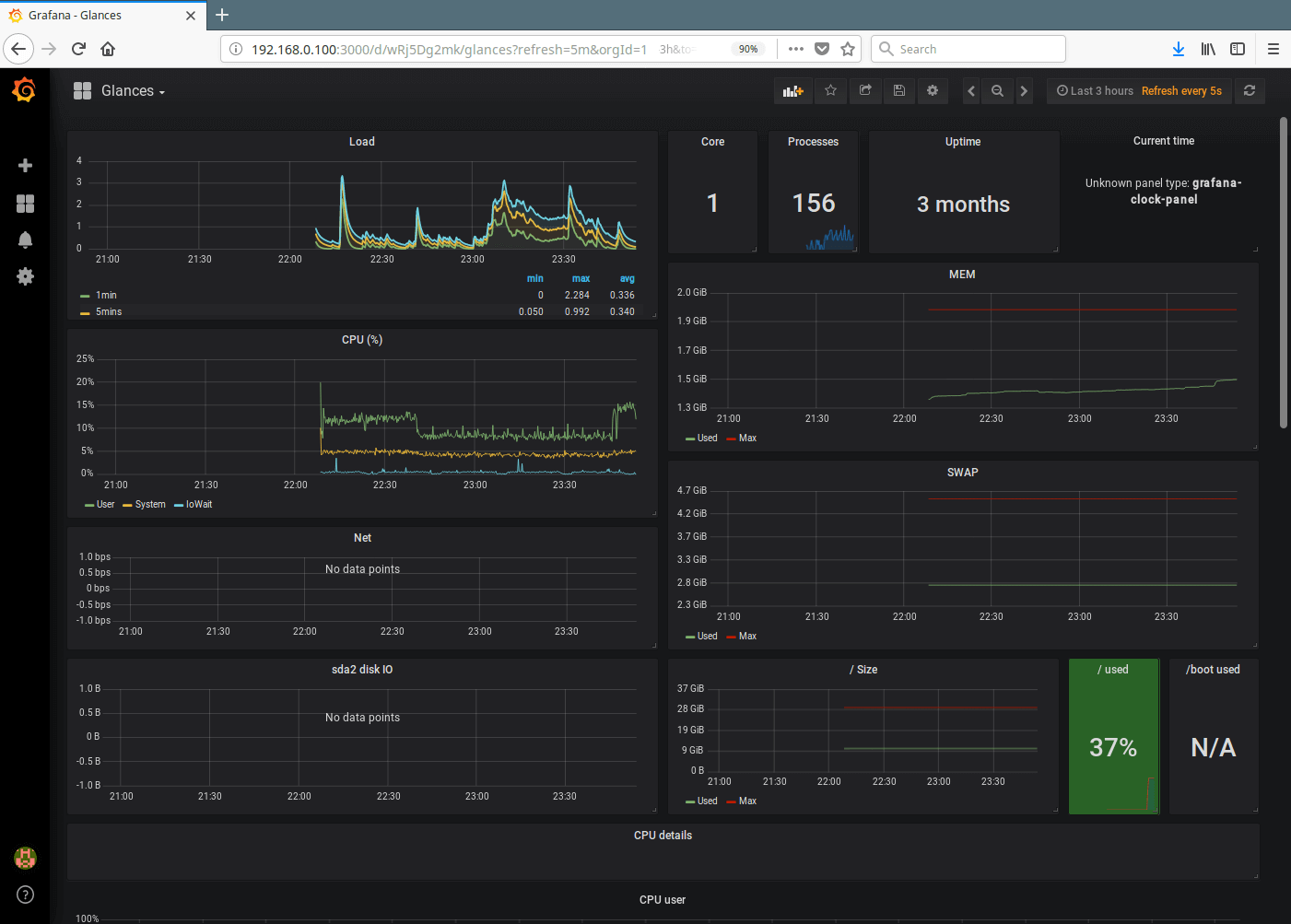
19. After successfully importing the Glances dashboard, you should be able to watch graphs showing metrics from your server as provided by glances via influxdb.
That’s all for now! In this article, we have explained how to monitor CentOS 7 server with Glances, InfluxDB and Grafana. If you have any queries, or information to share, use the comment form below to do so.