Nornir
is a Python library for automating network connected devices. You can compare it to Ansible, which is mainly used to automate configuration and management of Linux servers. The same way, you can use
Nornir
to automate the configuration and management of network connected devices. The reason it is exceptional is that with Nornir, you can use the power of Python programming language to do things in your own way. You can control every aspect of the automation process and collect data if required.
In this article, I will show you how to install Nornir Python library on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS and use it for network automation. I will automate tasks on 3 Linux servers with Python Nornir library just to show you how it works. Let’s get started.
PIP is really easy to install on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS. It is available in the official package repository of Ubuntu 18.04 LTS.
First, update the APT package repository cache of your Ubuntu 18.04 LTS machine with the following command:
If you want to use PIP to install Nornir for Python 2.x, then you have to install PIP for Python 2.x. To do that, run the following command:
$ sudo apt install python-pip
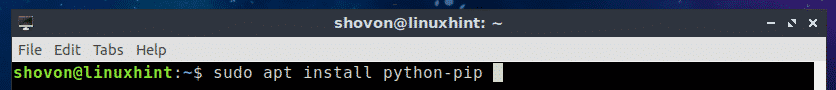
Now press y and then press <Enter> to continue.
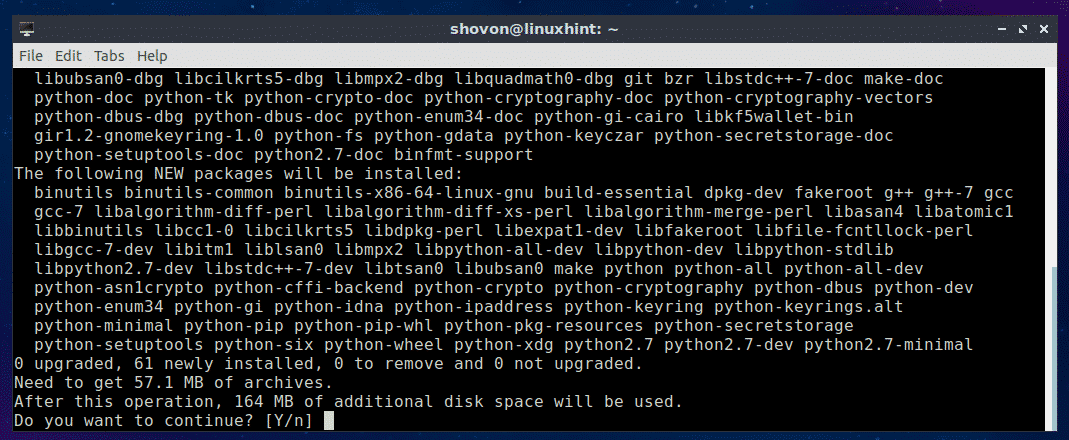
PIP for Python 2.x should be installed.

