Linux has traditionally suffered an embarrassment of riches when it comes to the selection of the distribution that that is used to deploy it.
What Is a Linux Distribution?
Linux is an Operating System, which is the program at the heart of controlling a computer. It decides how to partition the available resources (CPU, memory, disk, network) between all of the other programs vying for it. The operating system, while very important, isn’t useful on its own. Its purpose is to manage the compute resources for other programs. Without these other programs, the Operating System doesn’t serve much of a purpose.
That’s where the distribution comes in. A distribution provides a large number of other programs that, together with Linux, can be assembled into working sets for a vast number of purposes. These programs can range from basic program writing tools such as compilers and linkers to communications libraries to spreadsheets and editors to pretty much everything in between. A distribution tends to have a superset of what’s actually used for each individual computer or solution. It also provides many choices for each category of software components that users or companies can assemble into what they consider a working set. A rough analogy can be made to a supermarket in which there are many options for many items on the shelves, and each user picks and chooses what makes sense to them in their cart.
Binary-Based or Source-Based Distribution?
Distributions can largely be split into two categories: binary-based and source-based.
Binary-based distributions provide all of the software components already pre-compiled and ready to be installed. These components are compiled with “good-enough” build options that work fine for the majority of users. They also do provide sources for these components for the minority of users that need or want to compile their own components. Following our supermarket analogy, this supermarket contains all of the food pre-packaged and pre-cooked, but with clear instructions on how to get the ingredients and repeat the process for those that want to tweak a recipe or two. This kind of distribution is exemplified by Debian, Fedora Core, OpenSUSE, Ubuntu, and many others. And while they provide the same type of system, they all do so using different—and unfortunately, incompatible—methods. They’re the primary kind of distribution used in general purpose computers such as servers, desktops, and laptops.
Source-based distributions, on the other hand, focus on providing a framework in which the end users can build all of the components themselves from source code. These distributions also provide tools for easily choosing a sensible starting collection of components and tweaking each component’s build as necessary. These tweaks can be as simple as adding a compile flag to using a different version of the sources or modifying the sources in some way. A user will assemble a menu of what they want to build and then start the build. After minutes or hours, depending on the case, they will have a resulting image which they can use for their computer. Examples of this kind of distribution are Gentoo, Android, and Yocto. In our supermarket analogy, this is closer to a bulk foods store, where you can get pre-measured foods with detailed machine-readable cooking instructions, and you’d have a fancy cooker that can read those instructions and cook the meals for you. And handle tweaks to a range of recipes such as adjusting for brown rice over white rice. Sort of — the analogy gets a bit weak on this one.
These source-based distributions are generally preferred for embedded Linux-based devices in general and IoT devices in particular. While they are harder to set up and maintain, source-based distributions have the unique advantage of being able to tailor the installed image to the exact target hardware in order to maximize resource usage—or minimize resource wastage. And for embedded devices that tend to be a strong constraint. In addition, source based distributions are better suited for cross-building—where the machine on which you build your platform isn’t the same as the one on which you run it—while binary based distributions are better for self-hosted building—where you build and run on the same machine (or same architecture).
Given today’s prevalence of having Intel architecture machines as build machines—and using ARM architecture for IoT products—cross-building support is important for IoT devices.
New Kid On The Block: Container-Centered Distributions
The traditional Linux method—shipping a single unified userspace that contains all of the platform outside of the kernel—is changing. The new model is about having a collection of “containers” that componentize the userspace. The containerized model transforms a portion of the userspace into a federated collection of components with a high degree of independence between each component.
Containerized distribution brings many benefits, from allowing teams to work more independently to making it feasible to do granular platform upgrades. The downside is that they have a larger footprint than non-containerized solutions. If the evolution of technology has shown us anything, however, it’s that when the only downside of a new technology is the footprint, the resourcing available to it tends to expand to make that a smaller and smaller problem at every new generation.
Some of the early options are described below to compare to existing distributions.
The Contenders: Linux Distributions for IoT
Now we must delve into contentious territory. Many people have their favorite Linux distribution, and even if their requirements change wildly (for example going from a server setup to an embedded IoT device), they cling onto that distribution—sometimes to the point of fitting a square peg into a round hole.
I’ll preface the list below: this is a sampling of some well established Linux distributions and some up and comers. Many others exist and might be more suitable for some use cases.
Now with that out of the way…
Yocto
Yocto is a source-based distribution that’s used in many embedded and IoT devices. It tries to unite the benefits of binary-based distributions, such as clear separation of the packages and their dependencies, with the benefits of source-based distributions that allow you to alter your target binaries in significant ways as you make smaller changes.
