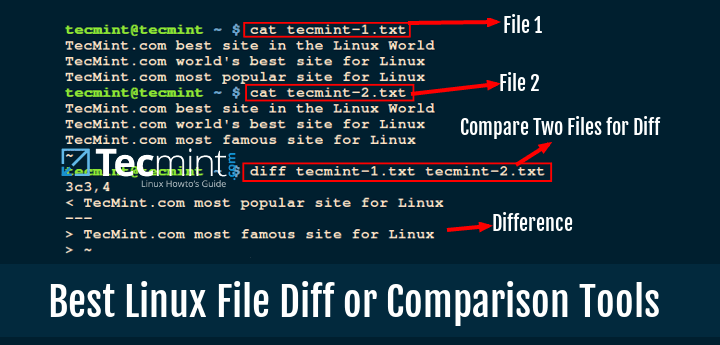
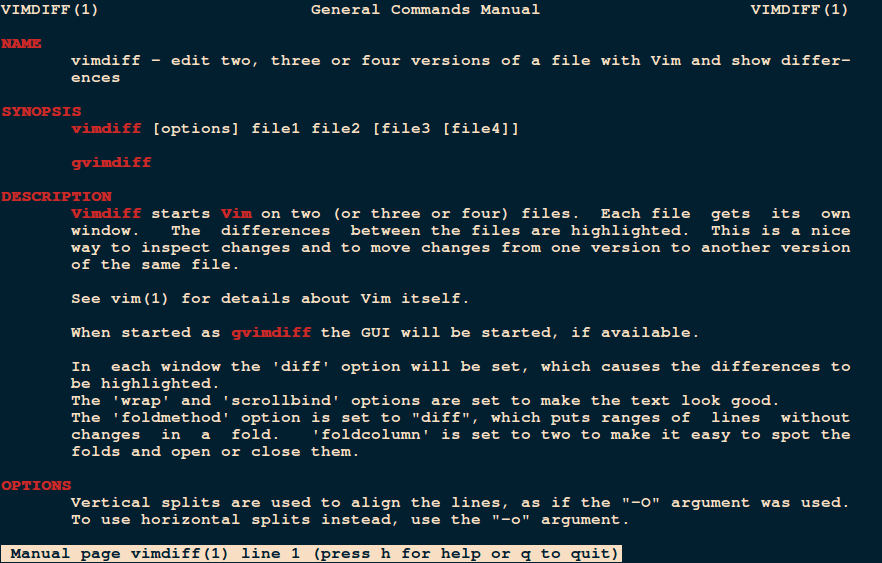
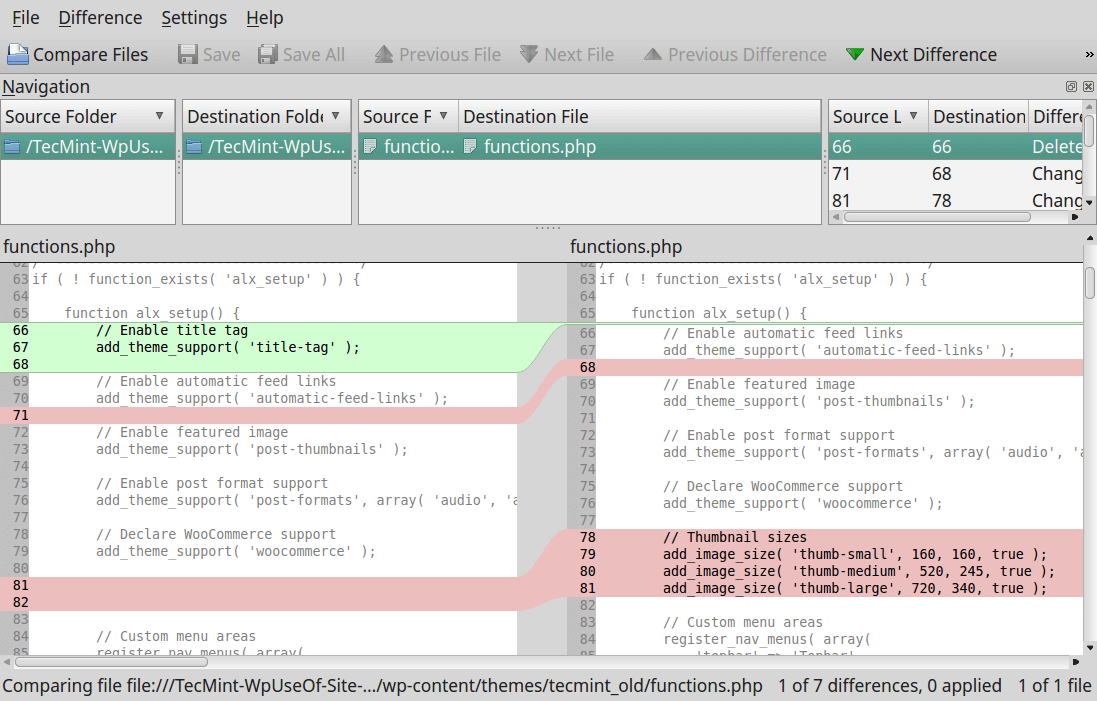
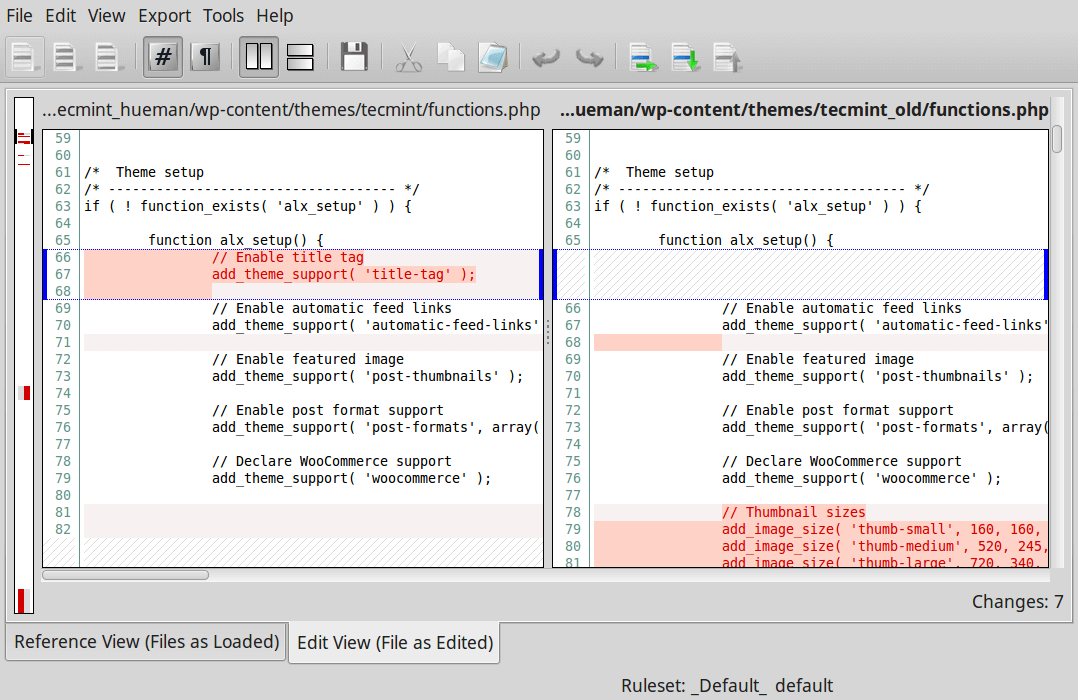
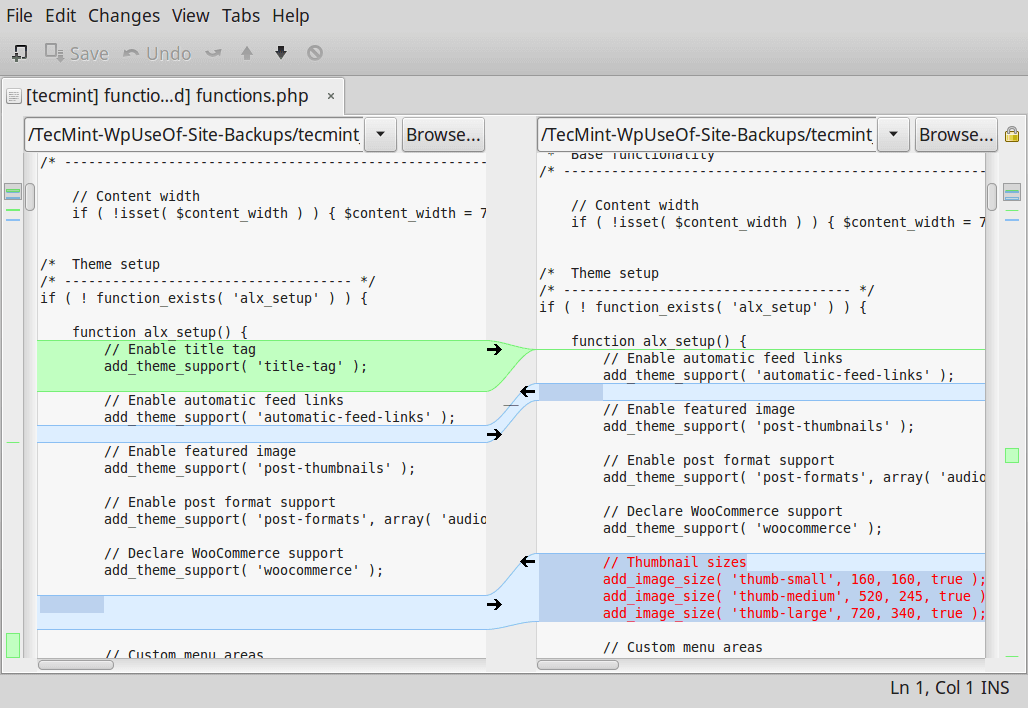
Cloud storage stands for virtualised pool of network storage most commonly hosted by third parties. Cloud storage is a network-based service which physically do not exist but remains somewhere in the cloud. To be more clear, cloud storage means sharing data over network, rather than having local servers or personal device.