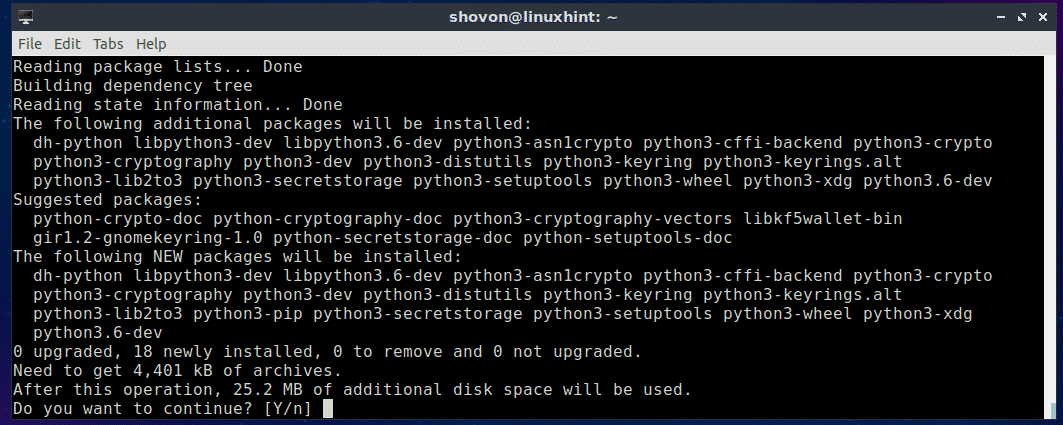
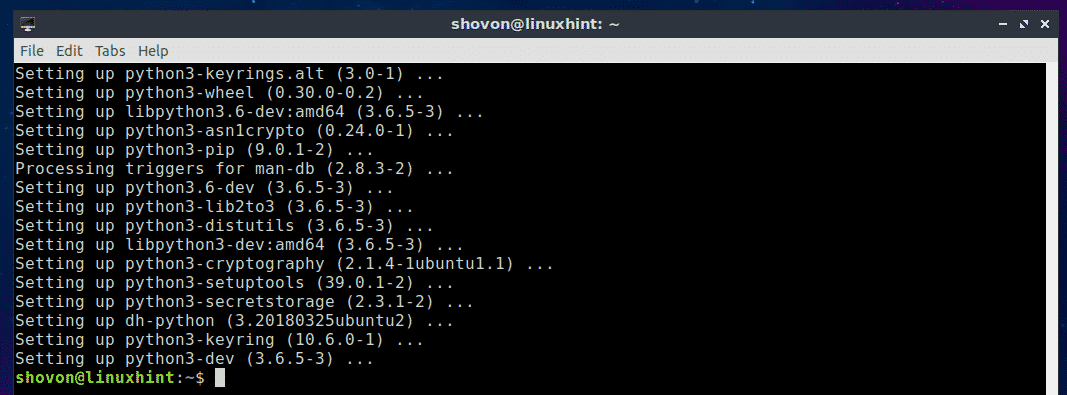
If you want to use PIP to install Nornir for Python 3.x, then you have to install PIP for Python 3.x. To do that, run the following command:
$ sudo apt install python3-pip

Now press y and then press <Enter> to continue.
PIP for Python 3.x should be installed.
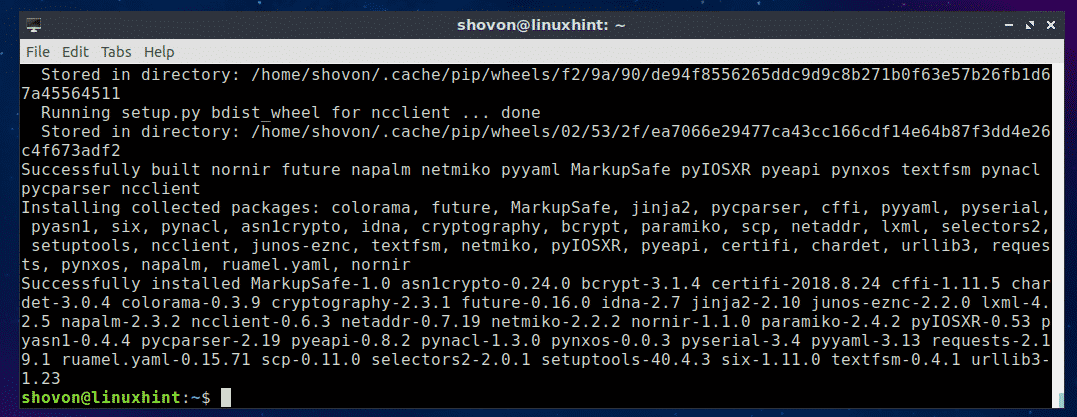
Installing nornir Python Library Using PIP:
You can easily install Nornir on Ubuntu 18.04 using Python PIP.
For Python 3.x:
If you want to use Nornir on Python 3.x (recommended), then install Nornir with the following command:
$ sudo pip3 install nornir