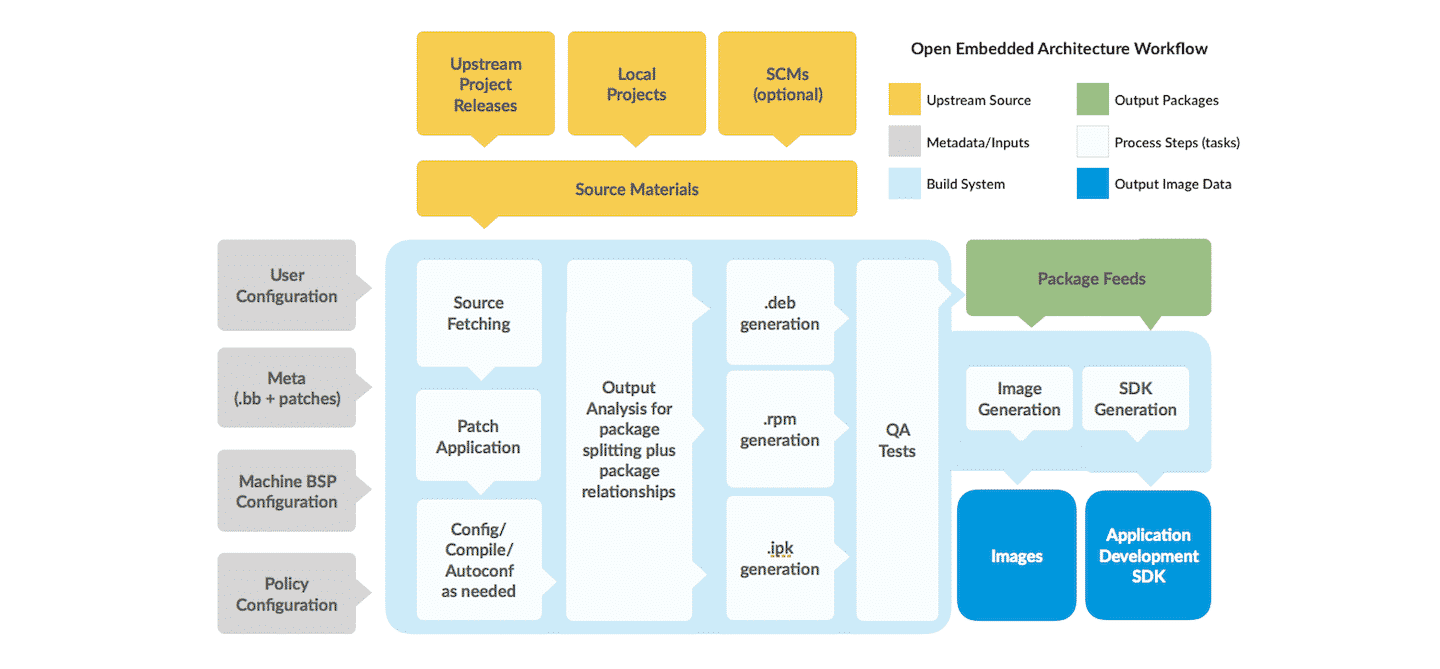
Yocto is composed of a series of recipes, each of which describes how to build one module of the system (e.g. library, daemon, application, etc.). These recipes are then collected into layers which collect a series recipes and configure various aspects of how they are supposed to be used together, from compile flags to recipe features, to details on how they show up on the target. Each target build will be composed of a few of these layers, each one adding or removing packages from the lower layers, or modifying their default behavior. This allows multiple parties to tweak their own layer to affect final images. So if the base layer uses a conservative set of compiler flags (which it usually does), a chip vendor can add compiler flags that are beneficial to their specific chip model, and a board vendor can remove chip functionality that their board might not support.
What this means in practice for your IoT product is that your effort to build a solution using a board that already supports Yocto will be to add or modify recipes that provide your value-add over the base functionality. You will also need to have a build and configuration management infrastructure setup that allows creating images for your target, though in today’s world of containers that is not too difficult to do
For more information on Yocto, you can start here. It’s also worth checking out how well supported Yocto is on any dev. boards that you’re considering for your IoT solution.
Debian
Debian is a venerable open source binary-based distribution. It’s both a distribution onto itself and also the baseline for other well-known derived distributions, the most famous of which is Ubuntu.
Debian has a sizeable collection of packages that are already pre-built for ARM (the architecture of choice for IoT), but the level of support and maintenance for the ARM binaries of these packages tends to be significantly less than the Intel counterparts given Debian’s strength in Intel ecosystems. So metrics such as “10,000+ packages built” aren’t all that meaningful. You’ll need to understand the packages that are important to you and how well-supported they are.