Cloud storage is all around us in our smart phones, on desktops and servers etc. The Dropbox application which is now available on smart phone is nothing but cloud storage application. Google Drive is another cloud storage application which lets you store and access your stored data from anywhere and anytime.
This article aims at – Building your personal cloud storage using ownCloud application. But what is the need of building personal cloud when there are third party hosting. Well all the third party hosting limits you to work with the given configuration and storage limit. With the ever expanding list of photos, videos, mp3’s of storage is not sufficient, moreover cloud storage is a relatively new concept and there are not many third party cloud storage host and the available one is too much costly.
ownCloud community has recently released their special release ownCloud 9. They have come up with incredible changes in terms of quality, performance and innovations to provide excellent cloud experience with “ownCloud“. If you are already working with its older version, you’ll definitely experience significant improvements in Document handling.
What is ownCloud
ownCloud is a free, open-source and powerful web application for data synchronization, file sharing, and remote storage of files. ownCloud is written in PHP/JavaScript languages. It is designed to work with several database management systems, including MySQL, MariaDB, SQLite, Oracle Database, and PostgreSQL. Moreover owncloud can be deployed on all known platforms viz., Linux, Macintosh, Windows and Android. In short it’s a robust, platform Independent, flexible in terms of configuration and usability, easy-to-use open source Application.

Install Owncloud in Linux
Features of owncloud
- Store files, folders, contacts, photo galleries, calendar, etc on the server of your choice, Later you can access it from mobile, desktop, or web browser.
- In the world of gadgets, a normal person have tablet, smart phone, laptop, etc. Own cloud lets you sync all your files, contacts, photo, calendar, etc synced among the devices.
- In the era of sharing aka Facebook, Twitter, Google+, etc, owncloud lets you share your data with others and share them publicly or privately as per your needs.
- Easy user interface lets you manage, upload, create user, etc in a very easy fashion.
- A special feature is that, even user can undelete the accidentally deleted data from Trash, is not it easy to handle and maintain.
- The search feature in owncloud is very responsive which is done in background and lets user search by name as well as file type.
- Contacts are organised in categories/group hence easy to access contacts on the basis of friends, co-worker, Family, etc.
- You can now access external storage be it Dropbox, FTP or anything else by mounting.
- Easy to migrate to/from other owncloud server.
What’s New in ownCloud 9
- Accessibility Improvement for app’s management page, updater app and search.
- Additional notification and direct download supported.
- Storage configuration file can be tuned to a higher level in this release.
- Apps management is now intelligent enough to store App’s dependency in XML file from where Apps container can solve the dependencies automatically.
- Documentation improved to next level, PDF viewer improved with the implementation of new version of PDF.js.
- Improved user management and structured settings and admin page improved.
- Link sharing has now gone better by shortening.
- Overall performance improved as compared to previous version.
- Contacts importing improved.
- Federated (United) cloud sharing which means setting up of shared folder across server is a cake walk. This feature makes it possible to collaborate organizations with the control at local owncloud deployment server.
- Apps now features rating and are category based.
- Set favorite icon to files and folder so that it is easy to sort and edit.
- Add files to favorites so that it is easy to find them later.
- Admin can edit email address of users, sort and select user as well as rename group.
- Basic feature includes – connecting to owncloud over HTTP(s), browse for files/folder in explorer, automatic sync, sharing files with other users, sync folders from PC, Pause and resume downloads and uploads and configure proxy.
System Requirements
For higher performance, stability, support, and full functionality we recommend following things:
- Minimum 128MB RAM, recommend 512MB.
- RHEL/CentOS 7/6, Fedora 18-23, Ubuntu 16.04-12.04, Debian 8/7, etc.