Nornir for Python 3.x should be installed.
For Python 2.x:
If you want to use Nornir on Python 2.x (not recommended), then install Nornir with the following command:
Nornir for Python 2.x should be installed.
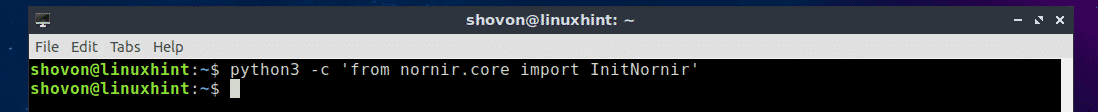
Now you can test whether Nornir was installed correctly and is working with the following command:
For Python 3.x:
$ python3 -c ‘from nornir.core import InitNornir’
For Python 2.x:
$ python -c ‘from nornir.core import InitNornir’
If it was installed correctly and is working, then you won’t see any output when you run any of these commands above as you can see in the screenshot below.
If it was not installed correctly, running the above commands would display errors as shown in the screenshot below.

Using Nornir Python Library:
In this section, I will show you how to run commands on Linux servers and workstation with Nornir python library.
First, create a new directory (let’s call it nornir) for the project with the following command:

Now navigate into the nornir/ directory with the following command:

Now create 2 YAML files with the following command:
$ touch hosts.yaml groups.yaml

Now add the following lines to the hosts.yaml file:

Add the following lines to the groups.yaml file:

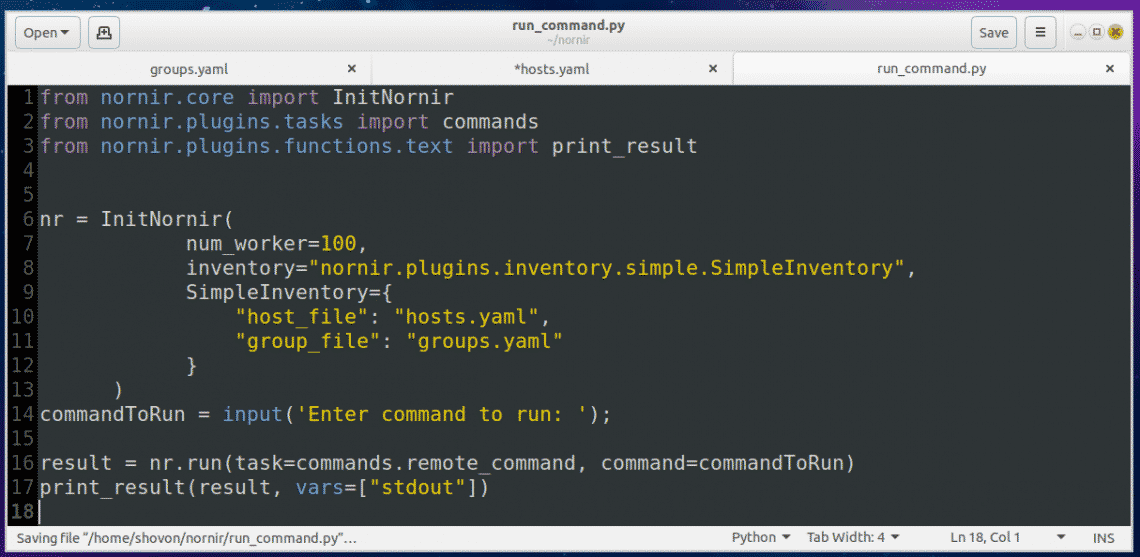
Now create a new Python script run_command.py with the following command:
Then add the following lines of codes to the run_command.py file:
Now run the Python script with the following command:

Now type in the command that you want to run on all the servers and workstation defined in the hosts.yaml file and press <Enter>.