A shortcoming of many distributions used in self-hosted setups (e.g. Debian) is that developers don’t understand or remember that package installation might not be done on the machine that will ultimately be running the package, and thus they can’t rely on any functionality from the target being available. Given that this nuisance is also a headache for docker environments, distributions have spent good effort in cleaning up these dependencies, so it’s a smaller problem than it used to be.
The effort to set up a build environment for a small set of packages is fairly trivial, but the infrastructure to build all the packages for a system can become significant.
Because of these, Debian for IoT is a good option as long as the board you can considering already has gone through the effort of supporting Debian, in which case you just need to add or create a few packages to complete your platform
EdgeX Foundry
EdgeX Foundry is not exactly a distribution in the strict sense, in that it does not have any opinion on the Board Support Package (BSP) component of distributions. The BSP is the portion that contains the Linux kernel itself, device drivers and libraries to enable the hardware platform. It starts from a level above that, requiring a working Linux system with docker support as the underlying substrate. From there it provides a wide variety of containers that provide a rich set of middleware and verticals for IoT devices, in particular edge devices(in docker parlance, a container is a self-contained module that usually provides a vertical function such as a database or a web service, in with little or no dependency on the host operating system, libraries, etc).
The concepts behind EdgeX Foundry point to the way forward for larger IoT devices, particularly edge devices, but work remains to be done to define a more constrained version that provides a good set of baseline services. Progress has been made in this regard with a move of some services from JVM to golang based implementations but the footprint will remain out of reach for low and mid-end Linux based IoT for the immediate future.
Foundries.io Microplatform
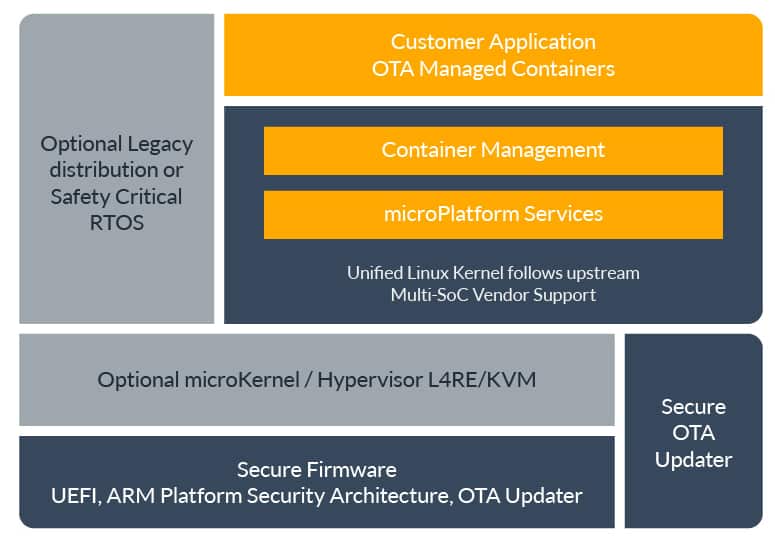
Foundries.io has created a Linux platform using a Yocto based approach to creating the board support layer and then layers a set of containerized microservices on top of it. Their set of containers is a smaller and more modest set than EdgeX Foundry approach, with a smaller footprint.
While full access to the Foundries.io product with automated updates and management is available via subscription, the underlying platform is open source and available here.
Conclusion
Linux-based IoT is starting a migration from a traditional embedded model where the complete vertical solution is created from a single team/worldview/toolchain/model to a more flexible model with greater separation of firmware, board, middleware, and applications components. This migration is not without cost however, and places higher demand on CPU, memory, and disk requirements. In order to choose a Linux baseline for your next IoT project, you’ll need to take into account what footprint you can afford and what lifespan you plan for your product. Smaller and more quickly replaced products are better off staying close to today’s tried and true solutions such as Yocto. Products that can afford more resources, and require new feature rollout into deployed products as a requirement should look into the more mainstream Linux distributions and the new container-focused solutions as a path forward.


 Aaeon launched a rugged, Linux-friendly line of “Boxer-6841M” industrial computers based on 6th or 7th Gen Core CPUs with either a PCIe x16 slot for Nvidia GPU cards or 2x PCIe x8 slots for frame grabbers.
Aaeon launched a rugged, Linux-friendly line of “Boxer-6841M” industrial computers based on 6th or 7th Gen Core CPUs with either a PCIe x16 slot for Nvidia GPU cards or 2x PCIe x8 slots for frame grabbers.








