How to install Dropbox on CentOS 7
How to install Dropbox on CentOS 7
Install Dropbox on CentOS 7
Dropbox is the online storage service supports Linux distros. Dropbox provides online storage to backup and store data automatically with security. It has both free and paid plan. In the free plan, it provides 2GB storage if you want more storage then you can buy paid plans. In this tutorial, you are going to learn how to install Dropbox on CentOS 7 server.
Prerequisites
Before you start to install Dropbox on CentOS. You must have the non-root user account on your server with sudo privileges.
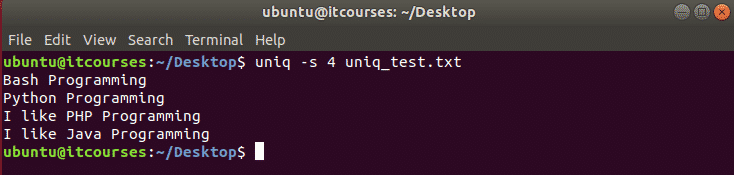
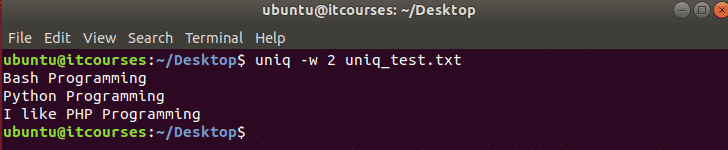
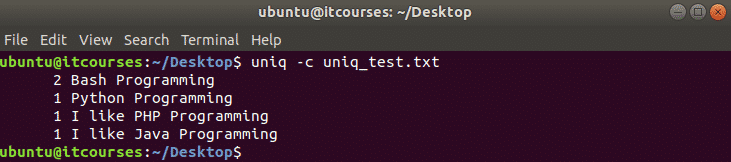
Install Dropbox Client
Here we will first install Dropbox Client. Download Dropbox Client using the following command.
curl -Lo dropbox-linux-x86_64.tar.gz https://www.dropbox.com/download?plat=lnx.x86_64
Create a directory for Dropbox installation by using the following command.
sudo mkdir -p /opt/dropbox
Now extract the downloaded file inside /opt/dropbox directory.
sudo tar xzfv dropbox-linux-x86_64.tar.gz –strip 1 -C /opt/dropbox
Setup account for Dropbox
In this section, we will link your Dropbox account to Dropbox client on your server to do so execute the following command.
/opt/dropbox/dropboxd
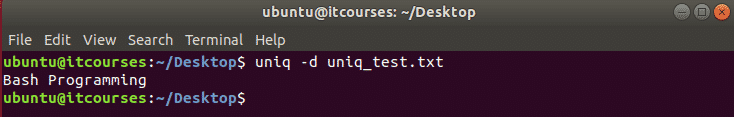
You will get the following output, just copy the link given inside output and run it inside your favorite browser on your local machine.
Host ID Link:
This computer isn’t linked to any Dropbox account…
Please visit https://www.dropbox.com/cli_link_nonce?nonce=3d88f2e1f2949265ebcac8d159913770 to link this device.
If you have existing Dropbox account then just Sign in otherwise create a new account on Dropbox.
 Install Dropbox on CentOS – Register to Dropbox
Install Dropbox on CentOS – Register to Dropbox
Once you complete above process you will see the following output on your CentOS system.
Link success output:
This computer is now linked to Dropbox. Welcome Sammy
You have successfully linked your Dropbox account to Dropbox client. A new Dropbox directory is created inside the HOME directory to store synchronized Dropbox files. Now Enter Ctrl+c to setup Dropbox as a service.
Setup Dropbox as a Service
To set up Dropbox as a service, you should create a init script and Systemd unit file to do so enter the following command.
sudo curl -o /etc/init.d/dropbox https://gist.githubusercontent.com/thisismitch/6293d3f7f5fa37ca6eab/raw/2b326bf77368cbe5d01af21c623cd4dd75528c3d/dropboxsudo curl -o /etc/systemd/system/dropbox.service https://gist.githubusercontent.com/thisismitch/6293d3f7f5fa37ca6eab/raw/99947e2ef986492fecbe1b7bfbaa303fefc42a62/dropbox.service
Run following script to make above files executables.
sudo chmod +x /etc/systemd/system/dropbox.service /etc/init.d/dropbox
/etc/sysconfig/dropbox file should contain system user names who will run Dropbox. Run following command to edit this file.
sudo nano /etc/sysconfig/dropbox
Set username as given in below example then save and exit the file.
DROPBOX_USERS=”john”
Now reload the Systemd daemon.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Now start and enable Dropbox service executing following command.
sudo systemctl start dropbox && sudo systemctl enable dropbox
Install Dropbox CLI
Enter following command to download the Dropbox CLI script.
cd ~ && curl -LO https://www.dropbox.com/download?dl=packages/dropbox.py
Make the file executable by running following command.
chmod +x ~/dropbox.py
As Dropbox CLI expects ~/.dropbox-dist to contain your Dropbox installation files to do so run following command.
ln -s /opt/dropbox ~/.dropbox-dist
Now you can run Dropbox client by using following command. It will instructions for how to use Dropbox CLI.
~/dropbox.py
You can check the status of Dropbox by typing following command.
~/dropbox.py status
You should get following output
Output:
Up to date
To turn off the automatic LAN sync use following command.
~/dropbox.py lansync n
If you want more information about a specific command enter following command
~/dropbox.py help sharelink
Above command will provide you more information about sharelink command.
dropbox running
Returns 1 if running 0 if not running.
Check status of dropbox by typing
~/dropbox.py status
If Dropbox is not active then start service by running following command
~/dropbox.py start
To stop dropbox service enter following command
~/dropbox.py stop
Get sync status of Dropbox file by typing
~/dropbox.py filestatus Dropbox/test.txt
Generate shareable link for a file by typing
~/dropbox.py sharelink Dropbox/test.txt
You can exclude the directory from syncing by using the following command
~/dropbox.py exclude add Dropbox/dir1
To list excluded directories type following command
~/dropbox.py exclude list
Remove directory from excluded list typing
~/dropbox.py exclude remove Dropbox/dir1
Link Additional Dropbox Account
To link additional Dropbox account run following command then copy the given url in output.
/opt/dropbox/dropboxd
Now go to the URL given in the output and complete the authentication process.
Then add the user inside /etc/default/dropbox file.
sudo nano /etc/default/dropbox
Unlink Dropbox Account
First stop the Dropbox service.
sudo service dropbox stop
Remove the user from /etc/default/dropbox file.
sudo nano /etc/default/dropbox
Then delete Dropbox user directry using following command replacing USERNAME with the real username of system.
sudo rm -r ~/USERNAME/Dropbox
Now start the Dropbox service.
Conclusion
You have successfully learned how to install Dropbox on CentOS 7. If you have any queries don’t forget to comment below.
Source

 How to install Dropbox on CentOS 7
How to install Dropbox on CentOS 7 Install Dropbox on CentOS – Register to Dropbox
Install Dropbox on CentOS – Register to Dropbox