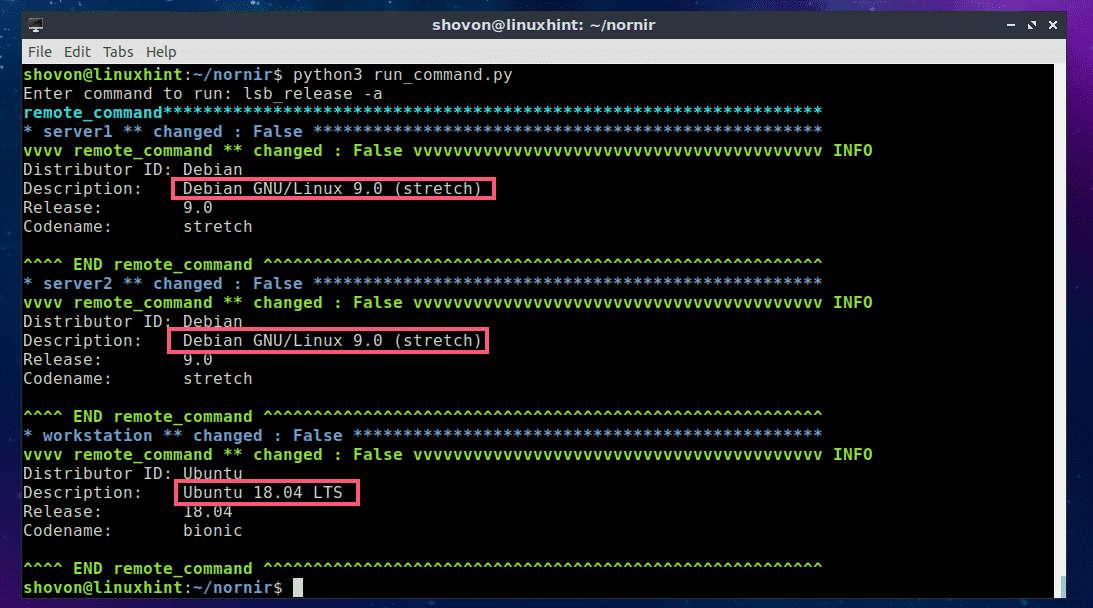
For example, I would like to see what operating system the servers and workstations are running. So I typed in the lsb_release -a command.
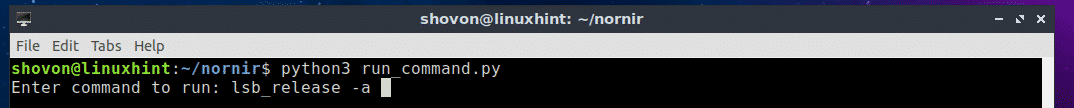
As you can see, the command was executed on each of the servers and workstations defined in the hosts.yaml file and the output is printed on the screen (in my case the terminal).
As you can see, I ran another command and listed all the installed storage devices and partitions of the servers and workstations.
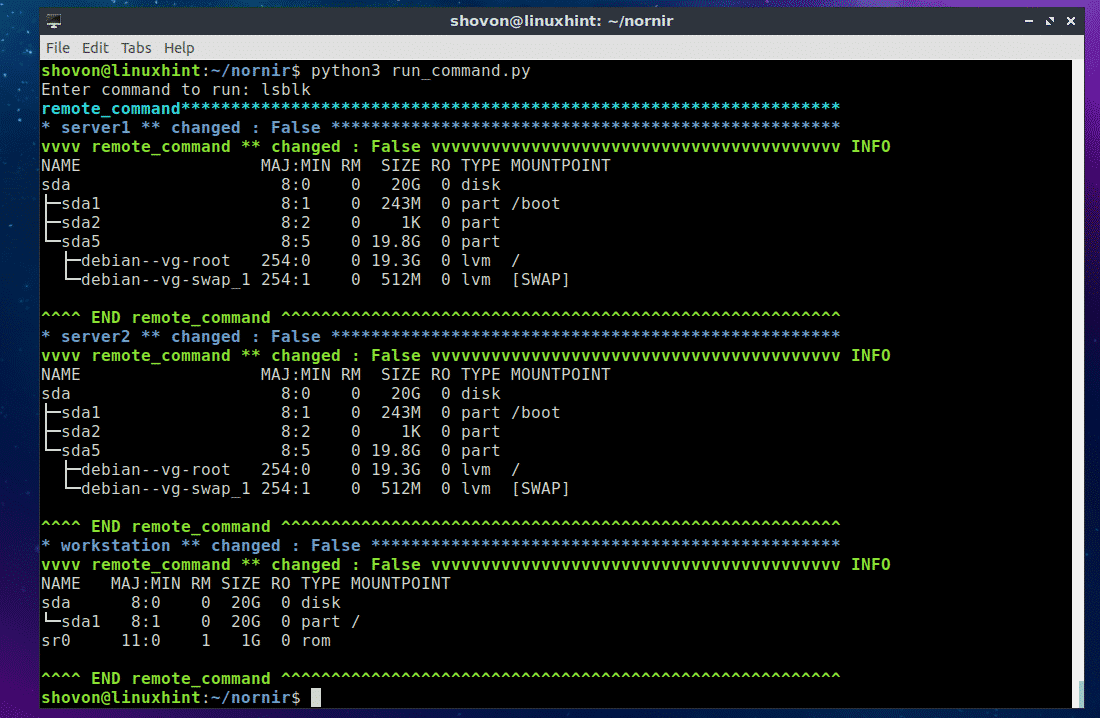