- MySQL/MariaDB
- PHP 5.4 +
- Apache 2.4 with mod_php
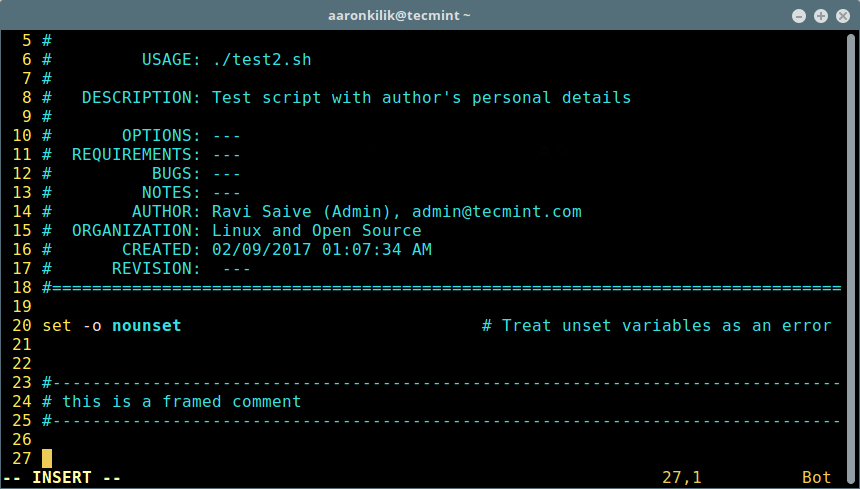
Step 1: Install ownCloud Storage in Linux
In order to setup your own personal cloud storage (ownCloud), you must have LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL/MariaDB, PHP) stack installed. Other than LAMP stack you might need Perl and Python based upon your use.
On Debian/Ubuntu/Linux Mint
---------------------- For MySQL Server ----------------------
# apt-get install apache2 apache2-doc apache2-utils mysql-server mysql-client php5 php5-mysql php5-curl
---------------------- For MariaDB Server ----------------------
# apt-get install apache2 apache2-doc apache2-utils mariadb-server php5 php5-mysql php5-curl
On RedHat/CentOS/Fedora
---------------------- For MySQL Server ----------------------
# yum install httpd mysql-server mysql-client php php-mysql php-curl
---------------------- For MariaDB Server ----------------------
# yum install httpd mariadb-server php php-mysql php-curl
Step 2: Create Cloud Database
Once you setup LAMP stack on your personal box, just login to your database (MySQL, here).
# mysql -u root -p
Enter mysql root password. Now we will be creating a database (say cloud).
mysql> create database cloud ;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
It is not a good idea to access your database from root, hence grant all the permission to a normal user (say tecmint).
mysql> grant all on cloud.* to tecmint@localhost identified by 'my_password';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Step 3: Download and Install ownCloud Application
Now its time to Download latest ownCloud (i.e version 8.0.0) application using below link.
- http://owncloud.org/install/
Alternatively, you may use wget command to download the source tar-ball package.
# wget https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
You may alternatively install from binary package using APT or YUM. The installation instruction can be found at:
- Install ownCloud using APT or YUM
However we choose the TAR package which is universally accepted and works on most of the known system.
After Downloading the owncloud package, move it to your Apache working directory, which is /var/www (for Debian) and /var/www/html (for RedHat).
# cp owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2 /var/www/ [For Debian based Systems]
# cp owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2 /var/www/html/ [For RedHat based Systems]
Next, extract the package using tar command as shown below.
# tar -jxvf owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
Since the TAR Archive is extracted you may remove the Archive.
# rm -rf owncloud-9.0.0.tar.bz2
We might need to change the file permission of owncloud, in our Apache working directory.
# chmod -R 777 owncloud/
Note: Remember we are giving read, write and execute permission to all, which is although risky but this time needed since several configuration file would be written automatically. We later need to change permission to 755, once the setup is finished.
Step 4: Configuring Apache for ownCloud
For security purpose ownCloud uses Apache‘s .htaccess files, in order to use them. We need to enable two Apache modules mod_rewrite and mod_headers for ownCloud to function properly. Type the following command to enable these modules under Debian based systems only, for RedHat systems they are enabled by default.
# a2enmod rewrite
# a2enmod headers
Additionally, we need to enable mod_rewrite rules to work properly under Apache‘s main configuration file. Open the Apache global configuation file.
# nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/default [For Debian based Systems]
# vi /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf [For RedHat based Systems]
There, find “AllowOverride None” and change this to “AllowOverride All” as shown.
AllowOverride None
Change this to:
AllowOverride All
Now we need to restart Apache to reload new changes.