Really easy!
Understanding hosts.yaml and groups.yaml Configuration Files:
The main part of the run_command.py script is hosts.yaml and groups.yaml files. Using these files, you create an Inventory object, which is used to create a Nornir object.
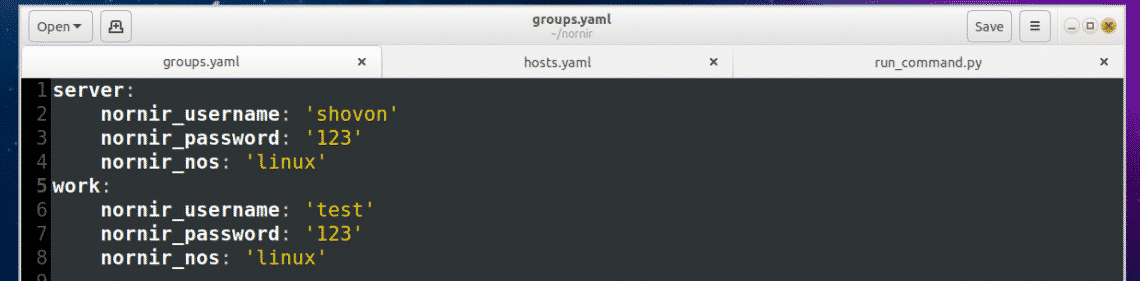
On the following hosts.yaml file, server2 and workstation (on line 5 and line 9 respectively) are identifiers. You may use the hostname of your server or workstation as identifiers. That way, it will be easy for you to remember what the entries are.