# service apache2 restart [For Debian based Systems]
# service httpd restart [For RedHat based Systems]
Step 5: Access ownCloud Application
Now you can acess your very personal cloud storage at:
http://localhost/owncloud
OR
http://your-ip-address/owncloud
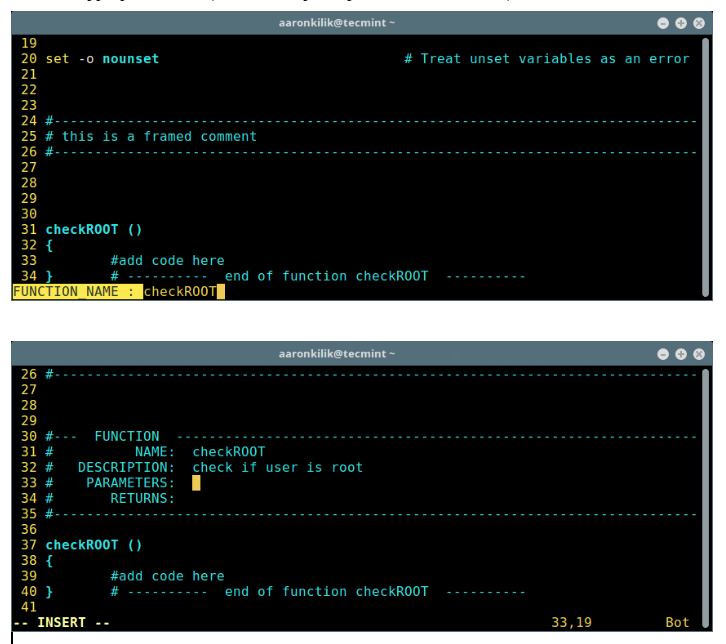
Once you get the Owncloud page, you need to create an admin account and a Data folder location, where all files/folders will be stored (or leave default location i.e. /var/www/owncloud/data or /var/www/html/owncloud/data). Next, you need to