On line 6-8, additional parameters/key-value pairs are defined for the server2 identifier. The nornir_host is the IP address or hostname of the server2 server.
groups tells the hosts.yaml file which group or groups to use from groups.yaml file. If some parameters are common to many identifiers, then it can be grouped and only the group name needs to be added in the hosts.yaml file. So you don’t have to type the same thing again and again. All the parameters in the defined group or groups will be automatically imported.
The format of the groups.yaml file is the same as the hosts.yaml file. So I don’t think you need further explanation of it. I will just explain the parameters in the groups.yaml file.
Here, nornir_username and nornir_password is the username and password used to login to the servers. Here, nornir_nos defines the operating system the servers have installed. As I am connecting to Ubuntu and Debian servers, the nornir_nos is linux.
Understanding the run_command.py Python script:
The run_command.py script is simple.
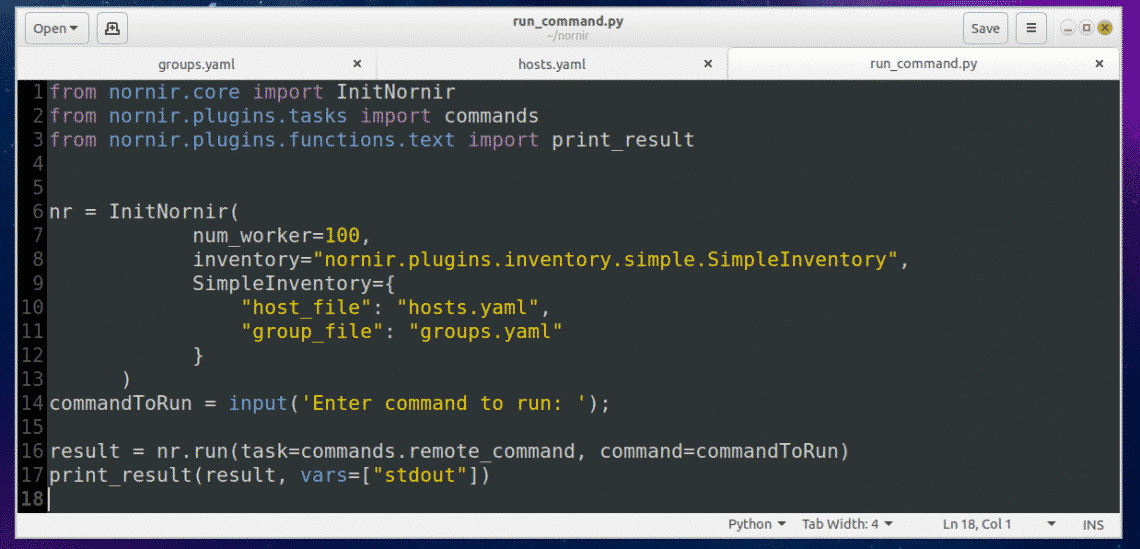
On line 1-3, nornir specific functions and classes are imported.
On line 6, a Nornir object is created using the InitNornir function. Here, the second parameter is used to tell InitNornir what type of inventory you would like to create. I created a SimpleInventory inventory. The third parameter tells InitNornir the location of the host (in my case hosts.yaml) file and group (in my case groups.yaml) file.
On line 14, Python’s build in input() function is used to input the command to run.
On line 16, the command is executed and the result is stored in the result variable.
Finally, on line 17, the contents of the result variable is printed on the screen.
For more information on Nornir, please check the official GitHub page of Nornir at https://github.com/nornir-automation/nornir
So that’s the basic of using Nornir Python library on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS. Thanks for reading this article.

 Cirrus7 unveiled an “AI-Box TX2” mini-PC with a Jetson TX2 module and -20 to 70°C support. The company also offers four, similarly Linux-friendly Kaby Lake-based mini-PCs and a new Gemini Lake model.
Cirrus7 unveiled an “AI-Box TX2” mini-PC with a Jetson TX2 module and -20 to 70°C support. The company also offers four, similarly Linux-friendly Kaby Lake-based mini-PCs and a new Gemini Lake model.




















 Kazam Version 1.4.5
Kazam Version 1.4.5 Kazam Version 1.5.3
Kazam Version 1.5.3 Screen recording with Kazam
Screen recording with Kazam Countdown before screen recording
Countdown before screen recording Pause or finish screen recording
Pause or finish screen recording Save recording
Save recording Accessing Kazam preferences
Accessing Kazam preferences Autosave in a chosen location
Autosave in a chosen location Don’t use RAW files
Don’t use RAW files Record mouse clicks
Record mouse clicks