enter mysql database username, password and database name, refer the screenshot below.
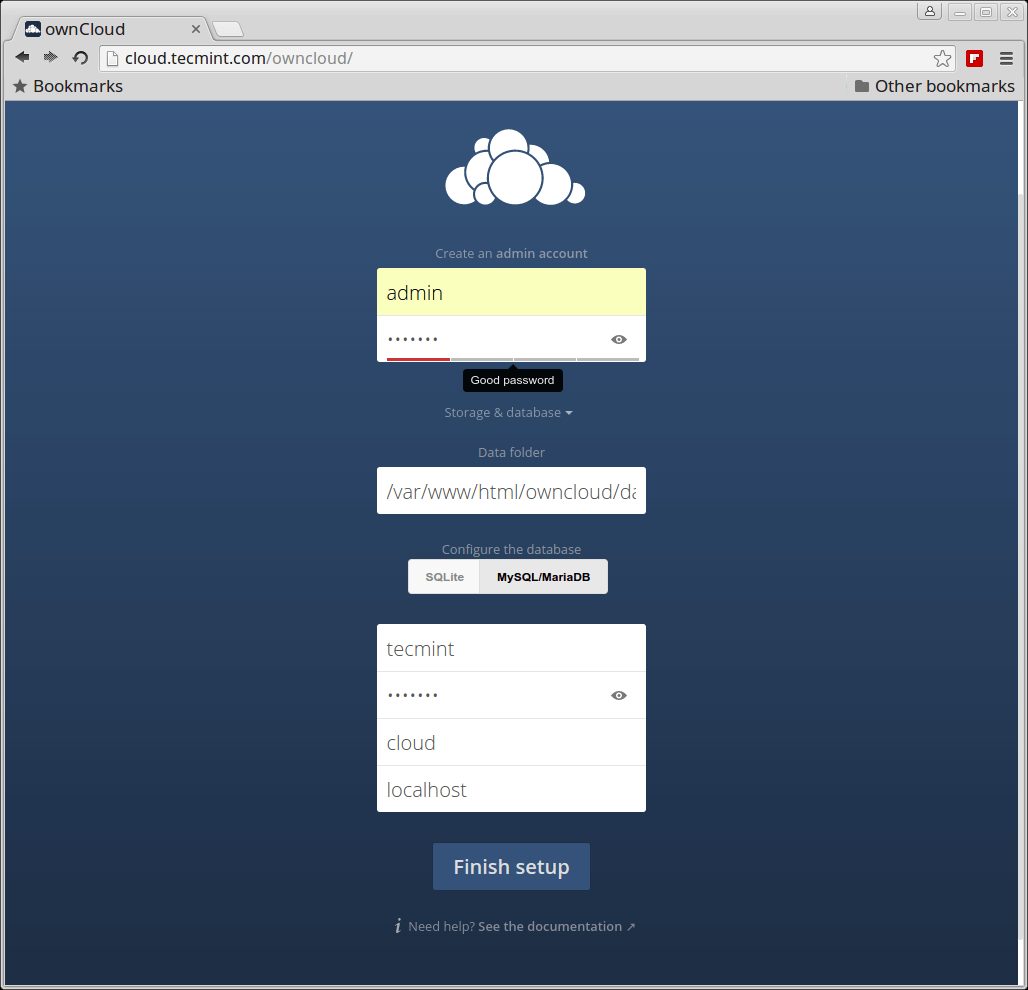
OwnCloud 9 Installation Wizard
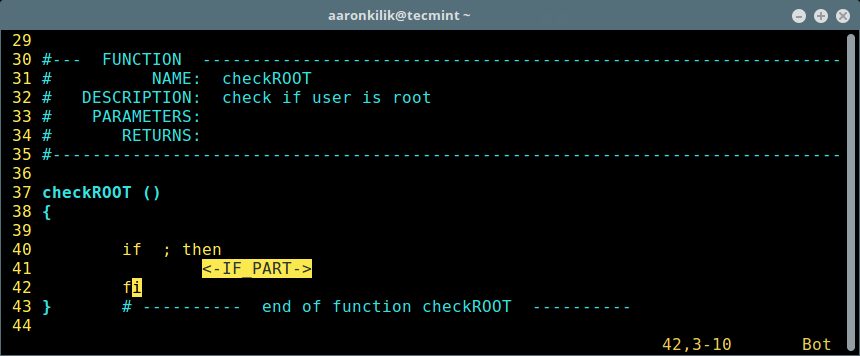
Once all the correct values are entered, click Finish and your private cloud storage is ready, you are greeted with the working interface:
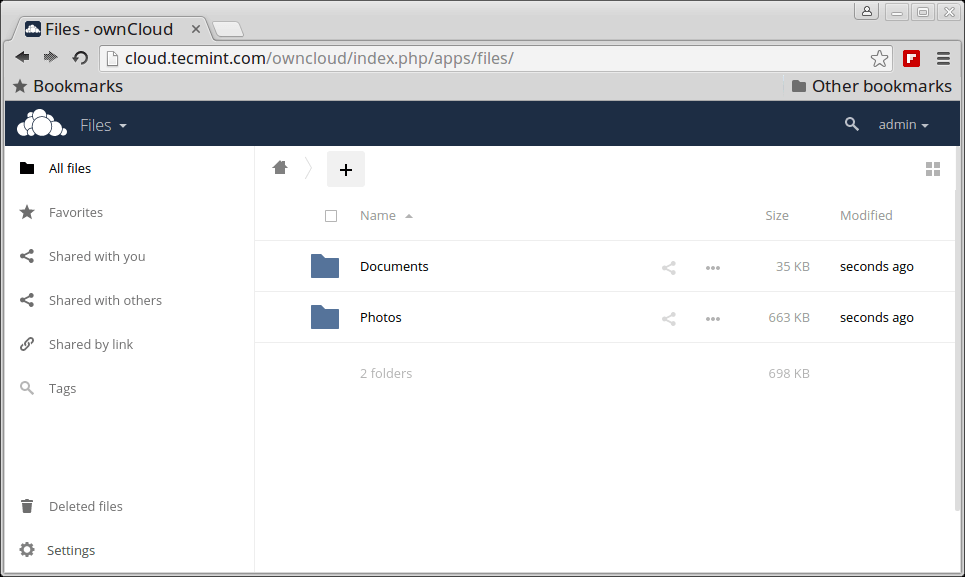
OwnCloud 9 Admin Dashboard
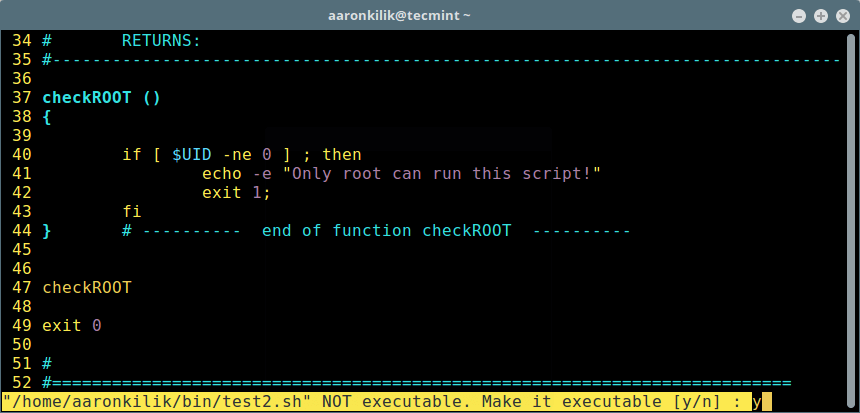
Notice the Favorites, edit, share, download, upload and new file options available for a file.
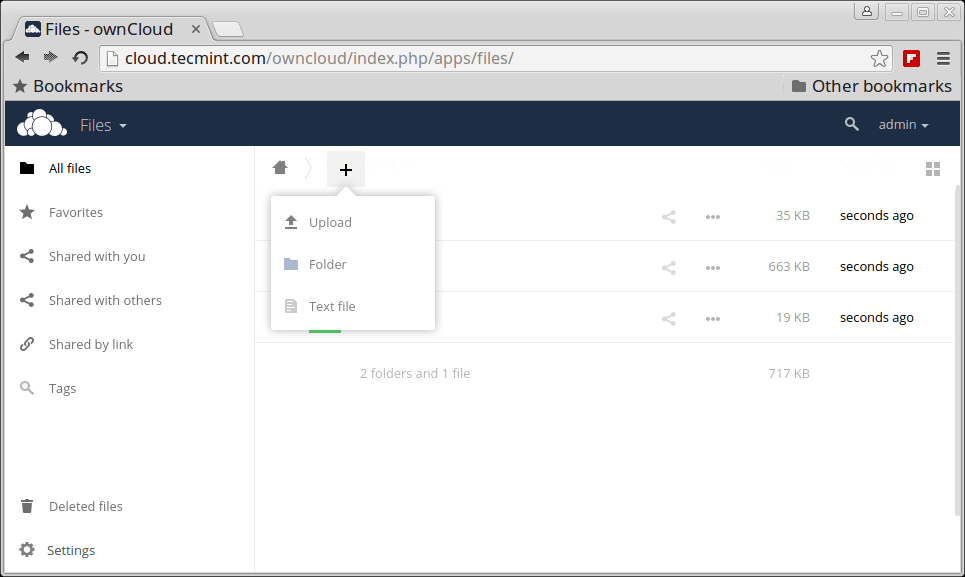
Upload Files to OwnCloud Storage
Activities log of oneself and others.
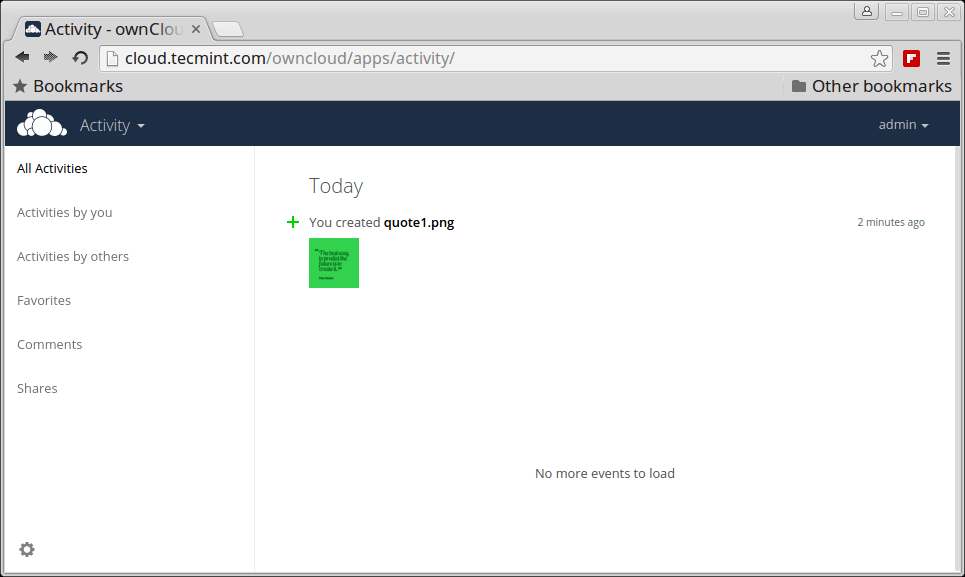
Owncloud Activity Log
Pictures library.
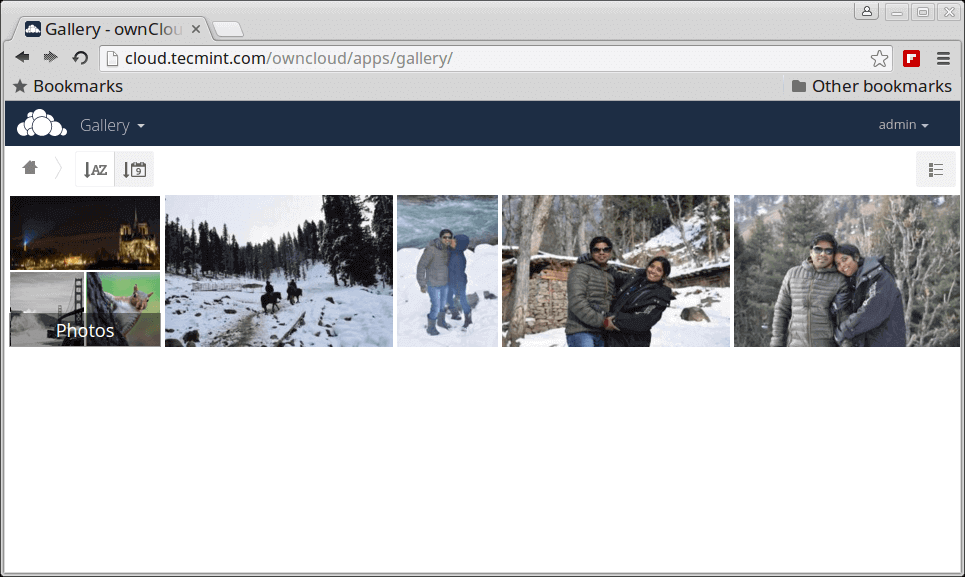
My Owncloud Picture Library
Apps enable and disable interface as well as recommendation with brief introduction.
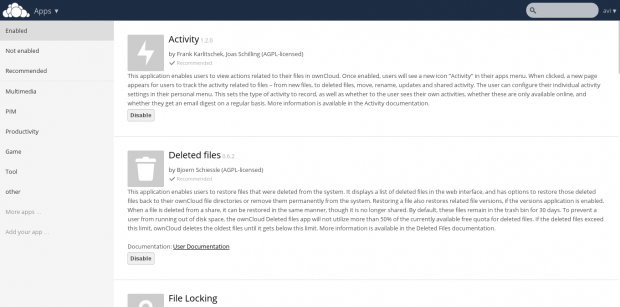
Enabled Application
Inbuilt PDF reader.
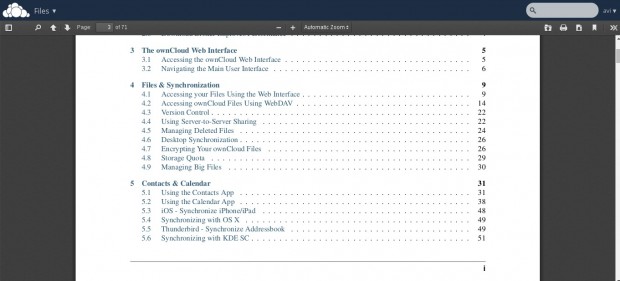
PDF Reader
From this admin panel you can view security and setup warnings, Fedrated cloud sharing, Mail Templates,
Updater, Cron, sharing, Security, Email Server, Log, etc.
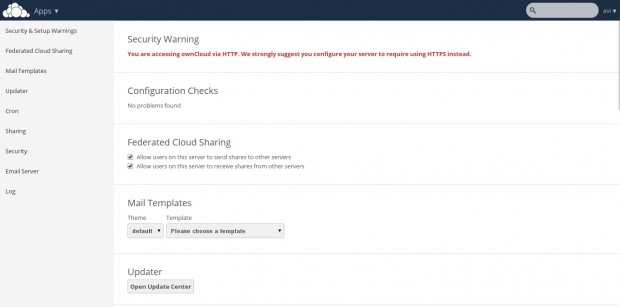
Security Setup Warning
User and Group information with quota.
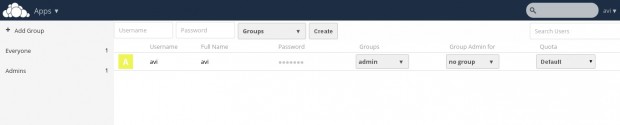
User Group Quota
Note: You can add users or imports user account, change password, assign user role and allocate space by clicking the Gear icon on left bottom of the page.
You may now add folder, sync media files be it pictures, images and videos from the mobile application. Owncloud lets you add new user, and sync calendar, contacts, Media files, etc.
It also has a built in MP3 Player, PDF Viewer, Document Viewer, and a lot many which is worth a try and explore. So what are you waiting for? Become a proud owner of private cloud storage, give it a try!
Upgrading to Owncloud 9 from Older Versions
To update earlier version of your owncloud to 9, you need to first update the old owncloud to latest point release of the same version.
For example, if you’re using owncloud 6.0.xy (where ‘xy‘ is the version number), you need to first update to 6.0.xof the same series, and then you able to upgrade to owncloud 7 using the following instructions.
Update Owncloud 6.0.xx to 6.0.2
1. Making proper backup of everything is always suggested.
2. Enable the updater plugin (if it is disabled).
3. Go to Admin Panel and fire update.
4. Refresh page using ‘Ctrl+F5‘, you’re done.
If above procedure doesn’t worked, you can do a full upgrade to update to the newest point release (see ‘Upgrade‘ instructions below).
Else, if you’re already using Owncloud 7 or 8 and want to update to Owncloud 9, you can follow the below same ‘Upgrade’ instructions to get the latest version of Owncloud.
Upgrading OwnCloud 8 to OwnCloud 9 Latest Release
1. Update your owncloud version to latest point release of your version.
2. Not to Mention, Make a full backup before upgrading.
3. Download the latest tarball using wget command.
# wget http://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-latest.tar.bz2
4. Deactivate all native and third party Applications and plugins.
5. Delete Everything from the owncloud Directory except DATA and CONFIG directory.
NOTE: Don’t touch DATA and CONFIG directory.
6. Untar the tar-ball and copy everything to the root of your owncloud directory within your working directory.
7. Grant required permissions and run Upgrade from the Next page and its done!.
8. Don’t forget to install and enable Third party Application and plug-ins only after checking the compatibility with the current version.
So what are you waiting for? Install the latest owncloud project or upgrade your last version to latest and start using it.
Reference Links
- ownCloud Homepage
That’s all for now. Don’t forget to provide us with your valuable feedback in comments.
Source